feat: giltracer shows actualy GIL using uprobes
This commit is contained in:
parent
2e3b74c06b
commit
67c25d37e5
210
README.md
210
README.md
@ -9,12 +9,13 @@ From PyPy
|
|||||||
$ pip install per4m
|
$ pip install per4m
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
## Linux side
|
## Linux side (minimal)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Install perf
|
Install perf
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo yum install perf
|
$ sudo yum install perf
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Enable perf as user
|
||||||
Enable users to run perf (use at own risk)
|
Enable users to run perf (use at own risk)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ sudo sysctl kernel.perf_event_paranoid=-1
|
$ sudo sysctl kernel.perf_event_paranoid=-1
|
||||||
@ -24,18 +25,191 @@ Enable users to see schedule trace events:
|
|||||||
$ sudo mount -o remount,mode=755 /sys/kernel/debug
|
$ sudo mount -o remount,mode=755 /sys/kernel/debug
|
||||||
$ sudo mount -o remount,mode=755 /sys/kernel/debug/tracing
|
$ sudo mount -o remount,mode=755 /sys/kernel/debug/tracing
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
### Create uprobes (to detect who has the GIL)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
We use uprobes to see who calls take_gil and drop_gil, so we need to add those uprobes manually:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
sudo perf probe -f -x `which python` python:take_gil=take_gil
|
||||||
|
sudo perf probe -f -x `which python` python:take_gil=take_gil%return
|
||||||
|
sudo perf probe -f -x `which python` python:drop_gil=drop_gil
|
||||||
|
sudo perf probe -f -x `which python` python:drop_gil=drop_gil%return
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
It should give outlike like:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
Failed to find "take_gil%return",
|
||||||
|
because take_gil is an inlined function and has no return point.
|
||||||
|
Added new event:
|
||||||
|
python:take_gil__return (on take_gil%return in /home/maartenbreddels/miniconda/envs/dev/bin/python3.7)
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Check if this works
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ perf record -e python:take_gil__return -- python -c "import time; time.sleep(1)"
|
||||||
|
[ perf record: Woken up 1 times to write data ]
|
||||||
|
[ perf record: Captured and wrote 0,063 MB perf.data (563 samples) ]
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In case you need to remove the uprobes:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
$ sudo perf probe --del 'py*'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Usage
|
# Usage
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ per4m giltracer -m per4m.example2
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Open the result.html, and identify the problem (GIL visible, possible low instruction counts/cycle):
|
## Detect who has the GIL
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ giltracer -m per4m.example2
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[ perf record: Woken up 1 times to write data ]
|
||||||
|
[ perf record: Captured and wrote 0,044 MB perf-gil.data (116 samples) ]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Wait for perf to finish...
|
||||||
|
Loading finish
|
||||||
|
Saving report to /home/maartenbreddels/github/maartenbreddels/per4m/viztracer.json ...
|
||||||
|
Dumping trace data to json, total entries: 72, estimated json file size: 8.4KiB
|
||||||
|
Report saved.
|
||||||
|
perf script -i perf-gil.data --no-inline --ns | per4m perf2trace gil -i viztracer.json -o giltracer.json -q -v
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Summary of threads:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
PID total(us) no gil%✅ has gil%❗ gil wait%❌
|
||||||
|
------- ----------- ----------- ------------ -------------
|
||||||
|
2718963 267335 95.8333 0.353181 3.81349
|
||||||
|
2719035 56845.9 0.10576 54.7924 45.1019
|
||||||
|
2719036 57043.1 0.0279231 54.6021 45.37
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
High 'no gil' is good (✅), we like low 'has gil' (❗), and we don't want 'gil wait' (❌)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Wrote to giltracer.json
|
||||||
|
Saving report to /home/maartenbreddels/github/maartenbreddels/per4m/giltracer.html ...
|
||||||
|
Dumping trace data to json, total entries: 362, estimated json file size: 42.4KiB
|
||||||
|
Generating HTML report
|
||||||
|
Report saved.
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
This gives an overview of which threads held the GIL, and who needed to wait to get the GIL:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
The giltracer.html file gives a visual overview of where a threads want to take the GIL, and where it has the GIL.
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## See process states
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Instead of detecting the GIL, we can also look at process states, and see if and where processes sleep due to the GIL:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ giltracer --no-gil-detect --state-detect -m per4m.example2
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
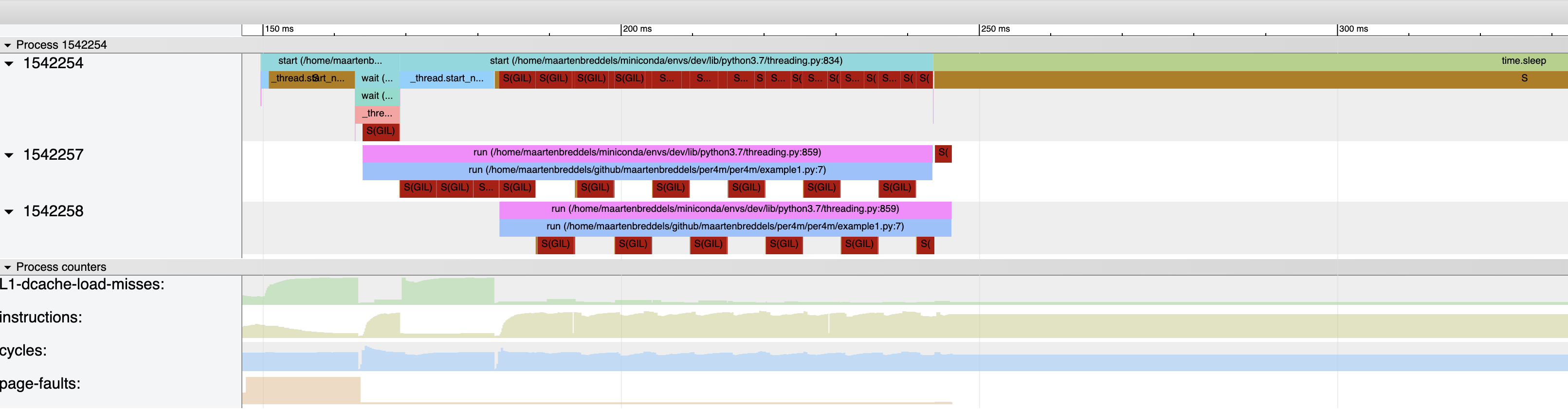
The dark red `S(GIL)` blocks indicate the threads/processes are in a waiting state due to the GIL, dark orange `S` is a due to other reasons (like `time.sleep(...)`). The regular pattern is due to Python switching threads after [`sys.getswitchinterval`](https://docs.python.org/3/library/sys.html#sys.getswitchinterval) (0.005 seconds)
|
The dark red `S(GIL)` blocks indicate the threads/processes are in a waiting state due to the GIL, dark orange `S` is a due to other reasons (like `time.sleep(...)`). The regular pattern is due to Python switching threads after [`sys.getswitchinterval`](https://docs.python.org/3/library/sys.html#sys.getswitchinterval) (0.005 seconds)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## GIL + Process states
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Although it is possible to do both:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ giltracer --no-gil-detect --state-detect -m per4m.example2
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
This causes clutter, and perf often loses messages.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## What you'd like to see
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
If you use NumPy, it will release the GIL, and you should see less waiting on the GIL, e.g the following should do much better.
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
# shows high gil load, but no wait
|
||||||
|
import threading
|
||||||
|
import numpy as np
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
N = 1024*1024*32
|
||||||
|
M = 4
|
||||||
|
x = np.arange(N, dtype='f8')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def run():
|
||||||
|
total = 0
|
||||||
|
for i in range(M):
|
||||||
|
total += x.sum()
|
||||||
|
return total
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
thread1 = threading.Thread(target=run)
|
||||||
|
thread2 = threading.Thread(target=run)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def main(args=None):
|
||||||
|
thread1.start()
|
||||||
|
thread2.start()
|
||||||
|
total = 0
|
||||||
|
for i in range(1_000_000):
|
||||||
|
total += i
|
||||||
|
for thread in [thread1, thread2]:
|
||||||
|
thread.join()
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ giltracer -m per4m.example3
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
[ perf record: Woken up 1 times to write data ]
|
||||||
|
[ perf record: Captured and wrote 0,045 MB perf-gil.data (112 samples) ]
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Wait for perf to finish...
|
||||||
|
Loading finish
|
||||||
|
Saving report to /home/maartenbreddels/github/maartenbreddels/per4m/viztracer.json ...
|
||||||
|
Dumping trace data to json, total entries: 95, estimated json file size: 11.1KiB
|
||||||
|
Report saved.
|
||||||
|
perf script -i perf-gil.data --no-inline --ns | per4m perf2trace gil -i viztracer.json -o giltracer.json -q -v
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Summary of threads:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
PID total(us) no gil%✅ has gil%❗ gil wait%❌
|
||||||
|
------- ----------- ----------- ------------ -------------
|
||||||
|
2724006 109011 71.0196 28.668 0.312345
|
||||||
|
2724077 58313.4 90.3658 0.558379 9.07583
|
||||||
|
2724078 55886.6 92.3029 0.459127 7.23798
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
High 'no gil' is good (✅), we like low 'has gil' (❗), and we don't want 'gil wait' (❌)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Wrote to giltracer.json
|
||||||
|
Saving report to /home/maartenbreddels/github/maartenbreddels/per4m/giltracer.html ...
|
||||||
|
Dumping trace data to json, total entries: 375, estimated json file size: 43.9KiB
|
||||||
|
Generating HTML report
|
||||||
|
Report saved.
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
We see that the two threads waiting on the GIL just 10% of the time (room for improvement, left as an excercise for the reader).
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
## Who is waiting on the GIL
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Analougous to [Brendan Gregg's off cpu analysis](http://www.brendangregg.com/offcpuanalysis.html) we'd like to know in Python who is waiting for the GIL, and we also want to see the the C stacktrace and possibly what the kernel is doing.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Note that we we are looking at stacktraces that are both off cpu and off gil (since off gil but on cpu should be good).
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ offgil | ~/github/FlameGraph/stackcollapse.pl | ~/github/FlameGraph/flamegraph.pl --countname=us --title="Off-GIL Time Flame Graph" --colors=python > offgil.svg
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Or, if you'd like to see the CPython evaluation stacktraces, and what happens in the kernel:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ offgil --no-strip-take-gil --keep-cpython-evals | ~/github/FlameGraph/stackcollapse.pl | ~/github/FlameGraph/flamegraph.pl --countname=us --title="Off-GIL Time Flame Graph" --colors=python > offgil.svg
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
We see that NumPy has trouble returning to Python land because the main thread has the GIL locked.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
# Usage - Jupyter notebook
|
# Usage - Jupyter notebook
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
First, load the magics
|
First, load the magics
|
||||||
@ -165,3 +339,31 @@ Show one thread that has a high GIL load, but it does not keep the others from r
|
|||||||
$ per4m giltracer --import="numpy,threading,time,gil_load" -m per4m.example3
|
$ per4m giltracer --import="numpy,threading,time,gil_load" -m per4m.example3
|
||||||
|
|
||||||

|

|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# Using uprobes
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
In case you are interested in using uprobes yourself, this is how you use it:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ perf record -e 'python:*' -- time python -m per4m.example3
|
||||||
|
1.73user 3.44system 0:00.95elapsed 544%CPU (0avgtext+0avgdata 297224maxresident)k
|
||||||
|
0inputs+0outputs (0major+6393minor)pagefaults 0swaps
|
||||||
|
[ perf record: Woken up 4 times to write data ]
|
||||||
|
[ perf record: Captured and wrote 0,969 MB perf.data (12217 samples) ]
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
And see what we got:
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
$ perf script --no-inline | tail
|
||||||
|
python 2397983 [058] 3846350.744446: python:take_gil__return: (563fc316fcc0 <- 563fc315691f)
|
||||||
|
python 2397982 [057] 3846350.749502: python:take_gil__return: (563fc316fcc0 <- 563fc315691f)
|
||||||
|
python 2397983 [058] 3846350.754557: python:take_gil__return: (563fc316fcc0 <- 563fc315691f)
|
||||||
|
python 2397982 [057] 3846350.759612: python:take_gil__return: (563fc316fcc0 <- 563fc315691f)
|
||||||
|
python 2397983 [058] 3846350.764668: python:take_gil__return: (563fc316fcc0 <- 563fc315691f)
|
||||||
|
python 2397982 [057] 3846350.769725: python:take_gil__return: (563fc316fcc0 <- 563fc315691f)
|
||||||
|
python 2397983 [058] 3846350.772506: python:take_gil__return: (563fc316fcc0 <- 563fc315691f)
|
||||||
|
python 2397918 [056] 3846350.777600: python:take_gil__return: (563fc316fcc0 <- 563fc309a0b4)
|
||||||
|
python 2397983 [058] 3846350.777614: python:take_gil__return: (563fc316fcc0 <- 563fc315691f)
|
||||||
|
python 2397918 [056] 3846350.842284: python:take_gil__return: (563fc316fcc0 <- 563fc309a0b4)
|
||||||
|
```
|
||||||
|
And we see the two threads exchanging the GIL at about every 0.005 seconds.
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -13,8 +13,9 @@ def run():
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
thread1 = threading.Thread(target=run)
|
thread1 = threading.Thread(target=run)
|
||||||
thread2 = threading.Thread(target=run)
|
thread2 = threading.Thread(target=run)
|
||||||
thread1.start()
|
def main(args=None):
|
||||||
thread2.start()
|
thread1.start()
|
||||||
time.sleep(0.2)
|
thread2.start()
|
||||||
for thread in [thread1, thread2]:
|
time.sleep(0.2)
|
||||||
thread.join()
|
for thread in [thread1, thread2]:
|
||||||
|
thread.join()
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -28,15 +28,17 @@ if use_gil_load:
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
thread1 = threading.Thread(target=run)
|
thread1 = threading.Thread(target=run)
|
||||||
thread2 = threading.Thread(target=run)
|
thread2 = threading.Thread(target=run)
|
||||||
thread1.start()
|
|
||||||
thread2.start()
|
|
||||||
total = 0
|
|
||||||
for i in range(1_000_000):
|
|
||||||
total += i
|
|
||||||
for thread in [thread1, thread2]:
|
|
||||||
thread.join()
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
if use_gil_load:
|
def main(args=None):
|
||||||
gil_load.stop()
|
thread1.start()
|
||||||
stats = gil_load.get()
|
thread2.start()
|
||||||
print(gil_load.format(stats))
|
total = 0
|
||||||
|
for i in range(1_000_000):
|
||||||
|
total += i
|
||||||
|
for thread in [thread1, thread2]:
|
||||||
|
thread.join()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if use_gil_load:
|
||||||
|
gil_load.stop()
|
||||||
|
stats = gil_load.get()
|
||||||
|
print(gil_load.format(stats))
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -17,20 +17,39 @@ Usage:
|
|||||||
$ giltracer -m per4m.example1
|
$ giltracer -m per4m.example1
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class GilTracer(PerfRecord):
|
class PerfRecordSched(PerfRecord):
|
||||||
def __init__(self, output='perf.data', trace_output='giltracer.json', verbose=1):
|
def __init__(self, output='perf-sched.data', trace_output='schedtracer.json', verbose=1):
|
||||||
super().__init__(output=output, verbose=verbose, args=["-e 'sched:*'"])
|
super().__init__(output=output, verbose=verbose, args=["-e 'sched:*'"])
|
||||||
self.trace_output = trace_output
|
self.trace_output = trace_output
|
||||||
self.verbose = verbose
|
self.verbose = verbose
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __exit__(self, *args):
|
def post_process(self, *args):
|
||||||
super().__exit__(self, *args)
|
|
||||||
verbose = '-q ' + '-v ' * self.verbose
|
verbose = '-q ' + '-v ' * self.verbose
|
||||||
cmd = f"perf script -i {self.output} --no-inline | per4m perf2trace -o {self.trace_output} {verbose}"
|
cmd = f"perf script -i {self.output} --no-inline | per4m perf2trace sched -o {self.trace_output} {verbose}"
|
||||||
|
if self.verbose >= 1:
|
||||||
|
print(cmd)
|
||||||
if os.system(cmd) != 0:
|
if os.system(cmd) != 0:
|
||||||
raise OSError(f'Failed to run perf or per4m perf2trace, command:\n$ {cmd}')
|
raise OSError(f'Failed to run perf or per4m perf2trace, command:\n$ {cmd}')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
class PerfRecordGIL(PerfRecord):
|
||||||
|
def __init__(self, output='perf-gil.data', trace_output='giltracer.json', viztracer_input="viztracer.json", verbose=1):
|
||||||
|
# TODO: check output of perf probe --list="python:*gil*" to see if probes are set
|
||||||
|
super().__init__(output=output, verbose=verbose, args=["-e 'python:*gil*'"], stacktrace=False)
|
||||||
|
# this is used to filter the giltracer data
|
||||||
|
self.viztracer_input = viztracer_input
|
||||||
|
self.trace_output = trace_output
|
||||||
|
self.verbose = verbose
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def post_process(self, *args):
|
||||||
|
verbose = '-q ' + '-v ' * self.verbose
|
||||||
|
# -i {self.viztracer_input} # we don't use this ftm
|
||||||
|
cmd = f"perf script -i {self.output} --no-inline --ns | per4m perf2trace gil -o {self.trace_output} {verbose}"
|
||||||
|
if self.verbose >= 1:
|
||||||
|
print(cmd)
|
||||||
|
if os.system(cmd) != 0:
|
||||||
|
raise OSError(f'Failed to run perf or per4m perf2trace, command:\n$ {cmd}')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def main(argv=sys.argv):
|
def main(argv=sys.argv):
|
||||||
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(argv[0],
|
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(argv[0],
|
||||||
formatter_class=argparse.RawDescriptionHelpFormatter,
|
formatter_class=argparse.RawDescriptionHelpFormatter,
|
||||||
@ -39,7 +58,12 @@ def main(argv=sys.argv):
|
|||||||
parser.add_argument('--import', dest="import_", help="Comma seperated list of modules to import before tracing (cleans up tracing output)")
|
parser.add_argument('--import', dest="import_", help="Comma seperated list of modules to import before tracing (cleans up tracing output)")
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('--verbose', '-v', action='count', default=1)
|
parser.add_argument('--verbose', '-v', action='count', default=1)
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('--quiet', '-q', action='count', default=0)
|
parser.add_argument('--quiet', '-q', action='count', default=0)
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('--output', '-o', dest="output", default='result.html', help="Output filename (default %(default)s)")
|
parser.add_argument('--output', '-o', dest="output", default='giltracer.html', help="Output filename (default %(default)s)")
|
||||||
|
parser.add_argument('--state-detect', help="Use perf sched events to detect if a process is sleeping due to the GIL (default: %(default)s)", default=False, action='store_true')
|
||||||
|
parser.add_argument('--no-state-detect', dest="state_detect", action='store_false')
|
||||||
|
parser.add_argument('--gil-detect', help="Use uprobes to detect who has the GIL (read README.md) (default: %(default)s)", default=True, action='store_true')
|
||||||
|
parser.add_argument('--no-gil-detect', dest="gil_detect", action='store_false')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('args', nargs=argparse.REMAINDER)
|
parser.add_argument('args', nargs=argparse.REMAINDER)
|
||||||
args = parser.parse_args(argv[1:])
|
args = parser.parse_args(argv[1:])
|
||||||
verbose = args.verbose - args.quiet
|
verbose = args.verbose - args.quiet
|
||||||
@ -50,14 +74,43 @@ def main(argv=sys.argv):
|
|||||||
print(f'importing {module}')
|
print(f'importing {module}')
|
||||||
__import__(module)
|
__import__(module)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
with GilTracer(verbose=verbose) as gt:
|
perf1 = PerfRecordSched(verbose=verbose) if args.state_detect else None
|
||||||
with viztracer.VizTracer(output_file="viztracer.json", verbose=verbose):
|
perf2 = PerfRecordGIL(verbose=verbose) if args.gil_detect else None
|
||||||
if args.module:
|
vt = viztracer.VizTracer(output_file="viztracer.json", verbose=verbose)
|
||||||
runpy.run_module(args.module)
|
|
||||||
else:
|
# pass on the rest of the arguments
|
||||||
sys.argv = args.args
|
sys.argv = args.args
|
||||||
runpy.run_path(sys.argv[0])
|
if args.module:
|
||||||
builder = ReportBuilder(['./viztracer.json', './giltracer.json'], verbose=verbose)
|
module = runpy.run_module(args.module)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
module = runpy.run_path(sys.argv[0])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if perf1:
|
||||||
|
perf1.start()
|
||||||
|
if perf2:
|
||||||
|
perf2.start()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
try:
|
||||||
|
vt.start()
|
||||||
|
module['main'](args.args)
|
||||||
|
finally:
|
||||||
|
vt.stop()
|
||||||
|
if perf1:
|
||||||
|
perf1.stop()
|
||||||
|
if perf2:
|
||||||
|
perf2.stop()
|
||||||
|
vt.save('viztracer.json')
|
||||||
|
if perf1:
|
||||||
|
perf1.post_process()
|
||||||
|
if perf2:
|
||||||
|
perf2.post_process()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
files = ['viztracer.json']
|
||||||
|
if perf1:
|
||||||
|
files.append('schedtracer.json')
|
||||||
|
if perf2:
|
||||||
|
files.append('giltracer.json')
|
||||||
|
builder = ReportBuilder(files, verbose=verbose)
|
||||||
builder.save(output_file=args.output)
|
builder.save(output_file=args.output)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -19,7 +19,10 @@ Take stacktraces from VizTracer, and inject them in perf script output and print
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
Usage:
|
Usage:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
$ giltracer -m per4m.example3
|
# for this we need the process states, and we can skip the GIL detection for performance
|
||||||
|
$ giltracer --no-gil-detect --state-detect -m per4m.example3
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# offgil will use perf-sched.data
|
||||||
$ offgil | ~/github/FlameGraph/stackcollapse.pl | ~/github/FlameGraph/flamegraph.pl --countname=us --title="Off-GIL Time Flame Graph" --colors=python > offgil.svg
|
$ offgil | ~/github/FlameGraph/stackcollapse.pl | ~/github/FlameGraph/flamegraph.pl --countname=us --title="Off-GIL Time Flame Graph" --colors=python > offgil.svg
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -39,7 +42,8 @@ def main(argv=sys.argv):
|
|||||||
parser.add_argument('--no-allow-mismatch', dest="allow_mismatch", action='store_false')
|
parser.add_argument('--no-allow-mismatch', dest="allow_mismatch", action='store_false')
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('--pedantic', help="If false, accept known stack mismatch issues (default: %(default)s)", default=False, action='store_true')
|
parser.add_argument('--pedantic', help="If false, accept known stack mismatch issues (default: %(default)s)", default=False, action='store_true')
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('--no-pedantic', dest="pedantic", action='store_false')
|
parser.add_argument('--no-pedantic', dest="pedantic", action='store_false')
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('--input', '-i', help="VizTracer input (default %(default)s)", default="viztracer.json")
|
parser.add_argument('--input-perf', help="Perf input (default %(default)s)", default="perf-sched.data")
|
||||||
|
parser.add_argument('--input-viztracer', help="VizTracer input (default %(default)s)", default="viztracer.json")
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('--output', '-o', dest="output", default=None, help="Output filename (default %(default)s)")
|
parser.add_argument('--output', '-o', dest="output", default=None, help="Output filename (default %(default)s)")
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
@ -48,7 +52,7 @@ def main(argv=sys.argv):
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
perf_script_args = ['--no-inline']
|
perf_script_args = ['--no-inline']
|
||||||
perf_script_args = ' '.join(perf_script_args)
|
perf_script_args = ' '.join(perf_script_args)
|
||||||
cmd = f"perf script {perf_script_args}"
|
cmd = f"perf script {perf_script_args} -i {args.input_perf}"
|
||||||
if verbose >= 2:
|
if verbose >= 2:
|
||||||
print(f"Running: {cmd}")
|
print(f"Running: {cmd}")
|
||||||
perf_args = shlex.split(cmd)
|
perf_args = shlex.split(cmd)
|
||||||
@ -61,14 +65,14 @@ def main(argv=sys.argv):
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
if verbose >= 1:
|
if verbose >= 1:
|
||||||
print_stderr("Loading snapshot")
|
print_stderr("Loading snapshot")
|
||||||
with open(args.input, "r") as f:
|
with open(args.input_viztracer, "r") as f:
|
||||||
json_data = f.read()
|
json_data = f.read()
|
||||||
snap = ProgSnapshot(json_data)
|
snap = ProgSnapshot(json_data)
|
||||||
# find all pids (or tids)
|
# find all pids (or tids)
|
||||||
pids = list(snap.func_trees)
|
pids = list(snap.func_trees)
|
||||||
for pid in pids.copy():
|
for pid in pids.copy():
|
||||||
pids.extend(list(snap.func_trees[pid]))
|
pids.extend(list(snap.func_trees[pid]))
|
||||||
t0 = min(event['ts'] for event in json.loads(json_data)['traceEvents'])
|
t0 = min(event['ts'] for event in json.loads(json_data)['traceEvents'] if 'ts' in event)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
for header, stacktrace, event in perf2trace(perf.stdout, verbose):
|
for header, stacktrace, event in perf2trace(perf.stdout, verbose):
|
||||||
if event['name'] == args.state:
|
if event['name'] == args.state:
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -1,6 +1,12 @@
|
|||||||
import sys
|
|
||||||
import json
|
|
||||||
import argparse
|
import argparse
|
||||||
|
import argparse
|
||||||
|
from collections import defaultdict
|
||||||
|
import json
|
||||||
|
import re
|
||||||
|
import sys
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
import tabulate
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
from .perfutils import read_events
|
from .perfutils import read_events
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def parse_values(parts, **types):
|
def parse_values(parts, **types):
|
||||||
@ -32,13 +38,22 @@ usage = """
|
|||||||
|
|
||||||
Convert perf.data to TraceEvent JSON data.
|
Convert perf.data to TraceEvent JSON data.
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Usage:
|
Usage for scheduling data:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
Always run perf with -e 'sched:*' --call-graph dwarf -k CLOCK_MONOTONIC, the rest of the events are extra
|
Always run perf with -e 'sched:*' --call-graph dwarf -k CLOCK_MONOTONIC, the rest of the events are extra
|
||||||
$ perf record -e 'sched:*' --call-graph dwarf -k CLOCK_MONOTONIC -e L1-dcache-load-misses -e instructions -e cycles -e page-faults -- python -m per4m.example1
|
$ perf record -e 'sched:*' --call-graph dwarf -k CLOCK_MONOTONIC -e L1-dcache-load-misses -e instructions -e cycles -e page-faults -- python -m per4m.example1
|
||||||
Run with --no-online, otherwise it may run slow
|
Run with --no-online, otherwise it may run slow
|
||||||
$ perf script --no-inline | per4m perf2trace --no-running -o example1perf.json
|
$ perf script --no-inline | per4m perf2trace sched --no-running -o example1sched.json
|
||||||
$ viztracer --combine example1.json example1perf.json -o example1.html
|
$ viztracer --combine example1sched.json example1perf.json -o example1.html
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
Usage for GIL:
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
(read the docs to install the GIL uprobes)
|
||||||
|
$ perf record -e 'python:*gil*' -k CLOCK_MONOTONIC -- python -m per4m.example1
|
||||||
|
$ perf script --ns --no-inline | per4m perf2trace gil -o example1gil.json
|
||||||
|
$ viztracer --combine example1.json example1gil.json -o example1.html
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def main(argv=sys.argv):
|
def main(argv=sys.argv):
|
||||||
@ -51,9 +66,16 @@ def main(argv=sys.argv):
|
|||||||
parser.add_argument('--no-sleeping', dest="sleeping", action='store_false')
|
parser.add_argument('--no-sleeping', dest="sleeping", action='store_false')
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('--running', help="show running phase (default: %(default)s)", default=False, action='store_true')
|
parser.add_argument('--running', help="show running phase (default: %(default)s)", default=False, action='store_true')
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('--no-running', dest="running", action='store_false')
|
parser.add_argument('--no-running', dest="running", action='store_false')
|
||||||
|
parser.add_argument('--as-async', help="show as async (above the events) (default: %(default)s)", default=True, action='store_true')
|
||||||
|
parser.add_argument('--no-as-async', dest="as_async", action='store_false')
|
||||||
|
parser.add_argument('--only-lock', help="show only when we have the GIL (default: %(default)s)", default=False, action='store_true')
|
||||||
|
parser.add_argument('--no-only-lock', dest="as_async", action='store_false')
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('--all-tracepoints', help="store all tracepoints phase (default: %(default)s)", default=False, action='store_true')
|
parser.add_argument('--all-tracepoints', help="store all tracepoints phase (default: %(default)s)", default=False, action='store_true')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# parser.add_argument('--input', '-i', help="Optional VizTracer input for filtering and gil load calculations")
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
parser.add_argument('--output', '-o', dest="output", default='perf.json', help="Output filename (default %(default)s)")
|
parser.add_argument('--output', '-o', dest="output", default='perf.json', help="Output filename (default %(default)s)")
|
||||||
|
parser.add_argument("type", help="Type of conversion to do", choices=['sched', 'gil'])
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
args = parser.parse_args(argv[1:])
|
args = parser.parse_args(argv[1:])
|
||||||
@ -62,14 +84,184 @@ def main(argv=sys.argv):
|
|||||||
store_sleeping = args.sleeping
|
store_sleeping = args.sleeping
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
trace_events = []
|
trace_events = []
|
||||||
for header, tb, event in perf2trace(sys.stdin, verbose=verbose, store_runing=store_runing, store_sleeping=store_sleeping, all_tracepoints=args.all_tracepoints):
|
if args.type == "sched":
|
||||||
trace_events.append(event)
|
for header, tb, event in perf2trace(sys.stdin, verbose=verbose, store_runing=store_runing, store_sleeping=store_sleeping, all_tracepoints=args.all_tracepoints):
|
||||||
|
trace_events.append(event)
|
||||||
|
elif args.type == "gil":
|
||||||
|
# we don't use this any more, lets keep it to maybe pull out thread information
|
||||||
|
# if args.input:
|
||||||
|
# with open(args.input) as f:
|
||||||
|
# input_events = json.load(f)['traceEvents']
|
||||||
|
# for event in input_events:
|
||||||
|
# if 'ts' in event:
|
||||||
|
# ts = event['ts']
|
||||||
|
# pid = int(event['tid'])
|
||||||
|
# t_min[pid] = min(t_min.get(pid, ts), ts)
|
||||||
|
# t_max[pid] = max(t_max.get(pid, ts), ts)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
for header, event in gil2trace(sys.stdin, verbose=verbose, as_async=args.as_async, only_lock=args.only_lock):
|
||||||
|
if verbose >= 3:
|
||||||
|
print(event)
|
||||||
|
trace_events.append(event)
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
raise ValueError(f'Unknown type {args.type}')
|
||||||
with open(args.output, 'w') as f:
|
with open(args.output, 'w') as f:
|
||||||
json.dump({'traceEvents': trace_events}, f)
|
json.dump({'traceEvents': trace_events}, f)
|
||||||
if verbose >= 1:
|
if verbose >= 1:
|
||||||
print(f"Wrote to {args.output}")
|
print(f"Wrote to {args.output}")
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def gil2trace(input, verbose=1, take_probe="python:take_gil(_\d)?$", take_probe_return="python:take_gil__return", drop_probe="python:drop_gil(_\d)?$", drop_probe_return="python:drop_gil__return", as_async=False, show_instant=True, duration_min_us=1, only_lock=True, t_min={}, t_max={}):
|
||||||
|
time_first = None
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# dicts that map pid -> time
|
||||||
|
wants_take_gil = {}
|
||||||
|
wants_drop_gil = {}
|
||||||
|
has_gil = {}
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
parent_pid = None
|
||||||
|
# to avoid printing out the same msg over and over
|
||||||
|
ignored = set()
|
||||||
|
# keep track of various times
|
||||||
|
time_on_gil = defaultdict(int)
|
||||||
|
time_wait_gil = defaultdict(int)
|
||||||
|
jitter = 1e-3 # add 1 ns for proper sorting
|
||||||
|
for header in input:
|
||||||
|
try:
|
||||||
|
header = header.rstrip()
|
||||||
|
if verbose >= 2:
|
||||||
|
print(header)
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# just ignore stack traces and seperators
|
||||||
|
if not header or header.split()[0].isdigit():
|
||||||
|
continue
|
||||||
|
# parse the header
|
||||||
|
comm, pid, cpu, time, event, *other = header.split()
|
||||||
|
pid = int(pid)
|
||||||
|
if parent_pid is None: # lets assume the first event is from the parent process
|
||||||
|
parent_pid = pid
|
||||||
|
assert event[-1] == ':'
|
||||||
|
event = event[:-1] # take off :
|
||||||
|
assert time[-1] == ':'
|
||||||
|
time = time[:-1] # take off :
|
||||||
|
time = float(time[:-1]) * 1e6
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# keeping track for statistics
|
||||||
|
t_min[pid] = min(time, t_min.get(pid, time))
|
||||||
|
t_max[pid] = max(time, t_max.get(pid, time))
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
# and proces it
|
||||||
|
if time_first is None:
|
||||||
|
time_first = time
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if re.match(take_probe, event):
|
||||||
|
wants_take_gil[pid] = time
|
||||||
|
scope = "t" # thread scope
|
||||||
|
yield header, {"pid": parent_pid, "tid": pid, "ts": time, "name": 'take', "ph": "i", "cat": "GIL state", 's': scope, 'cname': 'bad'}
|
||||||
|
elif re.match(take_probe_return, event):
|
||||||
|
if has_gil:
|
||||||
|
for other_pid in has_gil:
|
||||||
|
gap = time - has_gil[other_pid]
|
||||||
|
# optimistic overlap would be if we take it from the time it wanted to drop
|
||||||
|
# gap = time - wants_drop_gil[other_pid]
|
||||||
|
# print(gap)
|
||||||
|
if gap < 0: # this many us overlap is ok
|
||||||
|
# I think it happens when a thread has dropped the GIL, but it has not returned yet
|
||||||
|
# TODO: we should be able to correct the times
|
||||||
|
tip = "(If running as giltracer, try passing --no-state-detect to reduce CPU load"
|
||||||
|
print(f'Anomaly: PID {other_pid} already seems to have the GIL, {overlap} us overlap with {pid} {pid==parent_pid}) {tip}', file=sys.stderr)
|
||||||
|
# keep this for debugging
|
||||||
|
# yield header, {"pid": parent_pid, "tid": other_pid, "ts": has_gil[other_pid], "dur": overlap, "name": 'GIL overlap1', "ph": "X", "cat": "process state"}
|
||||||
|
# yield header, {"pid": parent_pid, "tid": pid, "ts": has_gil[other_pid], "dur": overlap, "name": 'GIL overlap1', "ph": "X", "cat": "process state"}
|
||||||
|
# yield header, {"pid": parent_pid, "tid": other_pid, "ts": wants_drop_gil[other_pid], "dur": overlap_relaxed, "name": 'GIL overlap2', "ph": "X", "cat": "process state"}
|
||||||
|
# yield header, {"pid": parent_pid, "tid": pid, "ts": wants_drop_gil[other_pid], "dur": overlap_relaxed, "name": 'GIL overlap2', "ph": "X", "cat": "process state"}
|
||||||
|
has_gil[pid] = time
|
||||||
|
time_wait_gil[pid] += time - max(t_min[pid], wants_take_gil[pid])
|
||||||
|
elif re.match(drop_probe, event):
|
||||||
|
wants_drop_gil[pid] = time
|
||||||
|
scope = "t" # thread scope
|
||||||
|
yield header, {"pid": parent_pid, "tid": pid, "ts": time, "name": 'drop', "ph": "i", "cat": "GIL state", 's': scope, 'cname': 'bad'}
|
||||||
|
elif re.match(drop_probe_return, event):
|
||||||
|
if pid not in has_gil:
|
||||||
|
print(f'Anomaly: this PIDs drops the GIL: {pid}, but never took it (maybe we missed it?)', file=sys.stderr)
|
||||||
|
time_gil_take = has_gil.get(pid, time_first)
|
||||||
|
time_gil_drop = time
|
||||||
|
duration = time_gil_drop - time_gil_take
|
||||||
|
time_on_gil[pid] += duration
|
||||||
|
if pid in has_gil:
|
||||||
|
del has_gil[pid]
|
||||||
|
if duration < duration_min_us:
|
||||||
|
if verbose >= 2:
|
||||||
|
print(f'Ignoring {duration}us duration GIL lock', file=sys.stderr)
|
||||||
|
continue
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
args = {'duraction': f'{duration} us'}
|
||||||
|
if show_instant:
|
||||||
|
# we do both tevent only after drop, so we can ignore 0 duraction event
|
||||||
|
# TODO: 'flush' out takes without a drop (e.g. perf stopped before drop happned)
|
||||||
|
name = "GIL-take"
|
||||||
|
scope = "t" # thread scope
|
||||||
|
event = {"pid": parent_pid, "tid": f'{pid}', "ts": time_gil_take, "name": name, "ph": "i", "cat": "GIL state", 's': scope, 'cname': 'terrible'}
|
||||||
|
yield header, event
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
name = "GIL-drop"
|
||||||
|
scope = "t" # thread scope
|
||||||
|
event = {"pid": parent_pid, "tid": f'{pid}', "ts": time_gil_drop, "name": name, "ph": "i", "cat": "GIL state", 's': scope, 'args': args, 'cname': 'good'}
|
||||||
|
yield header, event
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
if as_async:
|
||||||
|
begin, end = 'b', 'e'
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
begin, end = 'B', 'E'
|
||||||
|
event_id = int(time*1e3)
|
||||||
|
name = "GIL-flow"
|
||||||
|
common = {"pid": parent_pid if as_async else f'{parent_pid}-GIL', "tid": f'{pid}', 'cat': 'GIL state', 'args': args, 'id': event_id, 'cname': 'terrible'}
|
||||||
|
# we may have called take_gil earlier than we got it back
|
||||||
|
# sth like [called take [ take success [still dropping]]]
|
||||||
|
if not only_lock and pid in wants_take_gil:
|
||||||
|
yield header, {"name": 'GIL(take)', "ph": begin, "ts": wants_take_gil[pid], **common, 'cname': 'bad'}
|
||||||
|
yield header, {"name": 'GIL', "ph": begin, "ts": time_gil_take + jitter, **common}
|
||||||
|
if not only_lock:
|
||||||
|
yield header, {"name": 'GIL(drop)', "ph": begin, "ts": wants_drop_gil[pid], **common}
|
||||||
|
yield header, {"name": 'GIL(drop)', "ph": end, "ts": time_gil_drop, **common}
|
||||||
|
yield header, {"name": 'GIL', "ph": end, "ts": time_gil_drop, **common}
|
||||||
|
if not only_lock and pid in wants_take_gil:
|
||||||
|
yield header, {"name": 'GIL(take)', "ph": end, "ts": time_gil_drop, **common, 'cname': 'bad'}
|
||||||
|
else:
|
||||||
|
if event not in ignored:
|
||||||
|
print(f'ignoring {event}', file=sys.stderr)
|
||||||
|
ignored.add(event)
|
||||||
|
except:
|
||||||
|
print("error on line", header, file=sys.stderr)
|
||||||
|
raise
|
||||||
|
if verbose >= 1:
|
||||||
|
pids = ["PID"]
|
||||||
|
totals = ["total"]
|
||||||
|
wait = ["wait"]
|
||||||
|
table = []
|
||||||
|
for pid in t_min:
|
||||||
|
total = t_max[pid] - t_min[pid]
|
||||||
|
wait = time_wait_gil[pid]
|
||||||
|
on_gil = time_on_gil[pid]
|
||||||
|
no_gil = total - wait - on_gil
|
||||||
|
row = [pid, total, no_gil/total*100, on_gil/total*100, wait/total * 100]
|
||||||
|
if verbose >= 2:
|
||||||
|
row.extend([no_gil, on_gil, wait])
|
||||||
|
table.append(row)
|
||||||
|
headers = ['PID', 'total(us)', 'no gil%✅', 'has gil%❗', 'gil wait%❌']
|
||||||
|
if verbose:
|
||||||
|
headers.extend(['no gil(us)', 'has gil(us)', 'gil wait(us)'])
|
||||||
|
table = tabulate.tabulate(table, headers)
|
||||||
|
print()
|
||||||
|
print("Summary of threads:")
|
||||||
|
print()
|
||||||
|
print(table)
|
||||||
|
print()
|
||||||
|
print("High 'no gil' is good (✅), we like low 'has gil' (❗),\n and we don't want 'gil wait' (❌).")
|
||||||
|
print()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def perf2trace(input, verbose=1, store_runing=False, store_sleeping=True, all_tracepoints=False):
|
def perf2trace(input, verbose=1, store_runing=False, store_sleeping=True, all_tracepoints=False):
|
||||||
# useful for debugging, to have the pids a name
|
# useful for debugging, to have the pids a name
|
||||||
pid_names = {}
|
pid_names = {}
|
||||||
@ -214,7 +406,7 @@ def perf2trace(input, verbose=1, store_runing=False, store_sleeping=True, all_tr
|
|||||||
except BrokenPipeError:
|
except BrokenPipeError:
|
||||||
break
|
break
|
||||||
except:
|
except:
|
||||||
print("error on line", header, other)
|
print("error on line", header, other, file=sys.stderr)
|
||||||
raise
|
raise
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
|||||||
@ -25,16 +25,23 @@ $ perf-pyrecord -e cycles -m per4m.example2
|
|||||||
"""
|
"""
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
class PerfRecord:
|
class PerfRecord:
|
||||||
def __init__(self, output='perf.data', args=[], verbose=1):
|
def __init__(self, output='perf.data', args=[], verbose=1, stacktrace=True, buffer_size="128M"):
|
||||||
self.output = output
|
self.output = output
|
||||||
|
self.buffer_size = buffer_size
|
||||||
self.args = args
|
self.args = args
|
||||||
|
self.stacktrace = stacktrace
|
||||||
self.verbose = verbose
|
self.verbose = verbose
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __enter__(self):
|
def __enter__(self):
|
||||||
|
self.start()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def start(self):
|
||||||
pid = os.getpid()
|
pid = os.getpid()
|
||||||
# cmd = f"perf record -e 'sched:*' --call-graph dwarf -k CLOCK_MONOTONIC --pid {pid} -o {self.output}"
|
# cmd = f"perf record -e 'sched:*' --call-graph dwarf -k CLOCK_MONOTONIC --pid {pid} -o {self.output}"
|
||||||
perf_args = ' '.join(self.args)
|
perf_args = ' '.join(self.args)
|
||||||
cmd = f"perf record {perf_args} --call-graph dwarf -k CLOCK_MONOTONIC --pid {pid} -o {self.output}"
|
if self.stacktrace:
|
||||||
|
perf_args += " --call-graph dwarf"
|
||||||
|
cmd = f"perf record {perf_args} -k CLOCK_MONOTONIC --pid {pid} -o {self.output}"
|
||||||
if self.verbose >= 2:
|
if self.verbose >= 2:
|
||||||
print(f"Running: {cmd}")
|
print(f"Running: {cmd}")
|
||||||
args = shlex.split(cmd)
|
args = shlex.split(cmd)
|
||||||
@ -48,7 +55,7 @@ class PerfRecord:
|
|||||||
# we need to wait till perf creates the file
|
# we need to wait till perf creates the file
|
||||||
time.sleep(0.1)
|
time.sleep(0.1)
|
||||||
else:
|
else:
|
||||||
self.finish()
|
self._finish()
|
||||||
raise OSError(f'perf did not create {self.output}')
|
raise OSError(f'perf did not create {self.output}')
|
||||||
start_size = os.path.getsize(self.output)
|
start_size = os.path.getsize(self.output)
|
||||||
for _ in range(RETRIES):
|
for _ in range(RETRIES):
|
||||||
@ -58,13 +65,13 @@ class PerfRecord:
|
|||||||
# we need to wait till perf writes
|
# we need to wait till perf writes
|
||||||
time.sleep(0.1)
|
time.sleep(0.1)
|
||||||
else:
|
else:
|
||||||
self.finish()
|
self._finish()
|
||||||
raise OSError(f'perf did not write to {self.output}')
|
raise OSError(f'perf did not write to {self.output}')
|
||||||
# and give perf a bit more time
|
# and give perf a bit more time
|
||||||
time.sleep(0.05)
|
time.sleep(0.05)
|
||||||
return self
|
return self
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def finish(self):
|
def _finish(self):
|
||||||
self.perf.terminate()
|
self.perf.terminate()
|
||||||
outs, errs = self.perf.communicate(timeout=5)
|
outs, errs = self.perf.communicate(timeout=5)
|
||||||
if self.verbose >= 1:
|
if self.verbose >= 1:
|
||||||
@ -77,7 +84,10 @@ class PerfRecord:
|
|||||||
raise OSError(f'perf record fails, got exit code {self.perf.returncode}')
|
raise OSError(f'perf record fails, got exit code {self.perf.returncode}')
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
def __exit__(self, *args):
|
def __exit__(self, *args):
|
||||||
self.finish()
|
self.stop()
|
||||||
|
|
||||||
|
def stop(self):
|
||||||
|
self._finish()
|
||||||
if self.verbose >= 1:
|
if self.verbose >= 1:
|
||||||
print('Wait for perf to finish...')
|
print('Wait for perf to finish...')
|
||||||
self.perf.wait()
|
self.perf.wait()
|
||||||
|
|||||||
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user