commit
0cfb68cb26
tensorflow
compiler/xla
contrib
BUILD
bayesflow/python
kernel_tests
ops
cmake
distributions
BUILD__init__.py
python
hvx/hvx_ops_support_checker
layers
learn/python/learn
rnn
core
common_runtime
distributed_runtime
framework
graph
kernels
ops
docs_src
performance
programmers_guide
go/op
python
@ -406,7 +406,46 @@ class ReferenceUtil {
|
||||
const PaddingConfig& padding,
|
||||
const float pad);
|
||||
|
||||
// ApplyElementwise2D(f, x, y, ...) returns the Array2D formed by running
|
||||
// f(x[i], y[i], ...) for each array element in the Array2Ds x, y, ....
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The given arrays must have the same size and element type, and the return
|
||||
// type of f must be implicitly convertible to the arrays' element type.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Example usage:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Array2D<float> x, y, z = ...;
|
||||
// std::unique_ptr<Array2D> result = ReferenceUtil::ApplyElementwise2D(
|
||||
// [](float a, float b, float c) { return a * b + c; }, x, y, z);
|
||||
//
|
||||
template <typename F, typename T1, typename... Ts>
|
||||
static std::unique_ptr<Array2D<T1>> ApplyElementwise2D(
|
||||
F&& f, const Array2D<T1>& array1, const Array2D<Ts>&... arrays) {
|
||||
AssertSameSize2D(array1, arrays...);
|
||||
auto result = MakeUnique<Array2D<T1>>(array1.n1(), array1.n1());
|
||||
for (int64 i = 0; i < array1.n1(); ++i) {
|
||||
for (int64 j = 0; j < array1.n2(); ++j) {
|
||||
(*result)(i, j) = f(array1(i, j), arrays(i, j)...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
template <typename T1, typename T2, typename... Ts>
|
||||
static void AssertSameSize2D(const Array2D<T1>& array1,
|
||||
const Array2D<T2>& array2,
|
||||
const Array2D<Ts>&... arrays) {
|
||||
static_assert(std::is_same<T1, T2>::value, "Args must be same type.");
|
||||
CHECK_EQ(array1.n1(), array2.n1());
|
||||
CHECK_EQ(array1.n2(), array2.n2());
|
||||
AssertSameSize2D(array2, arrays...);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Recursive base case for AssertSameSize2D.
|
||||
template <typename Array1>
|
||||
static void AssertSameSize2D(const Array1& array1) {}
|
||||
|
||||
TF_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(ReferenceUtil);
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -52,9 +52,9 @@ class ReferenceUtilTest : public ::testing::Test {
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, TransposeArray2D) {
|
||||
auto result = ReferenceUtil::TransposeArray2D(*matrix_);
|
||||
auto result_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR2FromArray2D(*result);
|
||||
auto actual_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR2FromArray2D(*result);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR2Near<float>({{1.f, 4.f}, {2.f, 5.f}, {3.f, 6.f}},
|
||||
*result_literal, ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
*actual_literal, ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, MatmulArray2D) {
|
||||
@ -62,32 +62,32 @@ TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, MatmulArray2D) {
|
||||
{7.f, 8.f}, {9.f, 10.f}, {11.f, 12.f},
|
||||
});
|
||||
auto result = ReferenceUtil::MatmulArray2D(*matrix_, rhs);
|
||||
auto result_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR2FromArray2D(*result);
|
||||
auto actual_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR2FromArray2D(*result);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR2Near<float>({{58.f, 64.f}, {139.f, 154.f}},
|
||||
*result_literal, ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
*actual_literal, ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, ReduceToColArray2D) {
|
||||
auto add = [](float lhs, float rhs) { return lhs + rhs; };
|
||||
auto result = ReferenceUtil::ReduceToColArray2D(*matrix_, 0.0f, add);
|
||||
auto result_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR1<float>(*result);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR1Near<float>({6.f, 15.f}, *result_literal,
|
||||
auto actual_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR1<float>(*result);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR1Near<float>({6.f, 15.f}, *actual_literal,
|
||||
ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, ReduceToRowArray2D) {
|
||||
auto add = [](float lhs, float rhs) { return lhs + rhs; };
|
||||
auto result = ReferenceUtil::ReduceToRowArray2D(*matrix_, 0.0f, add);
|
||||
auto result_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR1<float>(*result);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR1Near<float>({5.f, 7.f, 9.f}, *result_literal,
|
||||
auto actual_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR1<float>(*result);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR1Near<float>({5.f, 7.f, 9.f}, *actual_literal,
|
||||
ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, MapArray2D) {
|
||||
auto identity = [](float value) { return log(exp(value)); };
|
||||
auto result = ReferenceUtil::MapArray2D(*matrix_, identity);
|
||||
auto result_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR2FromArray2D(*result);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR2NearArray2D(*matrix_, *result_literal,
|
||||
auto actual_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR2FromArray2D(*result);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR2NearArray2D(*matrix_, *actual_literal,
|
||||
ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -96,9 +96,9 @@ TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, MapWithIndexArray2D) {
|
||||
return value + row + col;
|
||||
};
|
||||
auto result = ReferenceUtil::MapWithIndexArray2D(*matrix_, add_index);
|
||||
auto result_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR2FromArray2D(*result);
|
||||
auto actual_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR2FromArray2D(*result);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR2Near<float>({{1.f, 3.f, 5.f}, {5.f, 7.f, 9.f}},
|
||||
*result_literal, ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
*actual_literal, ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, MapArray4D) {
|
||||
@ -107,11 +107,11 @@ TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, MapArray4D) {
|
||||
input->FillWithMultiples(1.0f);
|
||||
auto multiply_by_two = [](float value) { return 2 * value; };
|
||||
auto result = ReferenceUtil::MapArray4D(*input, multiply_by_two);
|
||||
auto result_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR4FromArray4D(*result);
|
||||
auto actual_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR4FromArray4D(*result);
|
||||
|
||||
Array4D<float> expected(/*planes=*/2, /*depth=*/3, /*height=*/4, /*width=*/5);
|
||||
expected.FillWithMultiples(2.0f);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR4NearArray4D(expected, *result_literal,
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR4NearArray4D(expected, *actual_literal,
|
||||
ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -124,11 +124,11 @@ TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, MapWithIndexArray4D) {
|
||||
return value - (3 * 4 * 5 * plane + 4 * 5 * depth + 5 * height + width);
|
||||
};
|
||||
auto result = ReferenceUtil::MapWithIndexArray4D(*input, subtract_index);
|
||||
auto result_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR4FromArray4D(*result);
|
||||
auto actual_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR4FromArray4D(*result);
|
||||
|
||||
Array4D<float> expected(/*planes=*/2, /*depth=*/3, /*height=*/4, /*width=*/5);
|
||||
expected.Fill(0.0f);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR4NearArray4D(expected, *result_literal,
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR4NearArray4D(expected, *actual_literal,
|
||||
ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -302,5 +302,17 @@ TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, ConvGeneralDimensionsWithValidPadding) {
|
||||
ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_F(ReferenceUtilTest, ApplyElementwise2D) {
|
||||
Array2D<float> a({{1, 2}, {3, 4}});
|
||||
Array2D<float> b({{10, 20}, {30, 40}});
|
||||
Array2D<float> c({{100, 200}, {300, 400}});
|
||||
|
||||
auto actual = ReferenceUtil::ApplyElementwise2D(
|
||||
[](float x, float y, float z) { return 100 * x + 10 * y + z; }, a, b, c);
|
||||
auto actual_literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR2FromArray2D(*actual);
|
||||
LiteralTestUtil::ExpectR2Near({{300.f, 600.f}, {900.f, 1200.f}},
|
||||
*actual_literal, ErrorSpec(0.0001));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace
|
||||
} // namespace xla
|
||||
|
||||
@ -859,7 +859,9 @@ cc_library(
|
||||
":hlo_pass",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/compiler/xla:literal_util",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/compiler/xla:shape_util",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/compiler/xla:status_macros",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/compiler/xla:util",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/core:lib",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -410,7 +410,9 @@ HloInstruction::CreateSelectAndScatter(
|
||||
/* static */ std::unique_ptr<HloInstruction> HloInstruction::CreateReshape(
|
||||
const Shape& shape, HloInstruction* operand) {
|
||||
CHECK_EQ(ShapeUtil::ElementsIn(shape),
|
||||
ShapeUtil::ElementsIn(operand->shape()));
|
||||
ShapeUtil::ElementsIn(operand->shape()))
|
||||
<< "shape: " << ShapeUtil::HumanString(shape)
|
||||
<< " operand: " << ShapeUtil::HumanString(operand->shape());
|
||||
auto instruction = WrapUnique(new HloInstruction(HloOpcode::kReshape, shape));
|
||||
instruction->AppendOperand(operand);
|
||||
return instruction;
|
||||
@ -1428,7 +1430,8 @@ string HloInstruction::ExtendedOpcodeStr() const {
|
||||
return opc_name;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
string HloInstruction::ToString(bool compact_operands) const {
|
||||
string HloInstruction::ToString(bool compact_operands,
|
||||
bool include_metadata) const {
|
||||
string operands;
|
||||
if (opcode() == HloOpcode::kConstant) {
|
||||
// For constants, show the actual value in place of an empty operand list.
|
||||
@ -1509,8 +1512,9 @@ string HloInstruction::ToString(bool compact_operands) const {
|
||||
if (opcode() == HloOpcode::kGetTupleElement) {
|
||||
StrAppend(&extra, ", index=", tuple_index());
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (!metadata_.op_type().empty() || !metadata_.op_name().empty() ||
|
||||
!metadata_.source_file().empty()) {
|
||||
if (include_metadata &&
|
||||
(!metadata_.op_type().empty() || !metadata_.op_name().empty() ||
|
||||
!metadata_.source_file().empty())) {
|
||||
StrAppend(&extra, " # metadata=", metadata_.ShortDebugString());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -489,7 +489,10 @@ class HloInstruction {
|
||||
string SignatureString() const;
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns a debugging string that represents this instruction.
|
||||
string ToString(bool compact_operands = false) const;
|
||||
string ToString(bool compact_operands = false,
|
||||
bool include_metadata = true) const;
|
||||
|
||||
string ToStringNoMetadata() const { return ToString(false, false); }
|
||||
|
||||
// As ToString, but returns a shorter string.
|
||||
string ToShortString() const;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,17 +13,8 @@ See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
==============================================================================*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/compiler/xla/service/reshape_mover.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <algorithm>
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/compiler/xla/literal_util.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/compiler/xla/shape_util.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/compiler/xla/util.h"
|
||||
|
||||
namespace xla {
|
||||
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
// Implementation note:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The general idea behind this pass is that we're converting from this:
|
||||
// %param.A = OldShape
|
||||
// %param.B = OldShape
|
||||
@ -44,6 +35,19 @@ namespace {
|
||||
// only implicit scalar broadcast is on Pred, not on A or B. Since reshapes or
|
||||
// transposes to a scalar should be cheap, we simply never move them.
|
||||
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/compiler/xla/service/reshape_mover.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include <algorithm>
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/compiler/xla/literal_util.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/compiler/xla/shape_util.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/compiler/xla/status_macros.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/compiler/xla/util.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/errors.h"
|
||||
|
||||
namespace xla {
|
||||
|
||||
namespace {
|
||||
|
||||
// Finds the first non-scalar operand of an instruction that is a reshape or
|
||||
// transpose and returns the operand if it is found or nullptr if not found.
|
||||
HloInstruction* FirstNonScalarReshapeOperand(const HloInstruction* hlo) {
|
||||
@ -51,6 +55,9 @@ HloInstruction* FirstNonScalarReshapeOperand(const HloInstruction* hlo) {
|
||||
if (!ShapeUtil::IsScalar(operand->shape()) &&
|
||||
(operand->opcode() == HloOpcode::kReshape ||
|
||||
operand->opcode() == HloOpcode::kTranspose)) {
|
||||
VLOG(5) << "Found first non-scalar reshape operand of "
|
||||
<< hlo->ToStringNoMetadata() << ":\n\t"
|
||||
<< operand->ToStringNoMetadata();
|
||||
return operand;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -70,6 +77,9 @@ bool OperandCanTrivallyChangeShape(const HloInstruction* instruction,
|
||||
// A constant can trivially reshape the literal it holds.
|
||||
if (operand->opcode() == HloOpcode::kConstant &&
|
||||
ShapeUtil::SameDimensions(operand->shape(), instruction->shape())) {
|
||||
VLOG(5) << "Constant had same dimensions as instruction:\n\toperand: "
|
||||
<< operand->ToStringNoMetadata()
|
||||
<< "\n\tinstruction: " << instruction->ToStringNoMetadata();
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -116,119 +126,159 @@ bool IsElementwiseOfEquivalentReshapesOrTransposes(
|
||||
if (!first_reshape_operand) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return (instruction->user_count() > 0 ||
|
||||
instruction == instruction->parent()->root_instruction()) &&
|
||||
instruction->IsElementwise() && !operands.empty() &&
|
||||
// Check whether all operands:
|
||||
// 1. are all reshapes or transposes that have the same input and
|
||||
// output shapes as all other reshaped or transposed operands.
|
||||
// or
|
||||
// 2. can be any shape like kConstant, kRng, and scalars.
|
||||
std::all_of(
|
||||
operands.begin(), operands.end(),
|
||||
[instruction,
|
||||
first_reshape_operand](const HloInstruction* operand) {
|
||||
return AreEquivalentReshapes(first_reshape_operand, operand) ||
|
||||
OperandCanTrivallyChangeShape(instruction, operand);
|
||||
});
|
||||
VLOG(3) << "** Checking whether instruction is an elementwise operation of "
|
||||
"equivalent reshapes/transposes: "
|
||||
<< instruction->ToStringNoMetadata();
|
||||
bool result =
|
||||
(instruction->user_count() > 0 ||
|
||||
instruction == instruction->parent()->root_instruction()) &&
|
||||
instruction->IsElementwise() && !operands.empty() &&
|
||||
// Check whether all operands:
|
||||
// 0. Have the same dimensions as the output -- if not, it may be
|
||||
// implicitly broadcast, which can confound the movement's
|
||||
// correctness.
|
||||
// 1. Are all reshapes or transposes that have the same input and
|
||||
// output shapes as all other reshaped or transposed operands.
|
||||
// or
|
||||
// 2. Can be any shape like kConstant, kRng, and scalars.
|
||||
std::all_of(
|
||||
operands.begin(), operands.end(),
|
||||
[instruction, first_reshape_operand](const HloInstruction* operand) {
|
||||
if (!ShapeUtil::SameDimensions(operand->shape(),
|
||||
instruction->shape())) {
|
||||
VLOG(5) << "Operand shape differs from output shape; may be "
|
||||
"implicitly broadcast, so preventing "
|
||||
"movement\n\toperand: "
|
||||
<< operand->ToStringNoMetadata() << "\n\tinstruction: "
|
||||
<< instruction->ToStringNoMetadata();
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (AreEquivalentReshapes(first_reshape_operand, operand)) {
|
||||
VLOG(5) << "Are equivalent reshapes:\n\tfirst_reshape_operand: "
|
||||
<< first_reshape_operand->ToStringNoMetadata()
|
||||
<< "\n\toperand: " << operand->ToStringNoMetadata();
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (OperandCanTrivallyChangeShape(instruction, operand)) {
|
||||
VLOG(5) << "Operand can trivially change shape: "
|
||||
<< operand->ToStringNoMetadata();
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
});
|
||||
VLOG(3) << "ElementwiseOfEquivalentReshapesOrTransposes result for "
|
||||
<< instruction->ToStringNoMetadata() << ": " << result;
|
||||
return result;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Try to sink any reshape or transpose operands of `instruction` across it. We
|
||||
// do so if `instruction` is elementwise and all operands are equivalent
|
||||
// reshapes or transposes.
|
||||
bool TrySinkReshapeOrTranspose(HloComputation* computation,
|
||||
HloInstruction* instruction) {
|
||||
if (IsElementwiseOfEquivalentReshapesOrTransposes(instruction)) {
|
||||
std::vector<HloInstruction*> operands = instruction->operands();
|
||||
HloInstruction* old_reshape = FirstNonScalarReshapeOperand(instruction);
|
||||
CHECK(old_reshape != nullptr);
|
||||
Shape new_elementwise_shape = old_reshape->operand(0)->shape();
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < operands.size(); ++i) {
|
||||
// All scalar operands remain as-is, even if they're reshape or transpose,
|
||||
// to simplify handling wrt special scalar broadcast rules for ops like
|
||||
// Select. Scalar reshapes should be cheap anyways.
|
||||
if (ShapeUtil::IsScalar(operands[i]->shape())) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto element_type = operands[i]->shape().element_type();
|
||||
switch (operands[i]->opcode()) {
|
||||
case HloOpcode::kConstant: {
|
||||
if (old_reshape->opcode() == HloOpcode::kReshape) {
|
||||
operands[i] = instruction->parent()->AddInstruction(
|
||||
HloInstruction::CreateReshape(
|
||||
ShapeUtil::ChangeElementType(new_elementwise_shape,
|
||||
element_type),
|
||||
operands[i]));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
CHECK_EQ(old_reshape->opcode(), HloOpcode::kTranspose);
|
||||
std::vector<int64> inverse_permutation =
|
||||
InversePermutation(old_reshape->dimensions());
|
||||
operands[i] = instruction->parent()->AddInstruction(
|
||||
HloInstruction::CreateTranspose(
|
||||
ShapeUtil::ChangeElementType(new_elementwise_shape,
|
||||
element_type),
|
||||
operands[i], inverse_permutation));
|
||||
}
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case HloOpcode::kRng: {
|
||||
CHECK_EQ(operands[i]->user_count(), 1);
|
||||
StatusOr<bool> TrySinkReshapeOrTranspose(HloComputation* computation,
|
||||
HloInstruction* instruction) {
|
||||
if (!IsElementwiseOfEquivalentReshapesOrTransposes(instruction)) {
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<HloInstruction*> operands = instruction->operands();
|
||||
HloInstruction* old_reshape = FirstNonScalarReshapeOperand(instruction);
|
||||
TF_RET_CHECK(old_reshape != nullptr);
|
||||
Shape new_elementwise_shape = old_reshape->operand(0)->shape();
|
||||
|
||||
VLOG(3) << "** Trying to sink reshape or transpose: "
|
||||
<< instruction->ToStringNoMetadata()
|
||||
<< "\n\told reshape: " << old_reshape->ToStringNoMetadata()
|
||||
<< "\n\tnew elementwise shape: "
|
||||
<< ShapeUtil::HumanString(new_elementwise_shape);
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < operands.size(); ++i) {
|
||||
// All scalar operands remain as-is, even if they're reshape or transpose,
|
||||
// to simplify handling wrt special scalar broadcast rules for ops like
|
||||
// Select. Scalar reshapes should be cheap anyways.
|
||||
if (ShapeUtil::IsScalar(operands[i]->shape())) {
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
PrimitiveType element_type = operands[i]->shape().element_type();
|
||||
switch (operands[i]->opcode()) {
|
||||
case HloOpcode::kConstant: {
|
||||
if (old_reshape->opcode() == HloOpcode::kReshape) {
|
||||
VLOG(3) << "Creating reshape for kConstant operand " << i << ": "
|
||||
<< operands[i]->ToStringNoMetadata();
|
||||
operands[i] = instruction->parent()->AddInstruction(
|
||||
operands[i]->CloneWithNewOperands(
|
||||
HloInstruction::CreateReshape(
|
||||
ShapeUtil::ChangeElementType(new_elementwise_shape,
|
||||
element_type),
|
||||
operands[i]->operands()));
|
||||
break;
|
||||
operands[i]));
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
TF_RET_CHECK(old_reshape->opcode() == HloOpcode::kTranspose);
|
||||
std::vector<int64> inverse_permutation =
|
||||
InversePermutation(old_reshape->dimensions());
|
||||
operands[i] = instruction->parent()->AddInstruction(
|
||||
HloInstruction::CreateTranspose(
|
||||
ShapeUtil::ChangeElementType(new_elementwise_shape,
|
||||
element_type),
|
||||
operands[i], inverse_permutation));
|
||||
}
|
||||
case HloOpcode::kReshape:
|
||||
case HloOpcode::kTranspose:
|
||||
operands[i] = operands[i]->mutable_operand(0);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
LOG(FATAL) << "Unexpected opcode while trying to sink reshapes or "
|
||||
"transposes.";
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (HloOpcode::kFusion == instruction->opcode()) {
|
||||
// Here we already know `instruction` is elementwise, and no operand is
|
||||
// implicit broadcast as if it were the operands would not be equivalent
|
||||
// reshapes, so all the fused instructions have the same dimensions.
|
||||
for (const auto& fused_instruction : instruction->fused_instructions()) {
|
||||
Shape* shape = fused_instruction->mutable_shape();
|
||||
*shape->mutable_dimensions() = new_elementwise_shape.dimensions();
|
||||
*shape->mutable_layout() = new_elementwise_shape.layout();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
auto new_elementwise =
|
||||
computation->AddInstruction(instruction->CloneWithNewOperands(
|
||||
// `instruction` may change the element type, e.g., from
|
||||
// operands[0] -> reshape -> convert (`instruction`)
|
||||
// to
|
||||
// operands[0] -> convert' -> reshape'
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In this case, convert' should have the same element type as
|
||||
// `convert` and the same dimensions as operands[0].
|
||||
ShapeUtil::ChangeElementType(new_elementwise_shape,
|
||||
instruction->shape().element_type()),
|
||||
operands));
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<HloInstruction> new_reshape;
|
||||
switch (old_reshape->opcode()) {
|
||||
case HloOpcode::kReshape:
|
||||
new_reshape = HloInstruction::CreateReshape(instruction->shape(),
|
||||
new_elementwise);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case HloOpcode::kRng: {
|
||||
CHECK_EQ(operands[i]->user_count(), 1);
|
||||
operands[i] = instruction->parent()->AddInstruction(
|
||||
operands[i]->CloneWithNewOperands(
|
||||
ShapeUtil::ChangeElementType(new_elementwise_shape,
|
||||
element_type),
|
||||
operands[i]->operands()));
|
||||
break;
|
||||
}
|
||||
case HloOpcode::kReshape:
|
||||
case HloOpcode::kTranspose:
|
||||
new_reshape = HloInstruction::CreateTranspose(
|
||||
instruction->shape(), new_elementwise, old_reshape->dimensions());
|
||||
operands[i] = operands[i]->mutable_operand(0);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
LOG(FATAL) << "Bad opcode";
|
||||
LOG(FATAL) << "Unexpected opcode while trying to sink reshapes or "
|
||||
"transposes.";
|
||||
}
|
||||
TF_CHECK_OK(computation->ReplaceWithNewInstruction(instruction,
|
||||
std::move(new_reshape)));
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
return false;
|
||||
if (HloOpcode::kFusion == instruction->opcode()) {
|
||||
// Here we already know `instruction` is elementwise, and no operand is
|
||||
// implicit broadcast as if it were the operands would not be equivalent
|
||||
// reshapes, so all the fused instructions have the same dimensions.
|
||||
for (const auto& fused_instruction : instruction->fused_instructions()) {
|
||||
Shape* shape = fused_instruction->mutable_shape();
|
||||
*shape->mutable_dimensions() = new_elementwise_shape.dimensions();
|
||||
*shape->mutable_layout() = new_elementwise_shape.layout();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
HloInstruction* new_elementwise =
|
||||
computation->AddInstruction(instruction->CloneWithNewOperands(
|
||||
// `instruction` may change the element type, e.g., from
|
||||
// operands[0] -> reshape -> convert (`instruction`)
|
||||
// to
|
||||
// operands[0] -> convert' -> reshape'
|
||||
//
|
||||
// In this case, convert' should have the same element type as
|
||||
// `convert` and the same dimensions as operands[0].
|
||||
ShapeUtil::ChangeElementType(new_elementwise_shape,
|
||||
instruction->shape().element_type()),
|
||||
operands));
|
||||
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<HloInstruction> new_reshape;
|
||||
switch (old_reshape->opcode()) {
|
||||
case HloOpcode::kReshape:
|
||||
VLOG(3) << "Creating new reshape for new elementwise op: "
|
||||
<< new_elementwise->ToStringNoMetadata();
|
||||
new_reshape =
|
||||
HloInstruction::CreateReshape(instruction->shape(), new_elementwise);
|
||||
break;
|
||||
case HloOpcode::kTranspose:
|
||||
new_reshape = HloInstruction::CreateTranspose(
|
||||
instruction->shape(), new_elementwise, old_reshape->dimensions());
|
||||
break;
|
||||
default:
|
||||
LOG(FATAL) << "Bad opcode";
|
||||
}
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(computation->ReplaceWithNewInstruction(
|
||||
instruction, std::move(new_reshape)));
|
||||
return true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace
|
||||
@ -237,9 +287,9 @@ StatusOr<bool> ReshapeMover::Run(HloModule* module) {
|
||||
bool changed = false;
|
||||
for (const auto& comp : module->computations()) {
|
||||
for (HloInstruction* instruction : comp->MakeInstructionPostOrder()) {
|
||||
if (TrySinkReshapeOrTranspose(comp.get(), instruction)) {
|
||||
changed = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
TF_ASSIGN_OR_RETURN(bool did_change,
|
||||
TrySinkReshapeOrTranspose(comp.get(), instruction));
|
||||
changed |= did_change;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return changed;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -234,6 +234,58 @@ TEST_F(ReshapeMoverTest, ScalarReshapeNotMovedAcrossSelect) {
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(select, computation->root_instruction());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Tree looks like:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// param0 [1,128,1]
|
||||
// |
|
||||
// reshape [128,1] constant [128,1024]
|
||||
// \ /
|
||||
// multiply w/implicit broadcast [128,1024]
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The reshape mover would like to sink the reshape below the multiply.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Previously we would attempt to insert a reshape of the constant to [1,128,1]
|
||||
// (which is unsound, because it has a different number of elements) as
|
||||
// preparation for sinking the reshape.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// To eliminate the unsoundness, we outlaw reshape sinking when one of the
|
||||
// operands is implicitly broadcast in the elementwise consumer.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// TODO(b/37799338) However, it would be possible in this case to do a more
|
||||
// in-depth analysis to get reshape movement to occur:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// 1. Note that the broadcast dimension (logical dimension 1) in the operands
|
||||
// would map back to logical dimension 2 in the param0 node.
|
||||
// 2. Match rank of the constant to the param0 node (by prepending a trivial 1
|
||||
// dimension).
|
||||
// 3. Reshape to [128,1024] at the root.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// But this is not currently done.
|
||||
TEST_F(ReshapeMoverTest, ImplicitlyBroadcastReshapeIsNotMovedBug37787999) {
|
||||
HloComputation::Builder builder(TestName());
|
||||
auto param0 = builder.AddInstruction(HloInstruction::CreateParameter(
|
||||
0, ShapeUtil::MakeShape(F32, {1, 128, 1}), "param0"));
|
||||
auto reshape = builder.AddInstruction(HloInstruction::CreateReshape(
|
||||
ShapeUtil::MakeShape(F32, {128, 1}), param0));
|
||||
Array2D<float> a(128, 1024);
|
||||
auto literal = LiteralUtil::CreateR2FromArray2D<float>(a);
|
||||
auto constant = builder.AddInstruction(
|
||||
HloInstruction::CreateConstant(std::move(literal)));
|
||||
auto multiply = builder.AddInstruction(HloInstruction::CreateBinary(
|
||||
constant->shape(), HloOpcode::kMultiply, constant, reshape));
|
||||
|
||||
auto module = MakeUnique<HloModule>(TestName());
|
||||
auto computation = module->AddEntryComputation(builder.Build());
|
||||
EXPECT_THAT(computation->root_instruction(),
|
||||
op::Multiply(op::Constant(), op::Reshape(param0)));
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_FALSE(ReshapeMover().Run(module.get()).ValueOrDie());
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_THAT(computation->root_instruction(),
|
||||
op::Multiply(op::Constant(), op::Reshape(param0)));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(multiply, computation->root_instruction());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Tree looks like this:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// add1
|
||||
|
||||
@ -78,7 +78,6 @@ cc_library(
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/batching:batch_ops_kernels",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/factorization/kernels:all_kernels",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/input_pipeline:input_pipeline_ops_kernels",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/layers:bucketization_op_kernel",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/layers:sparse_feature_cross_op_kernel",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/nccl:nccl_kernels",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/tensor_forest:tensor_forest_kernels",
|
||||
@ -93,7 +92,6 @@ cc_library(
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/factorization:all_ops",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/framework:all_ops",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/input_pipeline:input_pipeline_ops_op_lib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/layers:bucketization_op_op_lib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/layers:sparse_feature_cross_op_op_lib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/nccl:nccl_ops_op_lib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/tensor_forest:tensor_forest_ops_op_lib",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -95,7 +95,7 @@ class ElboRatioTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
n=n_samples,
|
||||
form=entropy.ELBOForms.sample,
|
||||
seed=42)
|
||||
actual_kl = distributions.kl(q, p)
|
||||
actual_kl = distributions.kl_divergence(q, p)
|
||||
|
||||
# Relative tolerance (rtol) chosen 2 times as large as minimim needed to
|
||||
# pass.
|
||||
@ -123,7 +123,7 @@ class ElboRatioTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
n=n_samples,
|
||||
form=entropy.ELBOForms.analytic_entropy,
|
||||
seed=42)
|
||||
actual_kl = distributions.kl(q, p)
|
||||
actual_kl = distributions.kl_divergence(q, p)
|
||||
|
||||
# Relative tolerance (rtol) chosen 2 times as large as minimim needed to
|
||||
# pass.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,11 +22,11 @@ import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.bayesflow.python.ops import stochastic_gradient_estimators
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.bayesflow.python.ops import stochastic_tensor_impl
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import normal
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import normal
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import test
|
||||
|
||||
sge = stochastic_gradient_estimators
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,12 +22,12 @@ from tensorflow.contrib import distributions as distributions_lib
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib import layers
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.bayesflow.python.ops import stochastic_tensor
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.bayesflow.python.ops import variational_inference_impl
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import normal
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import variables
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import normal
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import test
|
||||
|
||||
st = stochastic_tensor
|
||||
@ -68,7 +68,7 @@ class VariationalInferenceTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
def testDefaultVariationalAndPrior(self):
|
||||
_, prior, variational, _, log_likelihood = mini_vae()
|
||||
elbo = vi.elbo(log_likelihood)
|
||||
expected_elbo = log_likelihood - kullback_leibler.kl(
|
||||
expected_elbo = log_likelihood - kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(
|
||||
variational.distribution, prior)
|
||||
with self.test_session() as sess:
|
||||
sess.run(variables.global_variables_initializer())
|
||||
@ -80,7 +80,7 @@ class VariationalInferenceTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
prior = normal.Normal(loc=3., scale=2.)
|
||||
elbo = vi.elbo(
|
||||
log_likelihood, variational_with_prior={variational: prior})
|
||||
expected_elbo = log_likelihood - kullback_leibler.kl(
|
||||
expected_elbo = log_likelihood - kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(
|
||||
variational.distribution, prior)
|
||||
sess.run(variables.global_variables_initializer())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(*sess.run([expected_elbo, elbo]))
|
||||
@ -121,7 +121,7 @@ class VariationalInferenceTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
# No analytic KL available between prior and variational distributions.
|
||||
with self.assertRaisesRegexp(NotImplementedError, "No KL"):
|
||||
distributions.kl(variational.distribution, prior)
|
||||
distributions.kl_divergence(variational.distribution, prior)
|
||||
|
||||
elbo = vi.elbo(
|
||||
variational_with_prior={variational: prior},
|
||||
|
||||
@ -84,8 +84,9 @@ def elbo_ratio(log_p,
|
||||
KL[q || p] = E[ Log[q(Z)] - Log[p(Z)] ]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Note that if `p` is a `Distribution`, then `distributions.kl(q, p)` may be
|
||||
defined and available as an exact result.
|
||||
Note that if `p` is a `Distribution`, then
|
||||
`distributions.kl_divergence(q, p)` may be defined and available as an
|
||||
exact result.
|
||||
|
||||
#### ELBO
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -28,10 +28,10 @@ from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.bayesflow.python.ops import stochastic_graph_impl as sg
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.bayesflow.python.ops import stochastic_tensor_impl as st
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import distribution
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import tf_logging as logging
|
||||
|
||||
VI_PRIORS = "__vi_priors__"
|
||||
@ -259,7 +259,7 @@ def _elbo(form, log_likelihood, log_joint, variational_with_prior,
|
||||
kl = None
|
||||
if log_joint is None and form in {ELBOForms.default, ELBOForms.analytic_kl}:
|
||||
try:
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl(q, p)
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(q, p)
|
||||
logging.info("Using analytic KL between q:%s, p:%s", q, p)
|
||||
except NotImplementedError as e:
|
||||
if form == ELBOForms.analytic_kl:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -47,9 +47,7 @@ if(tensorflow_BUILD_CONTRIB_KERNELS)
|
||||
"${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/factorization/ops/factorization_ops.cc"
|
||||
#"${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/ffmpeg/decode_audio_op.cc"
|
||||
#"${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/ffmpeg/encode_audio_op.cc"
|
||||
"${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/layers/kernels/bucketization_kernel.cc"
|
||||
"${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/layers/kernels/sparse_feature_cross_kernel.cc"
|
||||
"${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/layers/ops/bucketization_op.cc"
|
||||
"${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/layers/ops/sparse_feature_cross_op.cc"
|
||||
"${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/nccl/kernels/nccl_manager.cc"
|
||||
"${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/nccl/kernels/nccl_ops.cc"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -70,7 +70,6 @@ GENERATE_CONTRIB_OP_LIBRARY(factorization_factorization "${tensorflow_source_dir
|
||||
GENERATE_CONTRIB_OP_LIBRARY(framework_variable "${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/framework/ops/variable_ops.cc")
|
||||
GENERATE_CONTRIB_OP_LIBRARY(input_pipeline "${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/input_pipeline/ops/input_pipeline_ops.cc")
|
||||
GENERATE_CONTRIB_OP_LIBRARY(image "${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/image/ops/image_ops.cc")
|
||||
GENERATE_CONTRIB_OP_LIBRARY(layers_bucketization "${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/layers/ops/bucketization_op.cc")
|
||||
GENERATE_CONTRIB_OP_LIBRARY(layers_sparse_feature_cross "${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/layers/ops/sparse_feature_cross_op.cc")
|
||||
GENERATE_CONTRIB_OP_LIBRARY(memory_stats "${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/memory_stats/ops/memory_stats_ops.cc")
|
||||
GENERATE_CONTRIB_OP_LIBRARY(nccl "${tensorflow_source_dir}/tensorflow/contrib/nccl/ops/nccl_ops.cc")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -623,8 +623,6 @@ GENERATE_PYTHON_OP_LIB("contrib_input_pipeline_ops"
|
||||
DESTINATION ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/tf_python/tensorflow/contrib/input_pipeline/ops/gen_input_pipeline_ops.py)
|
||||
GENERATE_PYTHON_OP_LIB("contrib_image_ops"
|
||||
DESTINATION ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/tf_python/tensorflow/contrib/image/ops/gen_image_ops.py)
|
||||
GENERATE_PYTHON_OP_LIB("contrib_layers_bucketization_ops"
|
||||
DESTINATION ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/tf_python/tensorflow/contrib/layers/ops/gen_bucketization_op.py)
|
||||
GENERATE_PYTHON_OP_LIB("contrib_layers_sparse_feature_cross_ops"
|
||||
DESTINATION ${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/tf_python/tensorflow/contrib/layers/ops/gen_sparse_feature_cross_op.py)
|
||||
GENERATE_PYTHON_OP_LIB("contrib_memory_stats_ops"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -496,24 +496,6 @@ cuda_py_test(
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
cuda_py_test(
|
||||
name = "normal_test",
|
||||
size = "medium",
|
||||
srcs = ["python/kernel_tests/normal_test.py"],
|
||||
additional_deps = [
|
||||
":distributions_py",
|
||||
"//third_party/py/numpy",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:array_ops",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:client_testlib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:framework_for_generated_wrappers",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:framework_test_lib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:gradients",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:nn_ops",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:platform_test",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:variables",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
cuda_py_test(
|
||||
name = "poisson_test",
|
||||
size = "small",
|
||||
@ -614,18 +596,6 @@ cuda_py_test(
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
cuda_py_test(
|
||||
name = "kullback_leibler_test",
|
||||
size = "small",
|
||||
srcs = ["python/kernel_tests/kullback_leibler_test.py"],
|
||||
additional_deps = [
|
||||
":distributions_py",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:array_ops",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:client_testlib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:platform_test",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
cuda_py_test(
|
||||
name = "normal_conjugate_posteriors_test",
|
||||
size = "small",
|
||||
@ -751,22 +721,6 @@ cuda_py_test(
|
||||
tags = ["no_pip"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
cuda_py_test(
|
||||
name = "special_math_test",
|
||||
size = "medium",
|
||||
srcs = ["python/kernel_tests/special_math_test.py"],
|
||||
additional_deps = [
|
||||
":distributions_py",
|
||||
"//third_party/py/numpy",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:client_testlib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:framework_for_generated_wrappers",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:framework_test_lib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:gradients",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:platform_test",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:variables",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
cuda_py_test(
|
||||
name = "distribution_util_test",
|
||||
size = "small",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -71,7 +71,7 @@ See the @{$python/contrib.distributions} guide.
|
||||
@@RelaxedOneHotCategorical
|
||||
|
||||
## Kullback-Leibler Divergence
|
||||
@@kl
|
||||
@@kl_divergence
|
||||
@@RegisterKL
|
||||
|
||||
## Helper Functions
|
||||
@ -106,7 +106,6 @@ from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.exponential import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.gamma import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.geometric import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.inverse_gamma import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.kullback_leibler import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.laplace import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.logistic import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.mixture import *
|
||||
@ -115,7 +114,6 @@ from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.mvn_diag import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.mvn_diag_plus_low_rank import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.mvn_tril import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.negative_binomial import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.normal import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.normal_conjugate_posteriors import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.onehot_categorical import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.poisson import *
|
||||
@ -129,6 +127,8 @@ from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.uniform import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.wishart import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions.conditional_distribution import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions.distribution import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions.kullback_leibler import *
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions.normal import *
|
||||
|
||||
# pylint: enable=unused-import,wildcard-import,line-too-long,g-importing-member
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,11 +21,11 @@ from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
import scipy.special
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import bernoulli
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import test
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -286,7 +286,7 @@ class BernoulliTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
a = bernoulli.Bernoulli(probs=a_p)
|
||||
b = bernoulli.Bernoulli(probs=b_p)
|
||||
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl(a, b)
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(a, b)
|
||||
kl_val = sess.run(kl)
|
||||
|
||||
kl_expected = (a_p * np.log(a_p / b_p) + (1. - a_p) * np.log(
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,13 +20,13 @@ import numpy as np
|
||||
from scipy import special
|
||||
from scipy import stats
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import beta as beta_lib
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.client import session
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import random_seed
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import tensor_shape
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import test
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -349,13 +349,13 @@ class BetaTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
for dist1 in [d1, d1_sp]:
|
||||
for dist2 in [d2, d2_sp]:
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl(dist1, dist2)
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(dist1, dist2)
|
||||
kl_val = sess.run(kl)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(kl.get_shape(), shape)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(kl_val, kl_expected)
|
||||
|
||||
# Make sure KL(d1||d1) is 0
|
||||
kl_same = sess.run(kullback_leibler.kl(d1, d1))
|
||||
kl_same = sess.run(kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(d1, d1))
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(kl_same, np.zeros_like(kl_expected))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -41,6 +41,12 @@ class SoftplusBijectorTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
"""Inverse log det jacobian, before being reduced."""
|
||||
return -np.log(1 - np.exp(-y))
|
||||
|
||||
def testHingeSoftnessZeroRaises(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
bijector = Softplus(event_ndims=0, hinge_softness=0., validate_args=True)
|
||||
with self.assertRaisesOpError("must be non-zero"):
|
||||
bijector.forward([1., 1.]).eval()
|
||||
|
||||
def testBijectorForwardInverseEventDimsZero(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
bijector = Softplus(event_ndims=0)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -21,7 +21,6 @@ from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import categorical
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import tensor_util
|
||||
@ -30,6 +29,7 @@ from tensorflow.python.ops import gradients_impl
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import random_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import test
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -278,10 +278,10 @@ class CategoricalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
a = categorical.Categorical(logits=a_logits)
|
||||
b = categorical.Categorical(logits=b_logits)
|
||||
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl(a, b)
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(a, b)
|
||||
kl_val = sess.run(kl)
|
||||
# Make sure KL(a||a) is 0
|
||||
kl_same = sess.run(kullback_leibler.kl(a, a))
|
||||
kl_same = sess.run(kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(a, a))
|
||||
|
||||
prob_a = np_softmax(a_logits)
|
||||
prob_b = np_softmax(b_logits)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,12 +22,12 @@ from scipy import special
|
||||
from scipy import stats
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import gamma as gamma_lib
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.client import session
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import tensor_shape
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import test
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -345,7 +345,7 @@ class GammaTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
g1 = gamma_lib.Gamma(concentration=alpha1, rate=beta1)
|
||||
x = g0.sample(int(1e4), seed=0)
|
||||
kl_sample = math_ops.reduce_mean(g0.log_prob(x) - g1.log_prob(x), 0)
|
||||
kl_actual = kullback_leibler.kl(g0, g1)
|
||||
kl_actual = kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(g0, g1)
|
||||
|
||||
# Execute graph.
|
||||
[kl_sample_, kl_actual_] = sess.run([kl_sample, kl_actual])
|
||||
|
||||
@ -185,19 +185,19 @@ class MultivariateNormalDiagPlusLowRankTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
sample_kl_identity = math_ops.reduce_mean(
|
||||
dist.log_prob(samps) - mvn_identity.log_prob(samps), 0)
|
||||
analytical_kl_identity = ds.kl(dist, mvn_identity)
|
||||
analytical_kl_identity = ds.kl_divergence(dist, mvn_identity)
|
||||
|
||||
sample_kl_scaled = math_ops.reduce_mean(
|
||||
dist.log_prob(samps) - mvn_scaled.log_prob(samps), 0)
|
||||
analytical_kl_scaled = ds.kl(dist, mvn_scaled)
|
||||
analytical_kl_scaled = ds.kl_divergence(dist, mvn_scaled)
|
||||
|
||||
sample_kl_diag = math_ops.reduce_mean(
|
||||
dist.log_prob(samps) - mvn_diag.log_prob(samps), 0)
|
||||
analytical_kl_diag = ds.kl(dist, mvn_diag)
|
||||
analytical_kl_diag = ds.kl_divergence(dist, mvn_diag)
|
||||
|
||||
sample_kl_chol = math_ops.reduce_mean(
|
||||
dist.log_prob(samps) - mvn_chol.log_prob(samps), 0)
|
||||
analytical_kl_chol = ds.kl(dist, mvn_chol)
|
||||
analytical_kl_chol = ds.kl_divergence(dist, mvn_chol)
|
||||
|
||||
n = int(10e3)
|
||||
baseline = ds.MultivariateNormalDiag(
|
||||
@ -208,19 +208,21 @@ class MultivariateNormalDiagPlusLowRankTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
sample_kl_identity_diag_baseline = math_ops.reduce_mean(
|
||||
baseline.log_prob(samps) - mvn_identity.log_prob(samps), 0)
|
||||
analytical_kl_identity_diag_baseline = ds.kl(baseline, mvn_identity)
|
||||
analytical_kl_identity_diag_baseline = ds.kl_divergence(
|
||||
baseline, mvn_identity)
|
||||
|
||||
sample_kl_scaled_diag_baseline = math_ops.reduce_mean(
|
||||
baseline.log_prob(samps) - mvn_scaled.log_prob(samps), 0)
|
||||
analytical_kl_scaled_diag_baseline = ds.kl(baseline, mvn_scaled)
|
||||
analytical_kl_scaled_diag_baseline = ds.kl_divergence(
|
||||
baseline, mvn_scaled)
|
||||
|
||||
sample_kl_diag_diag_baseline = math_ops.reduce_mean(
|
||||
baseline.log_prob(samps) - mvn_diag.log_prob(samps), 0)
|
||||
analytical_kl_diag_diag_baseline = ds.kl(baseline, mvn_diag)
|
||||
analytical_kl_diag_diag_baseline = ds.kl_divergence(baseline, mvn_diag)
|
||||
|
||||
sample_kl_chol_diag_baseline = math_ops.reduce_mean(
|
||||
baseline.log_prob(samps) - mvn_chol.log_prob(samps), 0)
|
||||
analytical_kl_chol_diag_baseline = ds.kl(baseline, mvn_chol)
|
||||
analytical_kl_chol_diag_baseline = ds.kl_divergence(baseline, mvn_chol)
|
||||
|
||||
[
|
||||
sample_mean_,
|
||||
|
||||
@ -241,7 +241,7 @@ class MultivariateNormalTriLTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
scale_tril=np.linalg.cholesky(sigma_b),
|
||||
validate_args=True)
|
||||
|
||||
kl = ds.kl(mvn_a, mvn_b)
|
||||
kl = ds.kl_divergence(mvn_a, mvn_b)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(batch_shape, kl.get_shape())
|
||||
|
||||
kl_v = kl.eval()
|
||||
@ -263,7 +263,7 @@ class MultivariateNormalTriLTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
scale_tril=np.linalg.cholesky(sigma_b),
|
||||
validate_args=True)
|
||||
|
||||
kl = ds.kl(mvn_a, mvn_b)
|
||||
kl = ds.kl_divergence(mvn_a, mvn_b)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(batch_shape, kl.get_shape())
|
||||
|
||||
kl_v = kl.eval()
|
||||
@ -285,7 +285,7 @@ class MultivariateNormalTriLTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
validate_args=True)
|
||||
|
||||
# Should be zero since KL(p || p) = =.
|
||||
kl = ds.kl(mvn_a, mvn_a)
|
||||
kl = ds.kl_divergence(mvn_a, mvn_a)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(batch_shape, kl.get_shape())
|
||||
|
||||
kl_v = kl.eval()
|
||||
@ -323,7 +323,7 @@ class MultivariateNormalTriLTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
sample_kl_chol = math_ops.reduce_mean(
|
||||
dist.log_prob(samps) - mvn_chol.log_prob(samps), 0)
|
||||
analytical_kl_chol = ds.kl(dist, mvn_chol)
|
||||
analytical_kl_chol = ds.kl_divergence(dist, mvn_chol)
|
||||
|
||||
scale = dist.scale.to_dense()
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -19,7 +19,6 @@ from __future__ import division
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import onehot_categorical
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
@ -27,6 +26,7 @@ from tensorflow.python.framework import tensor_util
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import random_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import test
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -178,8 +178,8 @@ class OneHotCategoricalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
kl_expected = np.sum(
|
||||
prob_p * (np.log(prob_p) - np.log(prob_q)), axis=-1)
|
||||
|
||||
kl_actual = kullback_leibler.kl(p, q)
|
||||
kl_same = kullback_leibler.kl(p, p)
|
||||
kl_actual = kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(p, q)
|
||||
kl_same = kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(p, p)
|
||||
x = p.sample(int(2e4), seed=0)
|
||||
x = math_ops.cast(x, dtype=dtypes.float32)
|
||||
# Compute empirical KL(p||q).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +18,6 @@ from __future__ import absolute_import
|
||||
from __future__ import division
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import tensor_shape
|
||||
@ -29,6 +28,7 @@ from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import random_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import distribution
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import util as distribution_util
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,7 +20,6 @@ from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
@ -32,6 +31,7 @@ from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import random_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import distribution
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import util as distribution_util
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -94,7 +94,9 @@ class Softplus(bijector.Bijector):
|
||||
if validate_args:
|
||||
nonzero_check = check_ops.assert_none_equal(
|
||||
ops.convert_to_tensor(
|
||||
0, dtype=self.hinge_softness.dtype), self.hinge_softness)
|
||||
0, dtype=self.hinge_softness.dtype),
|
||||
self.hinge_softness,
|
||||
message="hinge_softness must be non-zero")
|
||||
self._hinge_softness = control_flow_ops.with_dependencies(
|
||||
[nonzero_check], self.hinge_softness)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +18,6 @@ from __future__ import absolute_import
|
||||
from __future__ import division
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
@ -28,6 +27,7 @@ from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import random_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import distribution
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import util as distribution_util
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,7 +20,6 @@ from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
@ -32,6 +31,7 @@ from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import random_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import distribution
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import util as distribution_util
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -22,7 +22,6 @@ import math
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import special_math
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
@ -33,6 +32,7 @@ from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import random_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import distribution
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import special_math
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = [
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,8 +20,6 @@ from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib import linalg
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import bijectors
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import normal
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import transformed_distribution
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import tensor_shape
|
||||
@ -29,6 +27,8 @@ from tensorflow.python.framework import tensor_util
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import linalg_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import normal
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import util as distribution_util
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,9 +18,8 @@ from __future__ import absolute_import
|
||||
from __future__ import division
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops.normal import Normal # pylint: disable=line-too-long
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import normal
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def normal_conjugates_known_scale_posterior(prior, scale, s, n):
|
||||
@ -65,7 +64,7 @@ def normal_conjugates_known_scale_posterior(prior, scale, s, n):
|
||||
TypeError: if dtype of `s` does not match `dtype`, or `prior` is not a
|
||||
Normal object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not isinstance(prior, Normal):
|
||||
if not isinstance(prior, normal.Normal):
|
||||
raise TypeError("Expected prior to be an instance of type Normal")
|
||||
|
||||
if s.dtype != prior.dtype:
|
||||
@ -77,7 +76,7 @@ def normal_conjugates_known_scale_posterior(prior, scale, s, n):
|
||||
scale0_2 = math_ops.square(prior.scale)
|
||||
scale_2 = math_ops.square(scale)
|
||||
scalep_2 = 1.0/(1/scale0_2 + n/scale_2)
|
||||
return Normal(
|
||||
return normal.Normal(
|
||||
loc=(prior.loc/scale0_2 + s/scale_2) * scalep_2,
|
||||
scale=math_ops.sqrt(scalep_2))
|
||||
|
||||
@ -131,7 +130,7 @@ def normal_conjugates_known_scale_predictive(prior, scale, s, n):
|
||||
TypeError: if dtype of `s` does not match `dtype`, or `prior` is not a
|
||||
Normal object.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not isinstance(prior, Normal):
|
||||
if not isinstance(prior, normal.Normal):
|
||||
raise TypeError("Expected prior to be an instance of type Normal")
|
||||
|
||||
if s.dtype != prior.dtype:
|
||||
@ -143,6 +142,6 @@ def normal_conjugates_known_scale_predictive(prior, scale, s, n):
|
||||
scale0_2 = math_ops.square(prior.scale)
|
||||
scale_2 = math_ops.square(scale)
|
||||
scalep_2 = 1.0/(1/scale0_2 + n/scale_2)
|
||||
return Normal(
|
||||
return normal.Normal(
|
||||
loc=(prior.loc/scale0_2 + s/scale_2) * scalep_2,
|
||||
scale=math_ops.sqrt(scalep_2 + scale_2))
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,7 +18,6 @@ from __future__ import absolute_import
|
||||
from __future__ import division
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
|
||||
@ -28,6 +27,7 @@ from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import random_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import distribution
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import util as distribution_util
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -232,7 +232,7 @@ class QuantizedDistribution(distributions.Distribution):
|
||||
graph_parents = self._dist._graph_parents # pylint: disable=protected-access
|
||||
|
||||
checks = []
|
||||
if low is not None and high is not None:
|
||||
if validate_args and low is not None and high is not None:
|
||||
message = "low must be strictly less than high."
|
||||
checks.append(
|
||||
check_ops.assert_less(
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,6 +25,7 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/core/kernels/hexagon/hexagon_ops_definitions.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/status.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/strings/str_util.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/core/platform/init_main.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/core/platform/logging.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/core/util/command_line_flags.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/tools/graph_transforms/transform_utils.h"
|
||||
@ -36,6 +37,9 @@ static int ParseFlags(int argc, char* argv[], string* in_graph) {
|
||||
Flag("in_graph", in_graph, "input graph file name"),
|
||||
};
|
||||
CHECK(Flags::Parse(&argc, argv, flag_list));
|
||||
// We need to call this to set up global state for TensorFlow.
|
||||
port::InitMain(argv[0], &argc, &argv);
|
||||
|
||||
string usage = Flags::Usage(argv[0], flag_list);
|
||||
CHECK(!in_graph->empty()) << "in_graph graph can't be empty.\n" << usage;
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,35 +18,6 @@ load("//tensorflow:tensorflow.bzl", "tf_gen_op_libs")
|
||||
load("//tensorflow:tensorflow.bzl", "tf_gen_op_wrapper_py")
|
||||
load("//tensorflow:tensorflow.bzl", "tf_kernel_library")
|
||||
|
||||
tf_custom_op_library(
|
||||
# TODO(sibyl-Mooth6ku,ptucker): Understand why 'python/ops/_' is needed and fix it.
|
||||
name = "python/ops/_bucketization_op.so",
|
||||
srcs = [
|
||||
"ops/bucketization_op.cc",
|
||||
],
|
||||
deps = [
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/layers/kernels:bucketization_kernel",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tf_gen_op_libs(
|
||||
op_lib_names = ["bucketization_op"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tf_gen_op_wrapper_py(
|
||||
name = "bucketization_op",
|
||||
deps = [":bucketization_op_op_lib"],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tf_kernel_library(
|
||||
name = "bucketization_op_kernel",
|
||||
deps = [
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/layers/kernels:bucketization_kernel",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/core:framework",
|
||||
],
|
||||
alwayslink = 1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tf_custom_op_library(
|
||||
# TODO(sibyl-Mooth6ku,ptucker): Understand why 'python/ops/_' is needed and fix it.
|
||||
name = "python/ops/_sparse_feature_cross_op.so",
|
||||
@ -97,18 +68,14 @@ tf_custom_op_py_library(
|
||||
"python/ops/sparse_ops.py",
|
||||
],
|
||||
dso = [
|
||||
":python/ops/_bucketization_op.so",
|
||||
":python/ops/_sparse_feature_cross_op.so",
|
||||
],
|
||||
kernels = [
|
||||
":bucketization_op_kernel",
|
||||
":sparse_feature_cross_op_kernel",
|
||||
":bucketization_op_op_lib",
|
||||
":sparse_feature_cross_op_op_lib",
|
||||
],
|
||||
srcs_version = "PY2AND3",
|
||||
deps = [
|
||||
":bucketization_op",
|
||||
":sparse_feature_cross_op",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/framework:framework_py",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/contrib/lookup:lookup_py",
|
||||
@ -315,22 +282,6 @@ py_test(
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
py_test(
|
||||
name = "bucketization_op_test",
|
||||
size = "small",
|
||||
srcs = ["python/kernel_tests/bucketization_op_test.py"],
|
||||
srcs_version = "PY2AND3",
|
||||
deps = [
|
||||
":layers_py",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:client_testlib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:errors",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:framework_for_generated_wrappers",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:framework_test_lib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:platform_test",
|
||||
"//third_party/py/numpy",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
py_test(
|
||||
name = "sparse_feature_cross_op_test",
|
||||
size = "medium",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,17 +18,14 @@ these arguments.
|
||||
…,
|
||||
weight_init=<DEFAULT>,
|
||||
bias_init=<DEFAULT>,
|
||||
weight_collections=(tf.GraphKeys.WEIGHTS,),
|
||||
bias_collections=(tf.GraphKeys.BIASES,),
|
||||
output_collections=(tf.GraphKeys.ACTIVATIONS,),
|
||||
weight_regularizer=None,
|
||||
bias_regularizer=None,
|
||||
name=None) : Tensor`
|
||||
|
||||
`x` is the input tensor.
|
||||
|
||||
Weights, biases, and activations (i.e., outputs) are, by default, added to the specified collections. Weights and biases are also added to
|
||||
`tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES` and `tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
|
||||
Weights and biases are added to `tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES` and
|
||||
`tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES`.
|
||||
|
||||
## optimizers.py
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7,17 +7,6 @@ exports_files(["LICENSE"])
|
||||
|
||||
package(default_visibility = ["//tensorflow:__subpackages__"])
|
||||
|
||||
cc_library(
|
||||
name = "bucketization_kernel",
|
||||
srcs = ["bucketization_kernel.cc"],
|
||||
deps = [
|
||||
"//tensorflow/core:framework_headers_lib",
|
||||
"//third_party/eigen3",
|
||||
"@protobuf//:protobuf_headers",
|
||||
],
|
||||
alwayslink = 1,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
cc_library(
|
||||
name = "sparse_feature_cross_kernel",
|
||||
srcs = ["sparse_feature_cross_kernel.cc"],
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,46 +0,0 @@
|
||||
/* Copyright 2016 The TensorFlow Authors. All Rights Reserved.
|
||||
|
||||
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
|
||||
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
|
||||
You may obtain a copy of the License at
|
||||
|
||||
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
|
||||
|
||||
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
|
||||
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
|
||||
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
|
||||
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
==============================================================================*/
|
||||
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/core/framework/common_shape_fns.h"
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/core/framework/op.h"
|
||||
|
||||
namespace tensorflow {
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("Bucketize")
|
||||
.Input("input: T")
|
||||
.Output("output: int32")
|
||||
.Attr("T: {int32, int64, float, double}")
|
||||
.Attr("boundaries: list(float)")
|
||||
.SetShapeFn(shape_inference::UnchangedShape)
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Bucketizes 'input' based on 'boundaries'.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if the inputs are
|
||||
boundaries = [0, 10, 100]
|
||||
input = [[-5, 10000]
|
||||
[150, 10]
|
||||
[5, 100]]
|
||||
|
||||
then the output will be
|
||||
output = [[0, 3]
|
||||
[3, 2]
|
||||
[1, 3]]
|
||||
|
||||
input: Any shape of Tensor contains with int or float type.
|
||||
boundaries: A sorted list of floats gives the boundary of the buckets.
|
||||
output: Same shape with 'input', each value of input replaced with bucket index.
|
||||
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
} // namespace tensorflow
|
||||
@ -17,13 +17,7 @@ from __future__ import absolute_import
|
||||
from __future__ import division
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.layers.ops import gen_bucketization_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.util import loader
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import resource_loader
|
||||
|
||||
_bucketization_op = loader.load_op_library(
|
||||
resource_loader.get_path_to_datafile("_bucketization_op.so"))
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def bucketize(input_tensor, boundaries, name=None):
|
||||
@ -43,10 +37,5 @@ def bucketize(input_tensor, boundaries, name=None):
|
||||
Raises:
|
||||
TypeError: If boundaries is not a list.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
if not isinstance(boundaries, list):
|
||||
raise TypeError("boundaries must be a list")
|
||||
|
||||
return gen_bucketization_op.bucketize(input_tensor, boundaries, name=name)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
ops.NotDifferentiable("Bucketize")
|
||||
return math_ops._bucketize( # pylint: disable=protected-access
|
||||
input_tensor, boundaries=boundaries, name=name)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1,247 +0,0 @@
|
||||
# TF Learn
|
||||
|
||||
TF Learn is a simplified interface for TensorFlow, to get people started on predictive analytics and data mining. The library covers a variety of needs: from linear models to *Deep Learning* applications like text and image understanding.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why *TensorFlow*?
|
||||
|
||||
* TensorFlow provides a good backbone for building different shapes of machine learning applications.
|
||||
* It will continue to evolve both in the distributed direction and as general pipelining machinery.
|
||||
|
||||
### Why *TensorFlow Learn*?
|
||||
|
||||
- To smooth the transition from the [scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/) world of one-liner machine learning into the more open world of building different shapes of ML models. You can start by using [fit](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/Estimator#fit)/[predict](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/Estimator#predict) and slide into TensorFlow APIs as you are getting comfortable.
|
||||
- To provide a set of reference models that will be easy to integrate with existing code.
|
||||
|
||||
## Installation
|
||||
|
||||
[Install TensorFlow](https://www.tensorflow.org/install/), and then simply import `learn` via `from tensorflow.contrib.learn` or use `tf.contrib.learn`.
|
||||
|
||||
Optionally you can install [scikit-learn](http://scikit-learn.org/stable/) and [pandas](http://pandas.pydata.org/) for additional functionality.
|
||||
|
||||
### Tutorials
|
||||
|
||||
- [TF Learn Quickstart](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/tflearn). Build,
|
||||
train, and evaluate a neural network with just a few lines of code.
|
||||
- [Input Functions](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/input_fn). Learn how
|
||||
to create input functions to feed data into your models.
|
||||
- [Linear Model](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/wide). Learn the basics
|
||||
of building linear models.
|
||||
- [Wide and Deep Learning](https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/wide_and_deep).
|
||||
Jointly train a linear model and a deep neural network.
|
||||
- [Logging and Monitoring](https://www.tensorflow.org/get_started/monitors).
|
||||
Use the Monitor API to audit training of a neural network.
|
||||
- [Custom Estimators](https://www.tensorflow.org/extend/estimators). Learn
|
||||
how to create a custom estimator.
|
||||
- More coming soon.
|
||||
|
||||
### Community
|
||||
|
||||
- Twitter [#tensorflow](https://twitter.com/search?q=tensorflow&src=typd).
|
||||
- StackOverflow with [tensorflow tag](http://stackoverflow.com/questions/tagged/tensorflow) for questions and struggles.
|
||||
- GitHub [issues](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/issues) for technical discussions and feature requests.
|
||||
|
||||
### Existing Estimator Implementations
|
||||
|
||||
- [`LinearClassifier`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/learn/python/learn/estimators/linear.py)
|
||||
([docs](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/LinearClassifier))
|
||||
- [`LinearRegressor`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/learn/python/learn/estimators/linear.py)
|
||||
([docs](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/LinearRegressor))
|
||||
- [`DNNClassifier`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/learn/python/learn/estimators/dnn.py)
|
||||
([docs](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/DNNClassifier))
|
||||
- [`DNNRegressor`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/learn/python/learn/estimators/dnn.py)
|
||||
([docs](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/DNNRegressor))
|
||||
- [`DNNLinearCombinedClassifier`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/learn/python/learn/estimators/dnn_linear_combined.py)
|
||||
([docs](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/DNNLinearCombinedClassifier))
|
||||
- [`DNNLinearCombinedRegressor`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/learn/python/learn/estimators/dnn_linear_combined.py)
|
||||
([docs](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/DNNLinearCombinedRegressor))
|
||||
- [`SVM`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/learn/python/learn/estimators/svm.py)
|
||||
([docs](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/learn/python/learn/estimators/g3doc/svm.md))
|
||||
- [`GMM`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/factorization/python/ops/gmm.py)
|
||||
([docs](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/factorization/g3doc/gmm.md))
|
||||
- [`KMeansClustering`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/learn/python/learn/estimators/kmeans.py)
|
||||
([docs](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/contrib/factorization/g3doc/kmeans.md))
|
||||
|
||||
### Usage Examples
|
||||
|
||||
Below are a few simple examples of the API. For more examples, please see [examples](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/examples/learn).
|
||||
|
||||
General tips:
|
||||
|
||||
- It's useful to rescale a dataset to 0 mean and unit standard deviation before passing it to an [`Estimator`](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/contrib/learn/Estimator). [Stochastic Gradient Descent](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stochastic_gradient_descent) doesn't always do the right thing when variable are at very different scales.
|
||||
|
||||
- Categorical variables should be managed before passing input to the estimator.
|
||||
|
||||
## Linear Classifier
|
||||
|
||||
Simple linear classification:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn as learn
|
||||
from sklearn import datasets, metrics
|
||||
|
||||
iris = datasets.load_iris()
|
||||
feature_columns = learn.infer_real_valued_columns_from_input(iris.data)
|
||||
classifier = learn.LinearClassifier(n_classes=3, feature_columns=feature_columns)
|
||||
classifier.fit(iris.data, iris.target, steps=200, batch_size=32)
|
||||
iris_predictions = list(classifier.predict(iris.data, as_iterable=True))
|
||||
score = metrics.accuracy_score(iris.target, iris_predictions)
|
||||
print("Accuracy: %f" % score)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Linear Regressor
|
||||
|
||||
Simple linear regression:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn as learn
|
||||
from sklearn import datasets, metrics, preprocessing
|
||||
|
||||
boston = datasets.load_boston()
|
||||
x = preprocessing.StandardScaler().fit_transform(boston.data)
|
||||
feature_columns = learn.infer_real_valued_columns_from_input(x)
|
||||
regressor = learn.LinearRegressor(feature_columns=feature_columns)
|
||||
regressor.fit(x, boston.target, steps=200, batch_size=32)
|
||||
boston_predictions = list(regressor.predict(x, as_iterable=True))
|
||||
score = metrics.mean_squared_error(boston_predictions, boston.target)
|
||||
print ("MSE: %f" % score)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Deep Neural Network
|
||||
|
||||
Example of 3 layer network with 10, 20 and 10 hidden units respectively:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
import tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn as learn
|
||||
from sklearn import datasets, metrics
|
||||
|
||||
iris = datasets.load_iris()
|
||||
feature_columns = learn.infer_real_valued_columns_from_input(iris.data)
|
||||
classifier = learn.DNNClassifier(hidden_units=[10, 20, 10], n_classes=3, feature_columns=feature_columns)
|
||||
classifier.fit(iris.data, iris.target, steps=200, batch_size=32)
|
||||
iris_predictions = list(classifier.predict(iris.data, as_iterable=True))
|
||||
score = metrics.accuracy_score(iris.target, iris_predictions)
|
||||
print("Accuracy: %f" % score)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Custom model
|
||||
|
||||
Example of how to pass a custom model to the Estimator:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
from sklearn import datasets
|
||||
from sklearn import metrics
|
||||
import tensorflow as tf
|
||||
import tensorflow.contrib.layers.python.layers as layers
|
||||
import tensorflow.contrib.learn.python.learn as learn
|
||||
|
||||
iris = datasets.load_iris()
|
||||
|
||||
def my_model(features, labels):
|
||||
"""DNN with three hidden layers."""
|
||||
# Convert the labels to a one-hot tensor of shape (length of features, 3) and
|
||||
# with a on-value of 1 for each one-hot vector of length 3.
|
||||
labels = tf.one_hot(labels, 3, 1, 0)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create three fully connected layers respectively of size 10, 20, and 10.
|
||||
features = layers.stack(features, layers.fully_connected, [10, 20, 10])
|
||||
|
||||
# Create two tensors respectively for prediction and loss.
|
||||
prediction, loss = (
|
||||
tf.contrib.learn.models.logistic_regression(features, labels)
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
# Create a tensor for training op.
|
||||
train_op = tf.contrib.layers.optimize_loss(
|
||||
loss, tf.contrib.framework.get_global_step(), optimizer='Adagrad',
|
||||
learning_rate=0.1)
|
||||
|
||||
return {'class': tf.argmax(prediction, 1), 'prob': prediction}, loss, train_op
|
||||
|
||||
classifier = learn.Estimator(model_fn=my_model)
|
||||
classifier.fit(iris.data, iris.target, steps=1000)
|
||||
|
||||
y_predicted = [
|
||||
p['class'] for p in classifier.predict(iris.data, as_iterable=True)]
|
||||
score = metrics.accuracy_score(iris.target, y_predicted)
|
||||
print('Accuracy: {0:f}'.format(score))
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Saving / Restoring models
|
||||
|
||||
Each estimator supports a `model_dir` argument, which takes a folder path where all model information will be saved:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
classifier = learn.DNNClassifier(..., model_dir="/tmp/my_model")
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
If you run multiple `fit` operations on the same `Estimator`, training will resume where the last operation left off, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>classifier = learn.DNNClassifier(..., model_dir="/tmp/my_model")
|
||||
classifier.fit(..., steps=300)</strong>
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Create CheckpointSaverHook
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 2.40115, step = 1
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 1 into /tmp/leftoff/model.ckpt.
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.338706, step = 101
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.159414, step = 201
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 300 into /tmp/leftoff/model.ckpt.
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Loss for final step: 0.0953846.
|
||||
|
||||
<strong>classifier.fit(..., steps=300)</strong>
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Create CheckpointSaverHook
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.113173, step = 301
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 301 into /tmp/leftoff/model.ckpt.
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.175782, step = 401
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.119735, step = 501
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 600 into /tmp/leftoff/model.ckpt.
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Loss for final step: 0.0518137.</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
To restore checkpoints to a new `Estimator`, just pass it the same `model_dir` argument, e.g.:
|
||||
|
||||
<pre><strong>classifier = learn.DNNClassifier(..., model_dir="/tmp/my_model")
|
||||
classifier.fit(..., steps=300)</strong>
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Create CheckpointSaverHook
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 1.16335, step = 1
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 1 into /tmp/leftoff/model.ckpt.
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.176995, step = 101
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.184573, step = 201
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 300 into /tmp/leftoff/model.ckpt.
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Loss for final step: 0.0512496.
|
||||
|
||||
<strong>classifier2 = learn.DNNClassifier(..., model_dir="/tmp/my_model")
|
||||
classifier2.fit(..., steps=300)</strong>
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Create CheckpointSaverHook
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.0543797, step = 301
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 301 into /tmp/leftoff/model.ckpt.
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.101036, step = 401
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:loss = 0.137956, step = 501
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Saving checkpoints for 600 into /tmp/leftoff/model.ckpt.
|
||||
INFO:tensorflow:Loss for final step: 0.0162506.</pre>
|
||||
|
||||
## Summaries
|
||||
|
||||
If you supply a `model_dir` argument to your `Estimator`s, TensorFlow will write summaries for ``loss`` and histograms for variables in this directory. (You can also add custom summaries in your custom model function by calling [Summary](https://www.tensorflow.org/api_guides/python/summary) operations.)
|
||||
|
||||
To view the summaries in TensorBoard, run the following command, where `logdir` is the `model_dir` for your `Estimator`:
|
||||
|
||||
```shell
|
||||
tensorboard --logdir=/tmp/tf_examples/my_model_1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
and then load the reported URL.
|
||||
|
||||
**Graph visualization**
|
||||
|
||||
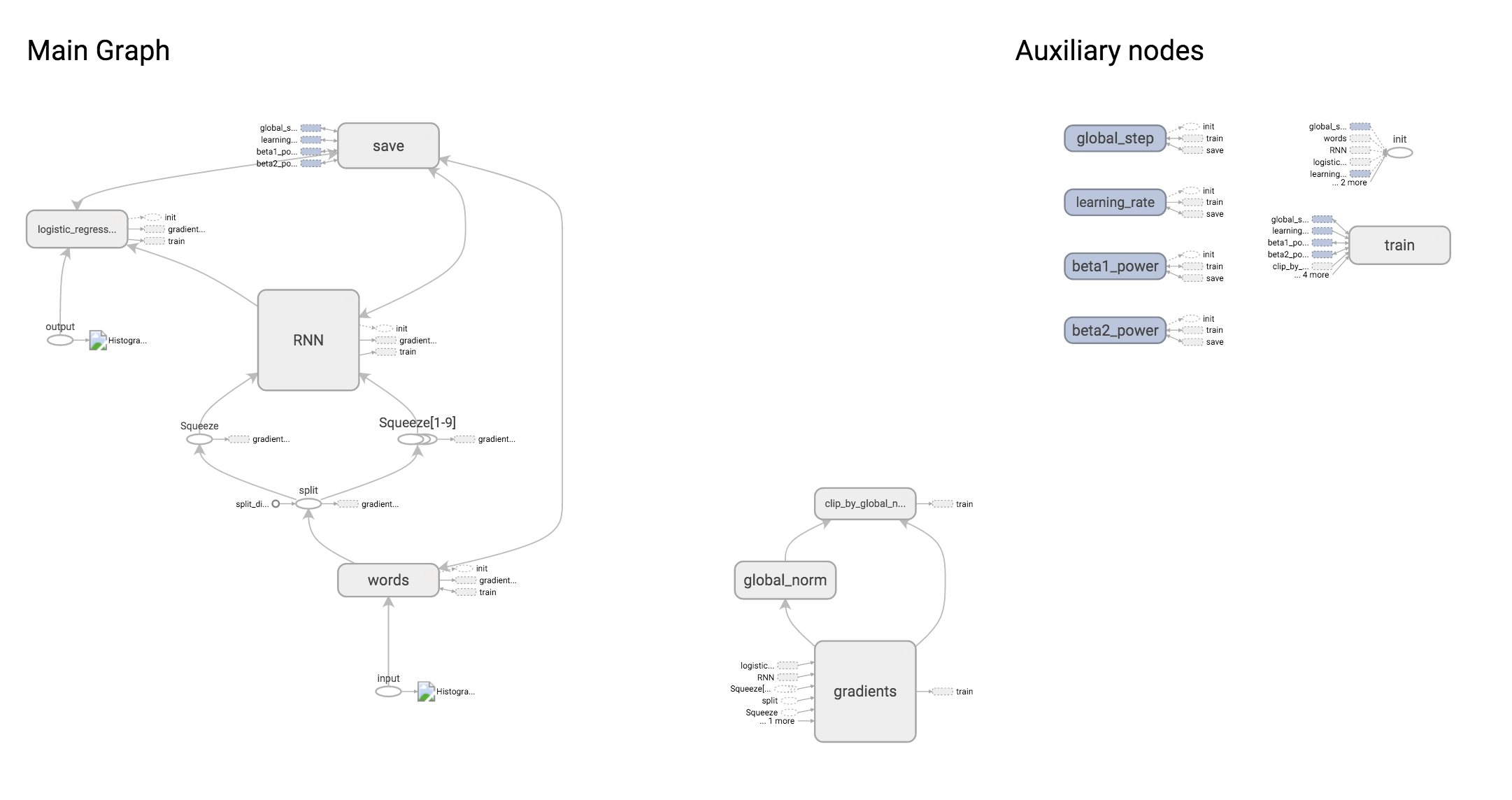
|
||||
|
||||
**Loss visualization**
|
||||
|
||||
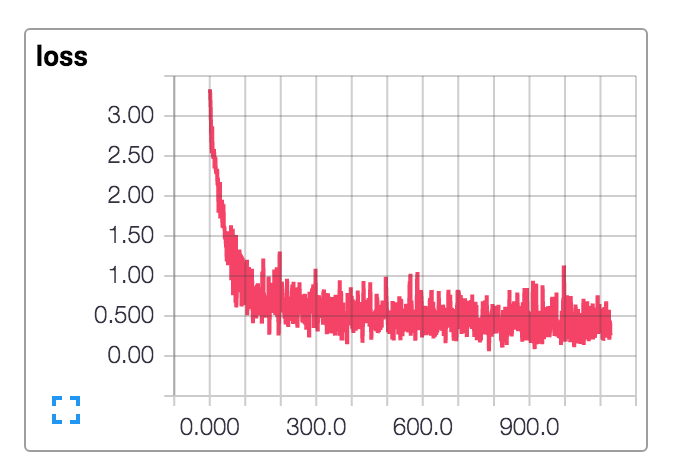
|
||||
|
||||
## More examples
|
||||
|
||||
See the [examples folder](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/examples/learn) for:
|
||||
|
||||
- An easy way to handle [categorical variables](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/examples/learn/text_classification.py) (words are just an example of a categorical variable)
|
||||
- Text Classification: see examples for [RNN](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/examples/learn/text_classification_character_rnn.py) and [CNN](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/examples/learn/text_classification_character_cnn.py) on characters
|
||||
- [Digit recognition using a CNN](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/examples/learn/mnist.py)
|
||||
- And much more!
|
||||
@ -1287,9 +1287,6 @@ class Estimator(BaseEstimator):
|
||||
else:
|
||||
saver_for_restore = saver.Saver(sharded=True)
|
||||
with tf_session.Session('') as session:
|
||||
variables.initialize_local_variables()
|
||||
data_flow_ops.tables_initializer()
|
||||
resources.initialize_resources(resources.shared_resources())
|
||||
saver_for_restore.restore(session, checkpoint_path)
|
||||
init_op = control_flow_ops.group(
|
||||
variables.local_variables_initializer(),
|
||||
|
||||
@ -37,6 +37,7 @@ from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import sparse_tensor
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import control_flow_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import logging_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import sparse_ops
|
||||
@ -613,7 +614,9 @@ def _create_model_fn_ops(features,
|
||||
if (mode != model_fn.ModeKeys.INFER) and (labels is not None):
|
||||
weight_tensor = _weight_tensor(features, weight_column_name)
|
||||
loss, weighted_average_loss = loss_fn(labels, logits, weight_tensor)
|
||||
summary.scalar(
|
||||
# Uses the deprecated API to set the tag explicitly.
|
||||
# Without it, trianing and eval losses will show up in different graphs.
|
||||
logging_ops.scalar_summary(
|
||||
_summary_key(head_name, mkey.LOSS), weighted_average_loss)
|
||||
|
||||
if mode == model_fn.ModeKeys.TRAIN:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -123,7 +123,7 @@ class PoissonHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
train_op_fn=head_lib.no_op_train_fn,
|
||||
logits=logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["regression_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
loss = self._log_poisson_loss(logits, labels)
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, loss, {"loss": loss}, model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -149,7 +149,7 @@ class RegressionHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
train_op_fn=head_lib.no_op_train_fn,
|
||||
logits=((1.,), (1.,), (3.,)))
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["regression_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, 5. / 3, {"loss": 5. / 3}, model_fn_ops)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -179,7 +179,7 @@ class RegressionHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
_assert_variables(
|
||||
self, expected_global=w, expected_model=w, expected_trainable=w)
|
||||
variables.global_variables_initializer().run()
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["regression_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, 2. / 3, {"loss": 2. / 3}, model_fn_ops)
|
||||
|
||||
def testRegressionWithLogitsAndLogitsInput(self):
|
||||
@ -207,7 +207,7 @@ class RegressionHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
self.assertIsNone(model_fn_ops.train_op)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["regression_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, 5. / 3, {"loss": 5. / 3}, model_fn_ops)
|
||||
|
||||
def testRegressionWithLabelName(self):
|
||||
@ -222,7 +222,7 @@ class RegressionHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=((1.,), (1.,), (3.,)))
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["regression_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, 5. / 3, {"loss": 5. / 3}, model_fn_ops)
|
||||
|
||||
def testRegressionWithWeights(self):
|
||||
@ -237,7 +237,7 @@ class RegressionHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=((1.,), (1.,), (3.,)))
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["regression_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, 2. / len(weights), {"loss": 2. / np.sum(weights)},
|
||||
model_fn_ops)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -260,7 +260,7 @@ class RegressionHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
expected_trainable=("regression_head/centered_bias_weight:0",))
|
||||
variables.global_variables_initializer().run()
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, [
|
||||
"regression_head/loss",
|
||||
"loss",
|
||||
"regression_head/centered_bias/bias_0"
|
||||
])
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, 5. / 3, {"loss": 5. / 3}, model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -331,7 +331,7 @@ class MultiLabelHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_label_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = .89985204
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -348,7 +348,7 @@ class MultiLabelHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
train_op_fn=head_lib.no_op_train_fn, logits=logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_label_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = 1.00320443
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss, {
|
||||
"accuracy": 0.,
|
||||
@ -388,7 +388,7 @@ class MultiLabelHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
_assert_variables(
|
||||
self, expected_global=w, expected_model=w, expected_trainable=w)
|
||||
variables.global_variables_initializer().run()
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_label_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = .69314718
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss, {
|
||||
"accuracy": 2. / 3,
|
||||
@ -433,7 +433,7 @@ class MultiLabelHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
self.assertIsNone(model_fn_ops.train_op)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_label_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = .89985204
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -452,7 +452,7 @@ class MultiLabelHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
self.assertIsNone(model_fn_ops.train_op)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_label_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = 1.377779
|
||||
expected_eval_metrics = {
|
||||
"accuracy": 1. / 3,
|
||||
@ -520,7 +520,7 @@ class MultiLabelHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
head_lib.no_op_train_fn, logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_label_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = .89985204
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -540,7 +540,7 @@ class MultiLabelHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_label_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, .089985214,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(.89985214), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -559,7 +559,7 @@ class MultiLabelHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_label_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, .089985214,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(.89985214), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -579,7 +579,7 @@ class MultiLabelHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_label_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = .089985214
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -604,7 +604,7 @@ class MultiLabelHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
expected_trainable=("multi_label_head/centered_bias_weight:0",))
|
||||
variables.global_variables_initializer().run()
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, (
|
||||
"multi_label_head/loss",
|
||||
"loss",
|
||||
"multi_label_head/centered_bias/bias_0",
|
||||
"multi_label_head/centered_bias/bias_1",
|
||||
"multi_label_head/centered_bias/bias_2"
|
||||
@ -629,7 +629,7 @@ class MultiLabelHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
train_op_fn=head_lib.no_op_train_fn,
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_label_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = .89985204
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -695,7 +695,7 @@ class BinaryClassificationHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["binary_logistic_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = .81326175
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -723,7 +723,7 @@ class BinaryClassificationHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
_assert_variables(
|
||||
self, expected_global=w, expected_model=w, expected_trainable=w)
|
||||
variables.global_variables_initializer().run()
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["binary_logistic_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = .69314718
|
||||
label_mean = np.mean(self._labels)
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss, {
|
||||
@ -759,7 +759,7 @@ class BinaryClassificationHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
self.assertIsNone(model_fn_ops.train_op)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["binary_logistic_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = .81326175
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -838,7 +838,7 @@ class BinaryClassificationHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["binary_logistic_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = .81326175
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -859,7 +859,7 @@ class BinaryClassificationHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["binary_logistic_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_total_loss = .31326166
|
||||
_assert_metrics(
|
||||
self,
|
||||
@ -892,7 +892,7 @@ class BinaryClassificationHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["binary_logistic_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
# logloss: z:label, x:logit
|
||||
# z * -log(sigmoid(x)) + (1 - z) * -log(1 - sigmoid(x))
|
||||
# expected_loss is (total_weighted_loss)/1 since htere is 1 nonzero
|
||||
@ -932,7 +932,7 @@ class BinaryClassificationHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
expected_trainable=("binary_logistic_head/centered_bias_weight:0",))
|
||||
variables.global_variables_initializer().run()
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, [
|
||||
"binary_logistic_head/loss",
|
||||
"loss",
|
||||
"binary_logistic_head/centered_bias/bias_0"
|
||||
])
|
||||
expected_loss = .81326175
|
||||
@ -983,7 +983,7 @@ class MultiClassHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_class_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = 1.5514447
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -1022,7 +1022,7 @@ class MultiClassHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
_assert_variables(
|
||||
self, expected_global=w, expected_model=w, expected_trainable=w)
|
||||
variables.global_variables_initializer().run()
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_class_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = 1.0986123
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss, {
|
||||
"accuracy": 0.,
|
||||
@ -1073,7 +1073,7 @@ class MultiClassHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
expected_trainable=("multi_class_head/centered_bias_weight:0",))
|
||||
variables.global_variables_initializer().run()
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self,
|
||||
["multi_class_head/loss",
|
||||
["loss",
|
||||
"multi_class_head/centered_bias/bias_0",
|
||||
"multi_class_head/centered_bias/bias_1",
|
||||
"multi_class_head/centered_bias/bias_2"])
|
||||
@ -1091,7 +1091,7 @@ class MultiClassHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
self.assertIsNone(model_fn_ops.train_op)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_class_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = 1.5514447
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -1110,7 +1110,7 @@ class MultiClassHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
self.assertIsNone(model_fn_ops.train_op)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_class_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = 3.1698461
|
||||
expected_eval_metrics = {
|
||||
"accuracy": 0.,
|
||||
@ -1149,7 +1149,7 @@ class MultiClassHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_class_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = 1.5514447
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss * weight,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -1173,7 +1173,7 @@ class MultiClassHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._logits)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_class_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = 1.5514447 * weight
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss,
|
||||
self._expected_eval_metrics(expected_loss), model_fn_ops)
|
||||
@ -1280,7 +1280,7 @@ class MultiClassHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
data_flow_ops.tables_initializer().run()
|
||||
self.assertIsNone(model_fn_ops.train_op)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_class_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = 1.5514447
|
||||
expected_eval_metrics = {
|
||||
"accuracy": 0.,
|
||||
@ -1306,7 +1306,7 @@ class MultiClassHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
data_flow_ops.tables_initializer().run()
|
||||
self.assertIsNone(model_fn_ops.train_op)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["multi_class_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = 0.5514447
|
||||
expected_eval_metrics = {
|
||||
"accuracy": 1.,
|
||||
@ -1345,7 +1345,7 @@ class BinarySvmHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._predictions)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["binary_svm_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = np.average(self._expected_losses)
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss, {
|
||||
"accuracy": 1.,
|
||||
@ -1375,7 +1375,7 @@ class BinarySvmHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
_assert_variables(
|
||||
self, expected_global=w, expected_model=w, expected_trainable=w)
|
||||
variables.global_variables_initializer().run()
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["binary_svm_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = 1.
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss, {
|
||||
"accuracy": .5,
|
||||
@ -1407,7 +1407,7 @@ class BinarySvmHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
self.assertIsNone(model_fn_ops.train_op)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["binary_svm_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = np.average(self._expected_losses)
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss, {
|
||||
"accuracy": 1.,
|
||||
@ -1426,7 +1426,7 @@ class BinarySvmHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._predictions)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["binary_svm_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_loss = np.average(self._expected_losses)
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, expected_loss, {
|
||||
"accuracy": 1.,
|
||||
@ -1446,7 +1446,7 @@ class BinarySvmHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
logits=self._predictions)
|
||||
self._assert_output_alternatives(model_fn_ops)
|
||||
_assert_no_variables(self)
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["binary_svm_head/loss"])
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, ["loss"])
|
||||
expected_weighted_losses = np.multiply(weights, self._expected_losses)
|
||||
_assert_metrics(self, np.mean(expected_weighted_losses), {
|
||||
"accuracy": 1.,
|
||||
@ -1473,7 +1473,7 @@ class BinarySvmHeadTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
expected_trainable=("binary_svm_head/centered_bias_weight:0",))
|
||||
variables.global_variables_initializer().run()
|
||||
_assert_summary_tags(self, [
|
||||
"binary_svm_head/loss",
|
||||
"loss",
|
||||
"binary_svm_head/centered_bias/bias_0"
|
||||
])
|
||||
expected_loss = np.average(self._expected_losses)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -45,6 +45,7 @@ See @{$python/contrib.rnn} guide.
|
||||
@@UGRNNCell
|
||||
@@IntersectionRNNCell
|
||||
@@PhasedLSTMCell
|
||||
@@HighwayWrapper
|
||||
|
||||
### RNNCell wrappers
|
||||
@@AttentionCellWrapper
|
||||
|
||||
@ -882,6 +882,30 @@ class RNNCellTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(res[1].c, expected_state_c)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(res[1].h, expected_state_h)
|
||||
|
||||
def testHighwayWrapper(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session() as sess:
|
||||
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
|
||||
"base_cell", initializer=init_ops.constant_initializer(0.5)):
|
||||
x = array_ops.zeros([1, 3])
|
||||
m = array_ops.zeros([1, 3])
|
||||
base_cell = core_rnn_cell_impl.GRUCell(3)
|
||||
g, m_new = base_cell(x, m)
|
||||
with variable_scope.variable_scope(
|
||||
"hw_cell", initializer=init_ops.constant_initializer(0.5)):
|
||||
hw_cell = rnn_cell.HighwayWrapper(
|
||||
core_rnn_cell_impl.GRUCell(3), carry_bias_init=-100.0)
|
||||
g_res, m_new_res = hw_cell(x, m)
|
||||
sess.run([variables.global_variables_initializer()])
|
||||
res = sess.run([g, g_res, m_new, m_new_res], {
|
||||
x: np.array([[1., 1., 1.]]),
|
||||
m: np.array([[0.1, 0.1, 0.1]])
|
||||
})
|
||||
# As carry_bias_init is very negative, the carry gate is 'open' and the
|
||||
# transform gate is 'closed'. This means the output equals the input.
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(res[1], res[0])
|
||||
# States are left untouched
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(res[2], res[3])
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class LayerNormBasicLSTMCellTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1157,6 +1157,89 @@ class AttentionCellWrapper(core_rnn_cell.RNNCell):
|
||||
return new_attns, new_attn_states
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class HighwayWrapper(core_rnn_cell.RNNCell):
|
||||
"""RNNCell wrapper that adds highway connection on cell input and output.
|
||||
|
||||
Based on:
|
||||
R. K. Srivastava, K. Greff, and J. Schmidhuber, "Highway networks",
|
||||
arXiv preprint arXiv:1505.00387, 2015.
|
||||
https://arxiv.org/abs/1505.00387
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
def __init__(self, cell,
|
||||
couple_carry_transform_gates=True,
|
||||
carry_bias_init=1.0):
|
||||
"""Constructs a `HighwayWrapper` for `cell`.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
cell: An instance of `RNNCell`.
|
||||
couple_carry_transform_gates: boolean, should the Carry and Transform gate
|
||||
be coupled.
|
||||
carry_bias_init: float, carry gates bias initialization.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
self._cell = cell
|
||||
self._couple_carry_transform_gates = couple_carry_transform_gates
|
||||
self._carry_bias_init = carry_bias_init
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def state_size(self):
|
||||
return self._cell.state_size
|
||||
|
||||
@property
|
||||
def output_size(self):
|
||||
return self._cell.output_size
|
||||
|
||||
def zero_state(self, batch_size, dtype):
|
||||
with ops.name_scope(type(self).__name__ + "ZeroState", values=[batch_size]):
|
||||
return self._cell.zero_state(batch_size, dtype)
|
||||
|
||||
def _highway(self, inp, out):
|
||||
input_size = inp.get_shape().with_rank(2)[1].value
|
||||
carry_weight = vs.get_variable("carry_w", [input_size, input_size])
|
||||
carry_bias = vs.get_variable(
|
||||
"carry_b", [input_size],
|
||||
initializer=init_ops.constant_initializer(
|
||||
self._carry_bias_init))
|
||||
carry = math_ops.sigmoid(nn_ops.xw_plus_b(inp, carry_weight, carry_bias))
|
||||
if self._couple_carry_transform_gates:
|
||||
transform = 1 - carry
|
||||
else:
|
||||
transform_weight = vs.get_variable("transform_w",
|
||||
[input_size, input_size])
|
||||
transform_bias = vs.get_variable(
|
||||
"transform_b", [input_size],
|
||||
initializer=init_ops.constant_initializer(
|
||||
-self._carry_bias_init))
|
||||
transform = math_ops.sigmoid(nn_ops.xw_plus_b(inp,
|
||||
transform_weight,
|
||||
transform_bias))
|
||||
return inp * carry + out * transform
|
||||
|
||||
def __call__(self, inputs, state, scope=None):
|
||||
"""Run the cell and add its inputs to its outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
inputs: cell inputs.
|
||||
state: cell state.
|
||||
scope: optional cell scope.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
Tuple of cell outputs and new state.
|
||||
|
||||
Raises:
|
||||
TypeError: If cell inputs and outputs have different structure (type).
|
||||
ValueError: If cell inputs and outputs have different structure (value).
|
||||
"""
|
||||
outputs, new_state = self._cell(inputs, state, scope=scope)
|
||||
nest.assert_same_structure(inputs, outputs)
|
||||
# Ensure shapes match
|
||||
def assert_shape_match(inp, out):
|
||||
inp.get_shape().assert_is_compatible_with(out.get_shape())
|
||||
nest.map_structure(assert_shape_match, inputs, outputs)
|
||||
res_outputs = nest.map_structure(self._highway, inputs, outputs)
|
||||
return (res_outputs, new_state)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class LayerNormBasicLSTMCell(core_rnn_cell.RNNCell):
|
||||
"""LSTM unit with layer normalization and recurrent dropout.
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -15,6 +15,8 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/core/common_runtime/debugger_state_interface.h"
|
||||
|
||||
#include "tensorflow/core/lib/core/errors.h"
|
||||
|
||||
namespace tensorflow {
|
||||
|
||||
// static
|
||||
@ -58,11 +60,17 @@ void DebuggerStateRegistry::RegisterFactory(
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// static
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebuggerStateInterface> DebuggerStateRegistry::CreateState(
|
||||
const DebugOptions& debug_options) {
|
||||
return (factory_ == nullptr || *factory_ == nullptr)
|
||||
? nullptr
|
||||
: (*factory_)(debug_options);
|
||||
Status DebuggerStateRegistry::CreateState(
|
||||
const DebugOptions& debug_options,
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebuggerStateInterface>* state) {
|
||||
if (factory_ == nullptr || *factory_ == nullptr) {
|
||||
return errors::Internal(
|
||||
"Creation of debugger state failed. "
|
||||
"It appears that TFDBG is not linked in this TensorFlow build.");
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
*state = (*factory_)(debug_options);
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// static
|
||||
@ -73,10 +81,17 @@ void DebugGraphDecoratorRegistry::RegisterFactory(
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// static
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebugGraphDecoratorInterface>
|
||||
DebugGraphDecoratorRegistry::CreateDecorator(const DebugOptions& options) {
|
||||
return (factory_ == nullptr || *factory_ == nullptr) ? nullptr
|
||||
: (*factory_)(options);
|
||||
Status DebugGraphDecoratorRegistry::CreateDecorator(
|
||||
const DebugOptions& options,
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebugGraphDecoratorInterface>* decorator) {
|
||||
if (factory_ == nullptr || *factory_ == nullptr) {
|
||||
return errors::Internal(
|
||||
"Creation of graph decorator failed. "
|
||||
"It appears that TFDBG is not linked in this TensorFlow build.");
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
*decorator = (*factory_)(options);
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
} // end namespace tensorflow
|
||||
|
||||
@ -83,11 +83,12 @@ class DebuggerStateRegistry {
|
||||
// implementation based on DebugOptions.
|
||||
static void RegisterFactory(const DebuggerStateFactory& factory);
|
||||
|
||||
// If RegisterFactory() has been called, creates and returns a concrete
|
||||
// If RegisterFactory() has been called, creates and supplies a concrete
|
||||
// DebuggerStateInterface implementation using the registered factory,
|
||||
// owned by the caller. Otherwise returns nullptr.
|
||||
static std::unique_ptr<DebuggerStateInterface> CreateState(
|
||||
const DebugOptions& debug_options);
|
||||
// owned by the caller and return an OK Status. Otherwise returns an error
|
||||
// Status.
|
||||
static Status CreateState(const DebugOptions& debug_options,
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebuggerStateInterface>* state);
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
static DebuggerStateFactory* factory_;
|
||||
@ -103,8 +104,9 @@ class DebugGraphDecoratorRegistry {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
static void RegisterFactory(const DebugGraphDecoratorFactory& factory);
|
||||
|
||||
static std::unique_ptr<DebugGraphDecoratorInterface> CreateDecorator(
|
||||
const DebugOptions& options);
|
||||
static Status CreateDecorator(
|
||||
const DebugOptions& options,
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebugGraphDecoratorInterface>* decorator);
|
||||
|
||||
private:
|
||||
static DebugGraphDecoratorFactory* factory_;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -376,31 +376,19 @@ Status DirectSession::CreateDebuggerState(
|
||||
const std::vector<string>& output_names,
|
||||
const std::vector<string>& target_names,
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebuggerStateInterface>* debugger_state) {
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebuggerStateInterface> state =
|
||||
DebuggerStateRegistry::CreateState(debug_options);
|
||||
if (!state) {
|
||||
return errors::Internal(
|
||||
"Debugger options are set, but creation of debugger state failed. "
|
||||
"It appears that debugger is not linked in this TensorFlow build.");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(state->PublishDebugMetadata(
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
|
||||
DebuggerStateRegistry::CreateState(debug_options, debugger_state));
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(debugger_state->get()->PublishDebugMetadata(
|
||||
debug_options.global_step(), session_run_count, executor_step_count,
|
||||
input_names, output_names, target_names));
|
||||
|
||||
*debugger_state = std::move(state);
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Status DirectSession::DecorateAndPublishGraphForDebug(
|
||||
const DebugOptions& debug_options, Graph* graph, Device* device) {
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebugGraphDecoratorInterface> decorator =
|
||||
DebugGraphDecoratorRegistry::CreateDecorator(debug_options);
|
||||
if (!decorator) {
|
||||
return errors::Internal(
|
||||
"Debugger options are set, but creation of debug graph publisher ",
|
||||
"failed.");
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebugGraphDecoratorInterface> decorator;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
|
||||
DebugGraphDecoratorRegistry::CreateDecorator(debug_options, &decorator));
|
||||
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(decorator->DecorateGraph(graph, device));
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(decorator->PublishGraph(*graph));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -456,7 +456,7 @@ Status FunctionLibraryRuntimeImpl::Instantiate(
|
||||
void DumpGraph(StringPiece label, const Graph* g) {
|
||||
// TODO(zhifengc): Change Graph to record #nodes.
|
||||
VLOG(1) << "Graph " << label << " #nodes " << g->num_nodes() << " #edges "
|
||||
<< g->edges().size();
|
||||
<< g->num_edges();
|
||||
if (VLOG_IS_ON(2)) {
|
||||
for (const auto& line : str_util::Split(DebugString(g), '\n')) {
|
||||
VLOG(2) << "|| " << line;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -424,7 +424,7 @@ TEST_F(FunctionLibraryRuntimeTest, ControlDeps) {
|
||||
n8 = NoOp() @ n4
|
||||
n9 = Identity[T=float](n3) @ n8
|
||||
n10 = Identity[T=float](n2) @ n8
|
||||
n11 = NoOp() @ n10, n9
|
||||
n11 = NoOp() @ n9, n10
|
||||
n5 = Mul[T=float](n2, n2) @ n11
|
||||
n6 = Add[T=float](n4, n5)
|
||||
}
|
||||
@ -500,8 +500,8 @@ TEST_F(FunctionLibraryRuntimeTest, Gradient_XTimesTwo) {
|
||||
OptimizeGraph(lib_, &g);
|
||||
const char* e2 = R"P(
|
||||
(n2:float, n3:float) -> (n9:float) {
|
||||
n11 = Const[dtype=int32, value=Tensor<type: int32 shape: [0] values: >]()
|
||||
n10 = Const[dtype=float, value=Tensor<type: float shape: [] values: 2>]()
|
||||
n11 = Const[dtype=int32, value=Tensor<type: int32 shape: [0] values: >]()
|
||||
n6 = Shape[T=float, out_type=int32](n2)
|
||||
n5 = Mul[T=float](n3, n10)
|
||||
n7 = BroadcastGradientArgs[T=int32](n6, n11)
|
||||
@ -614,10 +614,10 @@ TEST_F(FunctionLibraryRuntimeTest, Gradient_AddSum) {
|
||||
n17 = Sum[T=float, Tidx=int32, keep_dims=false](n14, n16)
|
||||
n19 = SymbolicGradient[Tin={float, int32, float}, Tout={float, int32}, f=Sum[T=float, Tidx=int32, keep_dims=false]](n14, n16, n26)
|
||||
n21 = SymbolicGradient[Tin={float, float, float}, Tout={float, float}, f=Add[T=float]](n24, n25, n19)
|
||||
n28 = Identity[T=float](n21:1)
|
||||
n27 = Identity[T=float](n21)
|
||||
n6 = Identity[T=float](n28)
|
||||
n28 = Identity[T=float](n21:1)
|
||||
n8 = Identity[T=float](n27)
|
||||
n6 = Identity[T=float](n28)
|
||||
}
|
||||
)P";
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(e1, DebugString(g.get()));
|
||||
@ -626,8 +626,8 @@ TEST_F(FunctionLibraryRuntimeTest, Gradient_AddSum) {
|
||||
const char* e2 = R"P(
|
||||
(n4:float, n3:float) -> (n25:float, n23:float) {
|
||||
n2 = Const[dtype=float, value=Tensor<type: float shape: [] values: 1>]()
|
||||
n8 = Const[dtype=int32, value=Tensor<type: int32 shape: [] values: 0>]()
|
||||
n7 = Const[dtype=int32, value=Tensor<type: int32 shape: [] values: 1>]()
|
||||
n8 = Const[dtype=int32, value=Tensor<type: int32 shape: [] values: 0>]()
|
||||
n19 = Shape[T=float, out_type=int32](n3)
|
||||
n9 = Add[T=float](n4, n3)
|
||||
n20 = Shape[T=float, out_type=int32](n4)
|
||||
@ -641,10 +641,10 @@ TEST_F(FunctionLibraryRuntimeTest, Gradient_AddSum) {
|
||||
n16 = Reshape[T=float, Tshape=int32](n2, n15)
|
||||
n17 = Div[T=int32](n14, n15)
|
||||
n18 = Tile[T=float, Tmultiples=int32](n16, n17)
|
||||
n24 = Sum[T=float, Tidx=int32, keep_dims=false](n18, n21)
|
||||
n22 = Sum[T=float, Tidx=int32, keep_dims=false](n18, n21:1)
|
||||
n25 = Reshape[T=float, Tshape=int32](n24, n20)
|
||||
n24 = Sum[T=float, Tidx=int32, keep_dims=false](n18, n21)
|
||||
n23 = Reshape[T=float, Tshape=int32](n22, n19)
|
||||
n25 = Reshape[T=float, Tshape=int32](n24, n20)
|
||||
}
|
||||
)P";
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(e2, DebugString(g.get()));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -97,16 +97,11 @@ static Status ValidateGraphDefForDevices(const GraphDef& gdef) {
|
||||
|
||||
Status GraphMgr::DecorateAndPublishGraphForDebug(
|
||||
const DebugOptions& debug_options, Graph* graph, Device* device) {
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebugGraphDecoratorInterface> decorator =
|
||||
DebugGraphDecoratorRegistry::CreateDecorator(debug_options);
|
||||
if (!decorator) {
|
||||
return errors::Internal(
|
||||
"Debugger options are set, but creation of debug graph publisher ",
|
||||
"failed.");
|
||||
}
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebugGraphDecoratorInterface> decorator;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
|
||||
DebugGraphDecoratorRegistry::CreateDecorator(debug_options, &decorator));
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(decorator->DecorateGraph(graph, device));
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(decorator->PublishGraph(*graph));
|
||||
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1337,13 +1337,8 @@ Status MasterSession::CreateDebuggerState(
|
||||
const DebugOptions& debug_options, const RunStepRequestWrapper& req,
|
||||
int64 rcg_execution_count,
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebuggerStateInterface>* debugger_state) {
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DebuggerStateInterface> state =
|
||||
DebuggerStateRegistry::CreateState(debug_options);
|
||||
if (!state) {
|
||||
return errors::Internal(
|
||||
"Debugger options are set, but creation of debugger state failed. "
|
||||
"It appears that debugger is not linked in this TensorFlow build.");
|
||||
}
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
|
||||
DebuggerStateRegistry::CreateState(debug_options, debugger_state));
|
||||
|
||||
std::vector<string> input_names;
|
||||
for (size_t i = 0; i < req.num_feeds(); ++i) {
|
||||
@ -1362,11 +1357,10 @@ Status MasterSession::CreateDebuggerState(
|
||||
// While this counter value is straightforward to define and obtain for
|
||||
// DirectSessions, it is less so for non-direct Sessions. Devise a better
|
||||
// way to get its value when the need arises.
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(state->PublishDebugMetadata(
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(debugger_state->get()->PublishDebugMetadata(
|
||||
debug_options.global_step(), -1, rcg_execution_count, input_names,
|
||||
output_names, target_names));
|
||||
|
||||
*debugger_state = std::move(state);
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -882,6 +882,12 @@ Status FunctionLibraryDefinition::AddFunctionDef(const FunctionDef& fdef) {
|
||||
fdef.signature().name(),
|
||||
" already exists in function library.");
|
||||
}
|
||||
const OpDef* op_def;
|
||||
if (default_registry_->LookUpOpDef(fdef.signature().name(), &op_def).ok()) {
|
||||
return errors::InvalidArgument(
|
||||
"Cannot add function '", fdef.signature().name(),
|
||||
"' because an op with the same name already exists.");
|
||||
}
|
||||
ptr.reset(new FunctionDefAndOpRegistration(fdef));
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -944,6 +944,15 @@ TEST(FunctionLibraryDefinitionTest, AddFunctionDef) {
|
||||
ASSERT_NE(second, nullptr);
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(second->DebugString(),
|
||||
test::function::WXPlusB().signature().DebugString());
|
||||
|
||||
// Can't add function with same name as existing op
|
||||
FunctionDef fdef = test::function::XTimesTwo();
|
||||
fdef.mutable_signature()->set_name("Add");
|
||||
Status s = lib_def.AddFunctionDef(fdef);
|
||||
EXPECT_FALSE(s.ok());
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(s.error_message(),
|
||||
"Cannot add function 'Add' because an op with the same name "
|
||||
"already exists.");
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
TEST(FunctionLibraryDefinitionTest, AddGradientDef) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -432,6 +432,7 @@ class OpOutputList {
|
||||
OpOutputList& operator=(const OpOutputList& other) = default;
|
||||
Tensor* operator[](int i);
|
||||
bool required(int i) const;
|
||||
DataType expected_output_dtype(int i) const;
|
||||
Status allocate(int i, const TensorShape& shape, Tensor** output);
|
||||
void set(int i, const Tensor& tensor);
|
||||
void set_ref(int i, mutex* mu, Tensor* tensor_for_ref);
|
||||
@ -1452,6 +1453,12 @@ inline bool OpOutputList::required(int i) const {
|
||||
return ctx_->output_required(start_ + i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline DataType OpOutputList::expected_output_dtype(int i) const {
|
||||
DCHECK_GE(i, 0);
|
||||
DCHECK_LT(i, stop_ - start_);
|
||||
return ctx_->expected_output_dtype(start_ + i);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
inline Status OpOutputList::allocate(int i, const TensorShape& shape,
|
||||
Tensor** output) {
|
||||
DCHECK_GE(i, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -613,6 +613,36 @@ TEST_F(OpKernelBuilderTest, BadConstraint) {
|
||||
error::INVALID_ARGUMENT);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("ListOut").Output("a: int32").Output("b: T").Attr("T: list(type)");
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("ListOut").Device(tensorflow::DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
DummyKernel);
|
||||
|
||||
TEST_F(OpKernelBuilderTest, OpOutputList) {
|
||||
Env* env = Env::Default();
|
||||
OpKernelContext::Params params;
|
||||
params.record_tensor_accesses = false;
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<DummyDevice> device(
|
||||
new DummyDevice(env, params.record_tensor_accesses));
|
||||
params.device = device.get();
|
||||
Status status;
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<OpKernel> op(CreateOpKernel(
|
||||
DEVICE_CPU, params.device, cpu_allocator(),
|
||||
CreateNodeDef("ListOut", {"T|list(type)|[DT_FLOAT, DT_INT32]"}),
|
||||
TF_GRAPH_DEF_VERSION, &status));
|
||||
EXPECT_TRUE(status.ok()) << status.ToString();
|
||||
params.op_kernel = op.get();
|
||||
gtl::InlinedVector<TensorValue, 4> inputs{};
|
||||
params.inputs = &inputs;
|
||||
std::unique_ptr<OpKernelContext> ctx(new OpKernelContext(¶ms));
|
||||
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(DT_INT32, ctx->expected_output_dtype(0));
|
||||
OpOutputList out_list;
|
||||
EXPECT_FALSE(ctx->output_list("non_existent_output", &out_list).ok());
|
||||
ASSERT_TRUE(ctx->output_list("b", &out_list).ok());
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(DT_FLOAT, out_list.expected_output_dtype(0));
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(DT_INT32, out_list.expected_output_dtype(1));
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
class GetAttrKernel : public ::tensorflow::OpKernel {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit GetAttrKernel(OpKernelConstruction* context) : OpKernel(context) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -246,6 +246,14 @@ ResourceHandle HandleFromInput(OpKernelContext* ctx, int input) {
|
||||
return ctx->input(input).flat<ResourceHandle>()(0);
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Status HandleFromInput(OpKernelContext* ctx, StringPiece input,
|
||||
ResourceHandle* handle) {
|
||||
const Tensor* tensor;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(ctx->input(input, &tensor));
|
||||
*handle = tensor->flat<ResourceHandle>()(0);
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Status DeleteResource(OpKernelContext* ctx, const ResourceHandle& p) {
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(internal::ValidateDevice(ctx, p));
|
||||
return ctx->resource_manager()->Delete(p);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -211,6 +211,8 @@ ResourceHandle MakePerStepResourceHandle(OpKernelContext* ctx,
|
||||
|
||||
// Returns a resource handle from a numbered op input.
|
||||
ResourceHandle HandleFromInput(OpKernelContext* ctx, int input);
|
||||
Status HandleFromInput(OpKernelContext* ctx, StringPiece input,
|
||||
ResourceHandle* handle);
|
||||
|
||||
// Create a resource pointed by a given resource handle.
|
||||
template <typename T>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -344,7 +344,7 @@ const Edge* Graph::AddEdge(Node* source, int x, Node* dest, int y) {
|
||||
CHECK(source->out_edges_.insert(e).second);
|
||||
CHECK(dest->in_edges_.insert(e).second);
|
||||
edges_.push_back(e);
|
||||
edge_set_.insert(e);
|
||||
++num_edges_;
|
||||
return e;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -354,8 +354,8 @@ void Graph::RemoveEdge(const Edge* e) {
|
||||
CHECK_EQ(e->src_->out_edges_.erase(e), size_t{1});
|
||||
CHECK_EQ(e->dst_->in_edges_.erase(e), size_t{1});
|
||||
CHECK_EQ(e, edges_[e->id_]);
|
||||
CHECK_GT(num_edges_, 0);
|
||||
|
||||
CHECK_EQ(edge_set_.erase(e), size_t{1});
|
||||
edges_[e->id_] = nullptr;
|
||||
|
||||
Edge* del = const_cast<Edge*>(e);
|
||||
@ -365,6 +365,7 @@ void Graph::RemoveEdge(const Edge* e) {
|
||||
del->src_output_ = kControlSlot - 1;
|
||||
del->dst_input_ = kControlSlot - 1;
|
||||
free_edges_.push_back(del);
|
||||
--num_edges_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Status Graph::AddFunctionLibrary(const FunctionDefLibrary& fdef_lib) {
|
||||
@ -380,13 +381,6 @@ Status Graph::AddFunctionLibrary(const FunctionDefLibrary& fdef_lib) {
|
||||
// Ignore duplicate FunctionDefs
|
||||
continue;
|
||||
}
|
||||
// TODO(skyewm): fix test breakages and reenable this check
|
||||
// const OpDef* op_def;
|
||||
// if (ops_.LookUpOpDef(fdef.signature().name(), &op_def).ok()) {
|
||||
// return errors::InvalidArgument(
|
||||
// "Cannot add function '", fdef.signature().name(),
|
||||
// "' because an op with the same name already exists.");
|
||||
// }
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(ops_.AddFunctionDef(fdef));
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (const GradientDef& grad : fdef_lib.gradient()) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -268,6 +268,66 @@ class Edge {
|
||||
int dst_input_;
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Allows for iteration of the edges of a Graph, by iterating the underlying
|
||||
// Graph.edges_ vector while skipping over null entries.
|
||||
class GraphEdgesIterable {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
const std::vector<Edge*>& edges_;
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
explicit GraphEdgesIterable(const std::vector<Edge*>& edges)
|
||||
: edges_(edges) {}
|
||||
|
||||
typedef Edge* value_type;
|
||||
|
||||
class const_iterator {
|
||||
private:
|
||||
// The underlying iterator.
|
||||
std::vector<value_type>::const_iterator iter_;
|
||||
|
||||
// The end of the underlying iterator.
|
||||
std::vector<value_type>::const_iterator end_;
|
||||
|
||||
// Advances iter_ until it reaches a non-null item, or reaches the end.
|
||||
void apply_filter() {
|
||||
while (iter_ != end_ && *iter_ == nullptr) {
|
||||
++iter_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
public:
|
||||
const_iterator(std::vector<value_type>::const_iterator iter,
|
||||
std::vector<value_type>::const_iterator end)
|
||||
: iter_(iter), end_(end) {
|
||||
apply_filter();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool operator==(const const_iterator& other) const {
|
||||
return iter_ == other.iter_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
bool operator!=(const const_iterator& other) const {
|
||||
return iter_ != other.iter_;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// This is the prefix increment operator (++x), which is the operator
|
||||
// used by C++ range iteration (for (x : y) ...). We intentionally do not
|
||||
// provide a postfix increment operator.
|
||||
const_iterator& operator++() {
|
||||
++iter_;
|
||||
apply_filter();
|
||||
return *this;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
value_type operator*() { return *iter_; }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
const_iterator begin() {
|
||||
return const_iterator(edges_.begin(), edges_.end());
|
||||
}
|
||||
const_iterator end() { return const_iterator(edges_.end(), edges_.end()); }
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
// Thread compatible but not thread safe.
|
||||
class Graph {
|
||||
public:
|
||||
@ -345,7 +405,7 @@ class Graph {
|
||||
// smaller than num_edge_ids(). If one needs to create an array of
|
||||
// edges indexed by edge ids, num_edge_ids() should be used as the
|
||||
// array's size.
|
||||
int num_edges() const { return edges().size(); }
|
||||
int num_edges() const { return num_edges_; }
|
||||
|
||||
// Serialize the nodes starting at `from_node_id` to a GraphDef.
|
||||
void ToGraphDefSubRange(GraphDef* graph_def, int from_node_id) const;
|
||||
@ -381,7 +441,7 @@ class Graph {
|
||||
|
||||
// Access to the set of all edges. Example usage:
|
||||
// for (const Edge* e : graph.edges()) { ... }
|
||||
const EdgeSet& edges() const { return edge_set_; }
|
||||
GraphEdgesIterable edges() const { return GraphEdgesIterable(edges_); }
|
||||
|
||||
// The pre-defined nodes.
|
||||
enum { kSourceId = 0, kSinkId = 1 };
|
||||
@ -421,9 +481,8 @@ class Graph {
|
||||
// the edge with that id was removed from the graph.
|
||||
std::vector<Edge*> edges_;
|
||||
|
||||
// For ease of iteration, we currently just keep a set of all live
|
||||
// edges. May want to optimize by removing this copy.
|
||||
EdgeSet edge_set_;
|
||||
// The number of entries in edges_ that are not nullptr.
|
||||
int num_edges_ = 0;
|
||||
|
||||
// Allocated but free nodes and edges.
|
||||
std::vector<Node*> free_nodes_;
|
||||
|
||||
@ -412,15 +412,14 @@ TEST_F(GraphTest, AddFunctionLibrary) {
|
||||
"Cannot add function 'XTimesTwo' because a different function with "
|
||||
"the same name already exists.");
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(skyewm): reenable along with duplicate op check
|
||||
// Function with same name as an existing op triggers an error
|
||||
// error_proto = proto;
|
||||
// error_proto.mutable_function(0)->mutable_signature()->set_name("Add");
|
||||
// s = graph_.AddFunctionLibrary(error_proto);
|
||||
// EXPECT_FALSE(s.ok());
|
||||
// EXPECT_EQ(s.error_message(),
|
||||
// "Cannot add function 'Add' because an op with the same name "
|
||||
// "already exists.");
|
||||
error_proto = proto;
|
||||
error_proto.mutable_function(0)->mutable_signature()->set_name("Add");
|
||||
s = graph_.AddFunctionLibrary(error_proto);
|
||||
EXPECT_FALSE(s.ok());
|
||||
EXPECT_EQ(s.error_message(),
|
||||
"Cannot add function 'Add' because an op with the same name "
|
||||
"already exists.");
|
||||
|
||||
// Adding a gradient function to an existing function is ok
|
||||
GradientDef* grad = proto.add_gradient();
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2249,6 +2249,7 @@ cc_library(
|
||||
":batch_matmul_op",
|
||||
":betainc_op",
|
||||
":bincount_op",
|
||||
":bucketize_op",
|
||||
":cast_op",
|
||||
":check_numerics_op",
|
||||
":cross_op",
|
||||
@ -2286,6 +2287,12 @@ tf_kernel_library(
|
||||
deps = MATH_DEPS,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tf_kernel_library(
|
||||
name = "bucketize_op",
|
||||
prefix = "bucketize_op",
|
||||
deps = MATH_DEPS,
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tf_kernel_library(
|
||||
name = "cast_op",
|
||||
prefix = "cast_op",
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13,6 +13,8 @@ See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
limitations under the License.
|
||||
==============================================================================*/
|
||||
|
||||
// See docs in ../ops/math_ops.cc.
|
||||
|
||||
#include <algorithm>
|
||||
#include <vector>
|
||||
|
||||
@ -367,7 +367,9 @@ class InitializeTableOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
GetInitializableLookupTable("table_handle", ctx, &table));
|
||||
core::ScopedUnref unref_me(table);
|
||||
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_inputs = {DT_STRING_REF, table->key_dtype(),
|
||||
DataType expected_input_0 =
|
||||
(ctx->input_dtype(0) == DT_RESOURCE) ? DT_RESOURCE : DT_STRING_REF;
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_inputs = {expected_input_0, table->key_dtype(),
|
||||
table->value_dtype()};
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_outputs = {};
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, ctx->MatchSignature(expected_inputs, expected_outputs));
|
||||
@ -408,6 +410,8 @@ class InitializeTableOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("InitializeTable").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
InitializeTableOp);
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("InitializeTableV2").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
InitializeTableOp);
|
||||
|
||||
// Kernel to initialize a lookup table from a text file.
|
||||
//
|
||||
@ -433,7 +437,9 @@ class InitializeTableFromTextFileOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
GetInitializableLookupTable("table_handle", ctx, &table));
|
||||
core::ScopedUnref unref_me(table);
|
||||
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_inputs = {DT_STRING_REF, DT_STRING};
|
||||
DataType expected_input_0 =
|
||||
(ctx->input_dtype(0) == DT_RESOURCE) ? DT_RESOURCE : DT_STRING_REF;
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_inputs = {expected_input_0, DT_STRING};
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_outputs = {};
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, ctx->MatchSignature(expected_inputs, expected_outputs));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -472,5 +478,8 @@ class InitializeTableFromTextFileOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("InitializeTableFromTextFile").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
InitializeTableFromTextFileOp);
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(
|
||||
Name("InitializeTableFromTextFileV2").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
InitializeTableFromTextFileOp);
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace tensorflow
|
||||
|
||||
@ -624,7 +624,10 @@ class LookupTableFindOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, GetLookupTable("table_handle", ctx, &table));
|
||||
core::ScopedUnref unref_me(table);
|
||||
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_inputs = {DT_STRING_REF, table->key_dtype(),
|
||||
// Input 0 could be a STRING_REF or a RESOURCE
|
||||
DataType expected_input_0 =
|
||||
(ctx->input_dtype(0) == DT_RESOURCE) ? DT_RESOURCE : DT_STRING_REF;
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_inputs = {expected_input_0, table->key_dtype(),
|
||||
table->value_dtype()};
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_outputs = {table->value_dtype()};
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, ctx->MatchSignature(expected_inputs, expected_outputs));
|
||||
@ -647,6 +650,8 @@ class LookupTableFindOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("LookupTableFind").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
LookupTableFindOp);
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("LookupTableFindV2").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
LookupTableFindOp);
|
||||
|
||||
// Table insert op.
|
||||
class LookupTableInsertOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
@ -658,7 +663,9 @@ class LookupTableInsertOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, GetLookupTable("table_handle", ctx, &table));
|
||||
core::ScopedUnref unref_me(table);
|
||||
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_inputs = {DT_STRING_REF, table->key_dtype(),
|
||||
DataType expected_input_0 =
|
||||
(ctx->input_dtype(0) == DT_RESOURCE) ? DT_RESOURCE : DT_STRING_REF;
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_inputs = {expected_input_0, table->key_dtype(),
|
||||
table->value_dtype()};
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, ctx->MatchSignature(expected_inputs, {}));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -680,6 +687,8 @@ class LookupTableInsertOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("LookupTableInsert").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
LookupTableInsertOp);
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("LookupTableInsertV2").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
LookupTableInsertOp);
|
||||
|
||||
// Op that returns the size of the given table.
|
||||
class LookupTableSizeOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
@ -699,6 +708,8 @@ class LookupTableSizeOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("LookupTableSize").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
LookupTableSizeOp);
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("LookupTableSizeV2").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
LookupTableSizeOp);
|
||||
|
||||
// Op that outputs tensors of all keys and all values.
|
||||
class LookupTableExportOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
@ -716,6 +727,8 @@ class LookupTableExportOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("LookupTableExport").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
LookupTableExportOp);
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("LookupTableExportV2").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
LookupTableExportOp);
|
||||
|
||||
// Clear the table and insert data.
|
||||
class LookupTableImportOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
@ -727,7 +740,9 @@ class LookupTableImportOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, GetLookupTable("table_handle", ctx, &table));
|
||||
core::ScopedUnref unref_me(table);
|
||||
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_inputs = {DT_STRING_REF, table->key_dtype(),
|
||||
DataType expected_input_0 =
|
||||
(ctx->input_dtype(0) == DT_RESOURCE) ? DT_RESOURCE : DT_STRING_REF;
|
||||
DataTypeVector expected_inputs = {expected_input_0, table->key_dtype(),
|
||||
table->value_dtype()};
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, ctx->MatchSignature(expected_inputs, {}));
|
||||
|
||||
@ -749,6 +764,8 @@ class LookupTableImportOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("LookupTableImport").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
LookupTableImportOp);
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("LookupTableImportV2").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
LookupTableImportOp);
|
||||
|
||||
// Register the HashTable op with the currently supported key and value types.
|
||||
#define REGISTER_KERNEL(key_dtype, value_dtype) \
|
||||
@ -757,6 +774,13 @@ REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER(Name("LookupTableImport").Device(DEVICE_CPU),
|
||||
.Device(DEVICE_CPU) \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<key_dtype>("key_dtype") \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<value_dtype>("value_dtype"), \
|
||||
LookupTableOp<lookup::HashTable<key_dtype, value_dtype>, key_dtype, \
|
||||
value_dtype>) \
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER( \
|
||||
Name("HashTableV2") \
|
||||
.Device(DEVICE_CPU) \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<key_dtype>("key_dtype") \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<value_dtype>("value_dtype"), \
|
||||
LookupTableOp<lookup::HashTable<key_dtype, value_dtype>, key_dtype, \
|
||||
value_dtype>)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -778,6 +802,13 @@ REGISTER_KERNEL(string, bool);
|
||||
.Device(DEVICE_CPU) \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<key_dtype>("key_dtype") \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<value_dtype>("value_dtype"), \
|
||||
LookupTableOp<lookup::MutableHashTableOfScalars<key_dtype, value_dtype>, \
|
||||
key_dtype, value_dtype>) \
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER( \
|
||||
Name("MutableHashTableV2") \
|
||||
.Device(DEVICE_CPU) \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<key_dtype>("key_dtype") \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<value_dtype>("value_dtype"), \
|
||||
LookupTableOp<lookup::MutableHashTableOfScalars<key_dtype, value_dtype>, \
|
||||
key_dtype, value_dtype>)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -796,6 +827,13 @@ REGISTER_KERNEL(int64, float);
|
||||
.Device(DEVICE_CPU) \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<key_dtype>("key_dtype") \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<value_dtype>("value_dtype"), \
|
||||
LookupTableOp<lookup::MutableHashTableOfTensors<key_dtype, value_dtype>, \
|
||||
key_dtype, value_dtype>) \
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER( \
|
||||
Name("MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2") \
|
||||
.Device(DEVICE_CPU) \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<key_dtype>("key_dtype") \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<value_dtype>("value_dtype"), \
|
||||
LookupTableOp<lookup::MutableHashTableOfTensors<key_dtype, value_dtype>, \
|
||||
key_dtype, value_dtype>)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -813,6 +851,13 @@ REGISTER_KERNEL(string, bool);
|
||||
.Device(DEVICE_CPU) \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<key_dtype>("key_dtype") \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<value_dtype>("value_dtype"), \
|
||||
LookupTableOp<lookup::MutableDenseHashTable<key_dtype, value_dtype>, \
|
||||
key_dtype, value_dtype>) \
|
||||
REGISTER_KERNEL_BUILDER( \
|
||||
Name("MutableDenseHashTableV2") \
|
||||
.Device(DEVICE_CPU) \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<key_dtype>("key_dtype") \
|
||||
.TypeConstraint<value_dtype>("value_dtype"), \
|
||||
LookupTableOp<lookup::MutableDenseHashTable<key_dtype, value_dtype>, \
|
||||
key_dtype, value_dtype>)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -51,40 +51,52 @@ class LookupTableOp : public OpKernel {
|
||||
// ctx is not owned by this function.
|
||||
void Compute(OpKernelContext* ctx) override {
|
||||
mutex_lock l(mu_);
|
||||
|
||||
if (!table_handle_set_) {
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, cinfo_.Init(ctx->resource_manager(), def(),
|
||||
use_node_name_sharing_));
|
||||
auto creator = [ctx, this](lookup::LookupInterface** ret) {
|
||||
lookup::LookupInterface* container = new Container(ctx, this);
|
||||
if (!ctx->status().ok()) {
|
||||
container->Unref();
|
||||
return ctx->status();
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (ctx->track_allocations()) {
|
||||
ctx->record_device_persistent_memory_allocation(
|
||||
container->MemoryUsed());
|
||||
}
|
||||
*ret = container;
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
lookup::LookupInterface* table = nullptr;
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(
|
||||
ctx, cinfo_.resource_manager()
|
||||
->template LookupOrCreate<lookup::LookupInterface>(
|
||||
cinfo_.container(), cinfo_.name(), &table, creator));
|
||||
core::ScopedUnref unref_me(table);
|
||||
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, lookup::CheckTableDataTypes(
|
||||
*table, DataTypeToEnum<key_dtype>::v(),
|
||||
DataTypeToEnum<value_dtype>::v(), cinfo_.name()));
|
||||
|
||||
auto h = table_handle_.AccessTensor(ctx)->template flat<string>();
|
||||
h(0) = cinfo_.container();
|
||||
h(1) = cinfo_.name();
|
||||
table_handle_set_ = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
ctx->set_output_ref(0, &mu_, table_handle_.AccessTensor(ctx));
|
||||
|
||||
auto creator = [ctx, this](lookup::LookupInterface** ret) {
|
||||
lookup::LookupInterface* container = new Container(ctx, this);
|
||||
if (!ctx->status().ok()) {
|
||||
container->Unref();
|
||||
return ctx->status();
|
||||
}
|
||||
if (ctx->track_allocations()) {
|
||||
ctx->record_device_persistent_memory_allocation(
|
||||
container->MemoryUsed());
|
||||
}
|
||||
*ret = container;
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
};
|
||||
|
||||
lookup::LookupInterface* table = nullptr;
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx,
|
||||
cinfo_.resource_manager()
|
||||
->template LookupOrCreate<lookup::LookupInterface>(
|
||||
cinfo_.container(), cinfo_.name(), &table, creator));
|
||||
core::ScopedUnref unref_me(table);
|
||||
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, lookup::CheckTableDataTypes(
|
||||
*table, DataTypeToEnum<key_dtype>::v(),
|
||||
DataTypeToEnum<value_dtype>::v(), cinfo_.name()));
|
||||
|
||||
if (ctx->expected_output_dtype(0) == DT_RESOURCE) {
|
||||
Tensor* handle;
|
||||
OP_REQUIRES_OK(ctx, ctx->allocate_output(0, TensorShape({}), &handle));
|
||||
handle->scalar<ResourceHandle>()() =
|
||||
MakeResourceHandle<lookup::LookupInterface>(ctx, cinfo_.container(),
|
||||
cinfo_.name());
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
if (!table_handle_set_) {
|
||||
auto h = table_handle_.AccessTensor(ctx)->template flat<string>();
|
||||
h(0) = cinfo_.container();
|
||||
h(1) = cinfo_.name();
|
||||
}
|
||||
ctx->set_output_ref(0, &mu_, table_handle_.AccessTensor(ctx));
|
||||
}
|
||||
table_handle_set_ = true;
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
~LookupTableOp() override {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -49,26 +49,48 @@ Status GetLookupTable(const string& input_name, OpKernelContext* ctx,
|
||||
LookupInterface** table) {
|
||||
string container;
|
||||
string table_handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
|
||||
GetTableHandle(input_name, ctx, &container, &table_handle));
|
||||
return ctx->resource_manager()->Lookup(container, table_handle, table);
|
||||
DataType handle_dtype;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(ctx->input_dtype(input_name, &handle_dtype));
|
||||
if (handle_dtype == DT_RESOURCE) {
|
||||
ResourceHandle handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(HandleFromInput(ctx, input_name, &handle));
|
||||
return LookupResource(ctx, handle, table);
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
|
||||
GetTableHandle(input_name, ctx, &container, &table_handle));
|
||||
return ctx->resource_manager()->Lookup(container, table_handle, table);
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Status GetInitializableLookupTable(const string& input_name,
|
||||
OpKernelContext* ctx,
|
||||
InitializableLookupTable** table) {
|
||||
string container;
|
||||
string table_handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
|
||||
GetTableHandle(input_name, ctx, &container, &table_handle));
|
||||
LookupInterface* lookup_table;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
|
||||
ctx->resource_manager()->Lookup(container, table_handle, &lookup_table));
|
||||
*table = lookup_table->GetInitializableLookupTable();
|
||||
if (*table == nullptr) {
|
||||
lookup_table->Unref();
|
||||
return errors::InvalidArgument("Table ", container, " ", table_handle,
|
||||
" is not initializable");
|
||||
DataType handle_dtype;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(ctx->input_dtype(input_name, &handle_dtype));
|
||||
if (handle_dtype == DT_RESOURCE) {
|
||||
ResourceHandle handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(HandleFromInput(ctx, input_name, &handle));
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(LookupResource(ctx, handle, &lookup_table));
|
||||
*table = lookup_table->GetInitializableLookupTable();
|
||||
if (*table == nullptr) {
|
||||
lookup_table->Unref();
|
||||
return errors::InvalidArgument("Table ", handle.container(), " ",
|
||||
handle.name(), " is not initializable");
|
||||
}
|
||||
} else {
|
||||
string container;
|
||||
string table_handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(
|
||||
GetTableHandle(input_name, ctx, &container, &table_handle));
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(ctx->resource_manager()->Lookup(container, table_handle,
|
||||
&lookup_table));
|
||||
*table = lookup_table->GetInitializableLookupTable();
|
||||
if (*table == nullptr) {
|
||||
lookup_table->Unref();
|
||||
return errors::InvalidArgument("Table ", container, " ", table_handle,
|
||||
" is not initializable");
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3592,6 +3592,33 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "Bucketize"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "input"
|
||||
type_attr: "T"
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "output"
|
||||
type: DT_INT32
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "T"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
allowed_values {
|
||||
list {
|
||||
type: DT_INT32
|
||||
type: DT_INT64
|
||||
type: DT_FLOAT
|
||||
type: DT_DOUBLE
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "boundaries"
|
||||
type: "list(float)"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "CTCBeamSearchDecoder"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -8878,6 +8905,43 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "HashTableV2"
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "container"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "shared_name"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "use_node_name_sharing"
|
||||
type: "bool"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
b: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "key_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "HistogramSummary"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -9309,6 +9373,70 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "InitializeTableFromTextFileV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "filename"
|
||||
type: DT_STRING
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "key_index"
|
||||
type: "int"
|
||||
has_minimum: true
|
||||
minimum: -2
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_index"
|
||||
type: "int"
|
||||
has_minimum: true
|
||||
minimum: -2
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "vocab_size"
|
||||
type: "int"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
i: -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
has_minimum: true
|
||||
minimum: -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "delimiter"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: "\t"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "InitializeTableV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "keys"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tkey"
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "values"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tval"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tkey"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tval"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "Inv"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -10155,6 +10283,30 @@ op {
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableExportV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "keys"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tkeys"
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "values"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tvalues"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tkeys"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tvalues"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableFind"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -10183,6 +10335,34 @@ op {
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableFindV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "keys"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "default_value"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tout"
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "values"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tout"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tin"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tout"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableImport"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -10207,6 +10387,30 @@ op {
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableImportV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "keys"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "values"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tout"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tin"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tout"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableInsert"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -10231,6 +10435,30 @@ op {
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableInsertV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "keys"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "values"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tout"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tin"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tout"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableSize"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -10243,6 +10471,18 @@ op {
|
||||
type: DT_INT64
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableSizeV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "size"
|
||||
type: DT_INT64
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LoopCond"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -12147,6 +12387,69 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "MutableDenseHashTableV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "empty_key"
|
||||
type_attr: "key_dtype"
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "container"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "shared_name"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "use_node_name_sharing"
|
||||
type: "bool"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
b: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "key_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_shape"
|
||||
type: "shape"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
shape {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "initial_num_buckets"
|
||||
type: "int"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
i: 131072
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "max_load_factor"
|
||||
type: "float"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
f: 0.8
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "MutableHashTable"
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
@ -12231,6 +12534,88 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2"
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "container"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "shared_name"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "use_node_name_sharing"
|
||||
type: "bool"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
b: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "key_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_shape"
|
||||
type: "shape"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
shape {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "MutableHashTableV2"
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "container"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "shared_name"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "use_node_name_sharing"
|
||||
type: "bool"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
b: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "key_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "Neg"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -210,10 +210,29 @@ Status TwoElementVectorInputsAndScalarOutputs(InferenceContext* c) {
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Status ScalarAndTwoElementVectorInputsAndScalarOutputs(InferenceContext* c) {
|
||||
ShapeHandle handle;
|
||||
DimensionHandle unused_handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRank(c->input(0), 0, &handle));
|
||||
for (int i = 1; i < c->num_inputs(); ++i) {
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRank(c->input(i), 1, &handle));
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithValue(c->Dim(handle, 0), 2, &unused_handle));
|
||||
}
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i < c->num_outputs(); ++i) {
|
||||
c->set_output(i, c->Scalar());
|
||||
}
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Status TwoElementOutput(InferenceContext* c) {
|
||||
c->set_output(0, c->Vector(2));
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
Status ScalarOutput(InferenceContext* c) {
|
||||
c->set_output(0, c->Scalar());
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
}
|
||||
} // namespace
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("RandomShuffleQueue")
|
||||
@ -1881,6 +1900,38 @@ values: Same shape as `keys`. Values found in the table, or `default_values`
|
||||
for missing keys.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("LookupTableFindV2")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: resource")
|
||||
.Input("keys: Tin")
|
||||
.Input("default_value: Tout")
|
||||
.Output("values: Tout")
|
||||
.Attr("Tin: type")
|
||||
.Attr("Tout: type")
|
||||
.SetShapeFn([](InferenceContext* c) {
|
||||
ShapeHandle handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRank(c->input(0), 0, &handle));
|
||||
|
||||
// Default value must be scalar or vector.
|
||||
ShapeHandle unused;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRankAtMost(c->input(2), 1, &unused));
|
||||
c->set_output(0, c->UnknownShape());
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
})
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Looks up keys in a table, outputs the corresponding values.
|
||||
|
||||
The tensor `keys` must of the same type as the keys of the table.
|
||||
The output `values` is of the type of the table values.
|
||||
|
||||
The scalar `default_value` is the value output for keys not present in the
|
||||
table. It must also be of the same type as the table values.
|
||||
|
||||
table_handle: Handle to the table.
|
||||
keys: Any shape. Keys to look up.
|
||||
values: Same shape as `keys`. Values found in the table, or `default_values`
|
||||
for missing keys.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("LookupTableInsert")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: Ref(string)")
|
||||
.Input("keys: Tin")
|
||||
@ -1893,6 +1944,30 @@ REGISTER_OP("LookupTableInsert")
|
||||
DimensionHandle unused_dim;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithValue(c->Dim(handle, 0), 2, &unused_dim));
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(ebrevdo): Validate keys and values shape.
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
})
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Updates the table to associates keys with values.
|
||||
|
||||
The tensor `keys` must be of the same type as the keys of the table.
|
||||
The tensor `values` must be of the type of the table values.
|
||||
|
||||
table_handle: Handle to the table.
|
||||
keys: Any shape. Keys to look up.
|
||||
values: Values to associate with keys.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("LookupTableInsertV2")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: resource")
|
||||
.Input("keys: Tin")
|
||||
.Input("values: Tout")
|
||||
.Attr("Tin: type")
|
||||
.Attr("Tout: type")
|
||||
.SetShapeFn([](InferenceContext* c) {
|
||||
ShapeHandle handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRank(c->input(0), 0, &handle));
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: Validate keys and values shape.
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
})
|
||||
@ -1918,6 +1993,17 @@ table_handle: Handle to the table.
|
||||
size: Scalar that contains number of elements in the table.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("LookupTableSizeV2")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: resource")
|
||||
.Output("size: int64")
|
||||
.SetShapeFn(ScalarAndTwoElementVectorInputsAndScalarOutputs)
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Computes the number of elements in the given table.
|
||||
|
||||
table_handle: Handle to the table.
|
||||
size: Scalar that contains number of elements in the table.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("LookupTableExport")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: Ref(string)")
|
||||
.Output("keys: Tkeys")
|
||||
@ -1945,6 +2031,31 @@ keys: Vector of all keys present in the table.
|
||||
values: Tensor of all values in the table. Indexed in parallel with `keys`.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("LookupTableExportV2")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: resource")
|
||||
.Output("keys: Tkeys")
|
||||
.Output("values: Tvalues")
|
||||
.Attr("Tkeys: type")
|
||||
.Attr("Tvalues: type")
|
||||
.SetShapeFn([](InferenceContext* c) {
|
||||
ShapeHandle handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRank(c->input(0), 0, &handle));
|
||||
|
||||
ShapeHandle values = c->UnknownShape();
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRankAtLeast(values, 1, &values));
|
||||
ShapeHandle keys = c->Vector(c->Dim(values, 0));
|
||||
c->set_output(0, keys);
|
||||
c->set_output(1, values);
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
})
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Outputs all keys and values in the table.
|
||||
|
||||
table_handle: Handle to the table.
|
||||
keys: Vector of all keys present in the table.
|
||||
values: Tensor of all values in the table. Indexed in parallel with `keys`.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("LookupTableImport")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: Ref(string)")
|
||||
.Input("keys: Tin")
|
||||
@ -1957,6 +2068,30 @@ REGISTER_OP("LookupTableImport")
|
||||
DimensionHandle unused_dim;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithValue(c->Dim(handle, 0), 2, &unused_dim));
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO(ebrevdo): Validate keys and values shape.
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
})
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Replaces the contents of the table with the specified keys and values.
|
||||
|
||||
The tensor `keys` must be of the same type as the keys of the table.
|
||||
The tensor `values` must be of the type of the table values.
|
||||
|
||||
table_handle: Handle to the table.
|
||||
keys: Any shape. Keys to look up.
|
||||
values: Values to associate with keys.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("LookupTableImportV2")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: resource")
|
||||
.Input("keys: Tin")
|
||||
.Input("values: Tout")
|
||||
.Attr("Tin: type")
|
||||
.Attr("Tout: type")
|
||||
.SetShapeFn([](InferenceContext* c) {
|
||||
ShapeHandle handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRank(c->input(0), 0, &handle));
|
||||
|
||||
// TODO: Validate keys and values shape.
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
})
|
||||
@ -1998,6 +2133,33 @@ key_dtype: Type of the table keys.
|
||||
value_dtype: Type of the table values.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("HashTableV2")
|
||||
.Output("table_handle: resource")
|
||||
.Attr("container: string = ''")
|
||||
.Attr("shared_name: string = ''")
|
||||
.Attr("use_node_name_sharing: bool = false")
|
||||
.Attr("key_dtype: type")
|
||||
.Attr("value_dtype: type")
|
||||
.SetIsStateful()
|
||||
.SetShapeFn(ScalarOutput)
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Creates a non-initialized hash table.
|
||||
|
||||
This op creates a hash table, specifying the type of its keys and values.
|
||||
Before using the table you will have to initialize it. After initialization the
|
||||
table will be immutable.
|
||||
|
||||
table_handle: Handle to a table.
|
||||
container: If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.
|
||||
Otherwise, a default container is used.
|
||||
shared_name: If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across
|
||||
multiple sessions.
|
||||
use_node_name_sharing: If true and shared_name is empty, the table is shared
|
||||
using the node name.
|
||||
key_dtype: Type of the table keys.
|
||||
value_dtype: Type of the table values.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("MutableHashTable")
|
||||
.Output("table_handle: Ref(string)")
|
||||
.Attr("container: string = ''")
|
||||
@ -2025,6 +2187,33 @@ key_dtype: Type of the table keys.
|
||||
value_dtype: Type of the table values.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("MutableHashTableV2")
|
||||
.Output("table_handle: resource")
|
||||
.Attr("container: string = ''")
|
||||
.Attr("shared_name: string = ''")
|
||||
.Attr("use_node_name_sharing: bool = false")
|
||||
.Attr("key_dtype: type")
|
||||
.Attr("value_dtype: type")
|
||||
.SetIsStateful()
|
||||
.SetShapeFn(ScalarOutput)
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Creates an empty hash table.
|
||||
|
||||
This op creates a mutable hash table, specifying the type of its keys and
|
||||
values. Each value must be a scalar. Data can be inserted into the table using
|
||||
the insert operations. It does not support the initialization operation.
|
||||
|
||||
table_handle: Handle to a table.
|
||||
container: If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.
|
||||
Otherwise, a default container is used.
|
||||
shared_name: If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across
|
||||
multiple sessions.
|
||||
use_node_name_sharing: If true and shared_name is empty, the table is shared
|
||||
using the node name.
|
||||
key_dtype: Type of the table keys.
|
||||
value_dtype: Type of the table values.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("MutableHashTableOfTensors")
|
||||
.Output("table_handle: Ref(string)")
|
||||
.Attr("container: string = ''")
|
||||
@ -2051,6 +2240,32 @@ key_dtype: Type of the table keys.
|
||||
value_dtype: Type of the table values.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2")
|
||||
.Output("table_handle: resource")
|
||||
.Attr("container: string = ''")
|
||||
.Attr("shared_name: string = ''")
|
||||
.Attr("use_node_name_sharing: bool = false")
|
||||
.Attr("key_dtype: type")
|
||||
.Attr("value_dtype: type")
|
||||
.Attr("value_shape: shape = {}")
|
||||
.SetIsStateful()
|
||||
.SetShapeFn(ScalarOutput)
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Creates an empty hash table.
|
||||
|
||||
This op creates a mutable hash table, specifying the type of its keys and
|
||||
values. Each value must be a vector. Data can be inserted into the table using
|
||||
the insert operations. It does not support the initialization operation.
|
||||
|
||||
table_handle: Handle to a table.
|
||||
container: If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.
|
||||
Otherwise, a default container is used.
|
||||
shared_name: If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across
|
||||
multiple sessions.
|
||||
key_dtype: Type of the table keys.
|
||||
value_dtype: Type of the table values.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("MutableDenseHashTable")
|
||||
.Input("empty_key: key_dtype")
|
||||
.Output("table_handle: Ref(string)")
|
||||
@ -2088,6 +2303,43 @@ max_load_factor: The maximum ratio between number of entries and number of
|
||||
buckets before growing the table. Must be between 0 and 1.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("MutableDenseHashTableV2")
|
||||
.Input("empty_key: key_dtype")
|
||||
.Output("table_handle: resource")
|
||||
.Attr("container: string = ''")
|
||||
.Attr("shared_name: string = ''")
|
||||
.Attr("use_node_name_sharing: bool = false")
|
||||
.Attr("key_dtype: type")
|
||||
.Attr("value_dtype: type")
|
||||
.Attr("value_shape: shape = {}")
|
||||
.Attr("initial_num_buckets: int = 131072") // 2^17
|
||||
.Attr("max_load_factor: float = 0.8")
|
||||
.SetIsStateful()
|
||||
.SetShapeFn(ScalarOutput)
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Creates an empty hash table that uses tensors as the backing store. It uses
|
||||
"open addressing" with quadratic reprobing to resolve collisions.
|
||||
|
||||
This op creates a mutable hash table, specifying the type of its keys and
|
||||
values. Each value must be a scalar. Data can be inserted into the table using
|
||||
the insert operations. It does not support the initialization operation.
|
||||
|
||||
empty_key: The key used to represent empty key buckets internally. Must not
|
||||
be used in insert or lookup operations.
|
||||
table_handle: Handle to a table.
|
||||
container: If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.
|
||||
Otherwise, a default container is used.
|
||||
shared_name: If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across
|
||||
multiple sessions.
|
||||
key_dtype: Type of the table keys.
|
||||
value_dtype: Type of the table values.
|
||||
value_shape: The shape of each value.
|
||||
initial_num_buckets: The initial number of hash table buckets. Must be a power
|
||||
to 2.
|
||||
max_load_factor: The maximum ratio between number of entries and number of
|
||||
buckets before growing the table. Must be between 0 and 1.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("InitializeTable")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: Ref(string)")
|
||||
.Input("keys: Tkey")
|
||||
@ -2113,6 +2365,29 @@ keys: Keys of type Tkey.
|
||||
values: Values of type Tval.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("InitializeTableV2")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: resource")
|
||||
.Input("keys: Tkey")
|
||||
.Input("values: Tval")
|
||||
.Attr("Tkey: type")
|
||||
.Attr("Tval: type")
|
||||
.SetShapeFn([](InferenceContext* c) {
|
||||
ShapeHandle handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRank(c->input(0), 0, &handle));
|
||||
|
||||
ShapeHandle keys;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRank(c->input(1), 1, &keys));
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->Merge(keys, c->input(2), &keys));
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
})
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Table initializer that takes two tensors for keys and values respectively.
|
||||
|
||||
table_handle: Handle to a table which will be initialized.
|
||||
keys: Keys of type Tkey.
|
||||
values: Values of type Tval.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("InitializeTableFromTextFile")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: Ref(string)")
|
||||
.Input("filename: string")
|
||||
@ -2152,6 +2427,43 @@ vocab_size: Number of elements of the file, use -1 if unknown.
|
||||
delimiter: Delimiter to separate fields in a line.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("InitializeTableFromTextFileV2")
|
||||
.Input("table_handle: resource")
|
||||
.Input("filename: string")
|
||||
.Attr("key_index: int >= -2")
|
||||
.Attr("value_index: int >= -2")
|
||||
.Attr("vocab_size: int >= -1 = -1")
|
||||
.Attr("delimiter: string = '\t'")
|
||||
.SetShapeFn([](InferenceContext* c) {
|
||||
ShapeHandle handle;
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRank(c->input(0), 0, &handle));
|
||||
|
||||
TF_RETURN_IF_ERROR(c->WithRank(c->input(1), 0, &handle));
|
||||
return Status::OK();
|
||||
})
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Initializes a table from a text file.
|
||||
|
||||
It inserts one key-value pair into the table for each line of the file.
|
||||
The key and value is extracted from the whole line content, elements from the
|
||||
split line based on `delimiter` or the line number (starting from zero).
|
||||
Where to extract the key and value from a line is specified by `key_index` and
|
||||
`value_index`.
|
||||
|
||||
- A value of -1 means use the line number(starting from zero), expects `int64`.
|
||||
- A value of -2 means use the whole line content, expects `string`.
|
||||
- A value >= 0 means use the index (starting at zero) of the split line based
|
||||
on `delimiter`.
|
||||
|
||||
table_handle: Handle to a table which will be initialized.
|
||||
filename: Filename of a vocabulary text file.
|
||||
key_index: Column index in a line to get the table `key` values from.
|
||||
value_index: Column index that represents information of a line to get the table
|
||||
`value` values from.
|
||||
vocab_size: Number of elements of the file, use -1 if unknown.
|
||||
delimiter: Delimiter to separate fields in a line.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("GetSessionHandle")
|
||||
.Input("value: T")
|
||||
.Output("handle: string")
|
||||
|
||||
@ -662,13 +662,12 @@ Compute the upper regularized incomplete Gamma function `Q(a, x)`.
|
||||
|
||||
The upper regularized incomplete Gamma function is defined as:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Q(a, x) = Gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - P(a, x)
|
||||
```
|
||||
\\(Q(a, x) = Gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - P(a, x)\\)
|
||||
|
||||
where
|
||||
```
|
||||
Gamma(a, x) = int_{x}^{\infty} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
\\(Gamma(a, x) = int_{x}^{\infty} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt\\)
|
||||
|
||||
is the upper incomplete Gama function.
|
||||
|
||||
Note, above `P(a, x)` (`Igamma`) is the lower regularized complete
|
||||
@ -686,13 +685,13 @@ Compute the lower regularized incomplete Gamma function `Q(a, x)`.
|
||||
|
||||
The lower regularized incomplete Gamma function is defined as:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
P(a, x) = gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - Q(a, x)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
\\(P(a, x) = gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - Q(a, x)\\)
|
||||
|
||||
where
|
||||
```
|
||||
gamma(a, x) = int_{0}^{x} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
\\(gamma(a, x) = int_{0}^{x} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt\\)
|
||||
|
||||
is the lower incomplete Gamma function.
|
||||
|
||||
Note, above `Q(a, x)` (`Igammac`) is the upper regularized complete
|
||||
@ -710,9 +709,9 @@ Compute the Hurwitz zeta function \\(\zeta(x, q)\\).
|
||||
|
||||
The Hurwitz zeta function is defined as:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
\zeta(x, q) = \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} (q + n)^{-x}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
\\(\zeta(x, q) = \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} (q + n)^{-x}\\)
|
||||
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("Polygamma")
|
||||
@ -726,9 +725,9 @@ Compute the polygamma function \\(\psi^{(n)}(x)\\).
|
||||
|
||||
The polygamma function is defined as:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
\psi^{(n)}(x) = \frac{d^n}{dx^n} \psi(x)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
\\(\psi^{(n)}(x) = \frac{d^n}{dx^n} \psi(x)\\)
|
||||
|
||||
where \\(\psi(x)\\) is the digamma function.
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
@ -790,14 +789,14 @@ Compute the regularized incomplete beta integral \\(I_x(a, b)\\).
|
||||
|
||||
The regularized incomplete beta integral is defined as:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
I_x(a, b) = \frac{B(x; a, b)}{B(a, b)}
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
\\(I_x(a, b) = \frac{B(x; a, b)}{B(a, b)}\\)
|
||||
|
||||
where
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
B(x; a, b) = \int_0^x t^{a-1} (1 - t)^{b-1} dt
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
\\(B(x; a, b) = \int_0^x t^{a-1} (1 - t)^{b-1} dt\\)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
is the incomplete beta function and \\(B(a, b)\\) is the *complete*
|
||||
beta function.
|
||||
@ -2371,4 +2370,35 @@ output_max: the computed max output.
|
||||
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
// --------------------------------------------------------------------------
|
||||
|
||||
REGISTER_OP("Bucketize")
|
||||
.Input("input: T")
|
||||
.Output("output: int32")
|
||||
.Attr("T: {int32, int64, float, double}")
|
||||
.Attr("boundaries: list(float)")
|
||||
.SetShapeFn(shape_inference::UnchangedShape)
|
||||
.Doc(R"doc(
|
||||
Bucketizes 'input' based on 'boundaries'.
|
||||
|
||||
For example, if the inputs are
|
||||
boundaries = [0, 10, 100]
|
||||
input = [[-5, 10000]
|
||||
[150, 10]
|
||||
[5, 100]]
|
||||
|
||||
then the output will be
|
||||
output = [[0, 3]
|
||||
[3, 2]
|
||||
[1, 3]]
|
||||
|
||||
input: Any shape of Tensor contains with int or float type.
|
||||
boundaries: A sorted list of floats gives the boundary of the buckets.
|
||||
output: Same shape with 'input', each value of input replaced with bucket index.
|
||||
|
||||
@compatibility(numpy)
|
||||
Equivalent to np.digitize.
|
||||
@end_compatibility
|
||||
)doc");
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace tensorflow
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3324,7 +3324,7 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Compute the regularized incomplete beta integral \\\\(I_x(a, b)\\\\)."
|
||||
description: "The regularized incomplete beta integral is defined as:\n\n```\nI_x(a, b) = \\frac{B(x; a, b)}{B(a, b)}\n```\nwhere\n\n```\nB(x; a, b) = \\int_0^x t^{a-1} (1 - t)^{b-1} dt\n```\n\nis the incomplete beta function and \\\\(B(a, b)\\\\) is the *complete*\nbeta function."
|
||||
description: "The regularized incomplete beta integral is defined as:\n\n\n\\\\(I_x(a, b) = \\frac{B(x; a, b)}{B(a, b)}\\\\)\n\nwhere\n\n\n\\\\(B(x; a, b) = \\int_0^x t^{a-1} (1 - t)^{b-1} dt\\\\)\n\n\nis the incomplete beta function and \\\\(B(a, b)\\\\) is the *complete*\nbeta function."
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "BiasAdd"
|
||||
@ -3633,6 +3633,38 @@ op {
|
||||
summary: "Return the reduction indices for computing gradients of s0 op s1 with broadcast."
|
||||
description: "This is typically used by gradient computations for a broadcasting operation."
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "Bucketize"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "input"
|
||||
description: "Any shape of Tensor contains with int or float type."
|
||||
type_attr: "T"
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "output"
|
||||
description: "Same shape with \'input\', each value of input replaced with bucket index.\n\n@compatibility(numpy)\nEquivalent to np.digitize.\n@end_compatibility"
|
||||
type: DT_INT32
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "T"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
allowed_values {
|
||||
list {
|
||||
type: DT_INT32
|
||||
type: DT_INT64
|
||||
type: DT_FLOAT
|
||||
type: DT_DOUBLE
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "boundaries"
|
||||
type: "list(float)"
|
||||
description: "A sorted list of floats gives the boundary of the buckets."
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Bucketizes \'input\' based on \'boundaries\'."
|
||||
description: "For example, if the inputs are\n boundaries = [0, 10, 100]\n input = [[-5, 10000]\n [150, 10]\n [5, 100]]\n\nthen the output will be\n output = [[0, 3]\n [3, 2]\n [1, 3]]"
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "CTCBeamSearchDecoder"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -8713,6 +8745,51 @@ op {
|
||||
description: "This op creates a hash table, specifying the type of its keys and values.\nBefore using the table you will have to initialize it. After initialization the\ntable will be immutable."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "HashTableV2"
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
description: "Handle to a table."
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "container"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.\nOtherwise, a default container is used."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "shared_name"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across\nmultiple sessions."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "use_node_name_sharing"
|
||||
type: "bool"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
b: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "If true and shared_name is empty, the table is shared\nusing the node name."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "key_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
description: "Type of the table keys."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
description: "Type of the table values."
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Creates a non-initialized hash table."
|
||||
description: "This op creates a hash table, specifying the type of its keys and values.\nBefore using the table you will have to initialize it. After initialization the\ntable will be immutable."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "HistogramSummary"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -8954,7 +9031,7 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Compute the lower regularized incomplete Gamma function `Q(a, x)`."
|
||||
description: "The lower regularized incomplete Gamma function is defined as:\n\n```\nP(a, x) = gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - Q(a, x)\n```\nwhere\n```\ngamma(a, x) = int_{0}^{x} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt\n```\nis the lower incomplete Gamma function.\n\nNote, above `Q(a, x)` (`Igammac`) is the upper regularized complete\nGamma function."
|
||||
description: "The lower regularized incomplete Gamma function is defined as:\n\n\n\\\\(P(a, x) = gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - Q(a, x)\\\\)\n\nwhere\n\n\\\\(gamma(a, x) = int_{0}^{x} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt\\\\)\n\nis the lower incomplete Gamma function.\n\nNote, above `Q(a, x)` (`Igammac`) is the upper regularized complete\nGamma function."
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "Igammac"
|
||||
@ -8981,7 +9058,7 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Compute the upper regularized incomplete Gamma function `Q(a, x)`."
|
||||
description: "The upper regularized incomplete Gamma function is defined as:\n\n```\nQ(a, x) = Gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - P(a, x)\n```\nwhere\n```\nGamma(a, x) = int_{x}^{\\infty} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt\n```\nis the upper incomplete Gama function.\n\nNote, above `P(a, x)` (`Igamma`) is the lower regularized complete\nGamma function."
|
||||
description: "The upper regularized incomplete Gamma function is defined as:\n\n\\\\(Q(a, x) = Gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - P(a, x)\\\\)\n\nwhere\n\n\\\\(Gamma(a, x) = int_{x}^{\\infty} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt\\\\)\n\nis the upper incomplete Gama function.\n\nNote, above `P(a, x)` (`Igamma`) is the lower regularized complete\nGamma function."
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "Imag"
|
||||
@ -9223,6 +9300,82 @@ op {
|
||||
summary: "Initializes a table from a text file."
|
||||
description: "It inserts one key-value pair into the table for each line of the file.\nThe key and value is extracted from the whole line content, elements from the\nsplit line based on `delimiter` or the line number (starting from zero).\nWhere to extract the key and value from a line is specified by `key_index` and\n`value_index`.\n\n- A value of -1 means use the line number(starting from zero), expects `int64`.\n- A value of -2 means use the whole line content, expects `string`.\n- A value >= 0 means use the index (starting at zero) of the split line based\n on `delimiter`."
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "InitializeTableFromTextFileV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
description: "Handle to a table which will be initialized."
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "filename"
|
||||
description: "Filename of a vocabulary text file."
|
||||
type: DT_STRING
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "key_index"
|
||||
type: "int"
|
||||
description: "Column index in a line to get the table `key` values from."
|
||||
has_minimum: true
|
||||
minimum: -2
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_index"
|
||||
type: "int"
|
||||
description: "Column index that represents information of a line to get the table\n`value` values from."
|
||||
has_minimum: true
|
||||
minimum: -2
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "vocab_size"
|
||||
type: "int"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
i: -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "Number of elements of the file, use -1 if unknown."
|
||||
has_minimum: true
|
||||
minimum: -1
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "delimiter"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: "\t"
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "Delimiter to separate fields in a line."
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Initializes a table from a text file."
|
||||
description: "It inserts one key-value pair into the table for each line of the file.\nThe key and value is extracted from the whole line content, elements from the\nsplit line based on `delimiter` or the line number (starting from zero).\nWhere to extract the key and value from a line is specified by `key_index` and\n`value_index`.\n\n- A value of -1 means use the line number(starting from zero), expects `int64`.\n- A value of -2 means use the whole line content, expects `string`.\n- A value >= 0 means use the index (starting at zero) of the split line based\n on `delimiter`."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "InitializeTableV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
description: "Handle to a table which will be initialized."
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "keys"
|
||||
description: "Keys of type Tkey."
|
||||
type_attr: "Tkey"
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "values"
|
||||
description: "Values of type Tval."
|
||||
type_attr: "Tval"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tkey"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tval"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Table initializer that takes two tensors for keys and values respectively."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "Inv"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -10035,6 +10188,34 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Outputs all keys and values in the table."
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableExportV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
description: "Handle to the table."
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "keys"
|
||||
description: "Vector of all keys present in the table."
|
||||
type_attr: "Tkeys"
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "values"
|
||||
description: "Tensor of all values in the table. Indexed in parallel with `keys`."
|
||||
type_attr: "Tvalues"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tkeys"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tvalues"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Outputs all keys and values in the table."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableFind"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -10068,6 +10249,39 @@ op {
|
||||
summary: "Looks up keys in a table, outputs the corresponding values."
|
||||
description: "The tensor `keys` must of the same type as the keys of the table.\nThe output `values` is of the type of the table values.\n\nThe scalar `default_value` is the value output for keys not present in the\ntable. It must also be of the same type as the table values."
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableFindV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
description: "Handle to the table."
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "keys"
|
||||
description: "Any shape. Keys to look up."
|
||||
type_attr: "Tin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "default_value"
|
||||
type_attr: "Tout"
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "values"
|
||||
description: "Same shape as `keys`. Values found in the table, or `default_values`\nfor missing keys."
|
||||
type_attr: "Tout"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tin"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tout"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Looks up keys in a table, outputs the corresponding values."
|
||||
description: "The tensor `keys` must of the same type as the keys of the table.\nThe output `values` is of the type of the table values.\n\nThe scalar `default_value` is the value output for keys not present in the\ntable. It must also be of the same type as the table values."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableImport"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -10097,6 +10311,35 @@ op {
|
||||
summary: "Replaces the contents of the table with the specified keys and values."
|
||||
description: "The tensor `keys` must be of the same type as the keys of the table.\nThe tensor `values` must be of the type of the table values."
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableImportV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
description: "Handle to the table."
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "keys"
|
||||
description: "Any shape. Keys to look up."
|
||||
type_attr: "Tin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "values"
|
||||
description: "Values to associate with keys."
|
||||
type_attr: "Tout"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tin"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tout"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Replaces the contents of the table with the specified keys and values."
|
||||
description: "The tensor `keys` must be of the same type as the keys of the table.\nThe tensor `values` must be of the type of the table values."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableInsert"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -10126,6 +10369,35 @@ op {
|
||||
summary: "Updates the table to associates keys with values."
|
||||
description: "The tensor `keys` must be of the same type as the keys of the table.\nThe tensor `values` must be of the type of the table values."
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableInsertV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
description: "Handle to the table."
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "keys"
|
||||
description: "Any shape. Keys to look up."
|
||||
type_attr: "Tin"
|
||||
}
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "values"
|
||||
description: "Values to associate with keys."
|
||||
type_attr: "Tout"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tin"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "Tout"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Updates the table to associates keys with values."
|
||||
description: "The tensor `keys` must be of the same type as the keys of the table.\nThe tensor `values` must be of the type of the table values."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableSize"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -10141,6 +10413,21 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Computes the number of elements in the given table."
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LookupTableSizeV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
description: "Handle to the table."
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "size"
|
||||
description: "Scalar that contains number of elements in the table."
|
||||
type: DT_INT64
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Computes the number of elements in the given table."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "LoopCond"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -11845,6 +12132,80 @@ op {
|
||||
description: "\"open addressing\" with quadratic reprobing to resolve collisions.\n\nThis op creates a mutable hash table, specifying the type of its keys and\nvalues. Each value must be a scalar. Data can be inserted into the table using\nthe insert operations. It does not support the initialization operation."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "MutableDenseHashTableV2"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
name: "empty_key"
|
||||
description: "The key used to represent empty key buckets internally. Must not\nbe used in insert or lookup operations."
|
||||
type_attr: "key_dtype"
|
||||
}
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
description: "Handle to a table."
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "container"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.\nOtherwise, a default container is used."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "shared_name"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across\nmultiple sessions."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "use_node_name_sharing"
|
||||
type: "bool"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
b: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "key_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
description: "Type of the table keys."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
description: "Type of the table values."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_shape"
|
||||
type: "shape"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
shape {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "The shape of each value."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "initial_num_buckets"
|
||||
type: "int"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
i: 131072
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "The initial number of hash table buckets. Must be a power\nto 2."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "max_load_factor"
|
||||
type: "float"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
f: 0.8
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "The maximum ratio between number of entries and number of\nbuckets before growing the table. Must be between 0 and 1."
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Creates an empty hash table that uses tensors as the backing store. It uses"
|
||||
description: "\"open addressing\" with quadratic reprobing to resolve collisions.\n\nThis op creates a mutable hash table, specifying the type of its keys and\nvalues. Each value must be a scalar. Data can be inserted into the table using\nthe insert operations. It does not support the initialization operation."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "MutableHashTable"
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
@ -11944,6 +12305,103 @@ op {
|
||||
description: "This op creates a mutable hash table, specifying the type of its keys and\nvalues. Each value must be a vector. Data can be inserted into the table using\nthe insert operations. It does not support the initialization operation."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2"
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
description: "Handle to a table."
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "container"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.\nOtherwise, a default container is used."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "shared_name"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across\nmultiple sessions."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "use_node_name_sharing"
|
||||
type: "bool"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
b: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "key_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
description: "Type of the table keys."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
description: "Type of the table values."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_shape"
|
||||
type: "shape"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
shape {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Creates an empty hash table."
|
||||
description: "This op creates a mutable hash table, specifying the type of its keys and\nvalues. Each value must be a vector. Data can be inserted into the table using\nthe insert operations. It does not support the initialization operation."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "MutableHashTableV2"
|
||||
output_arg {
|
||||
name: "table_handle"
|
||||
description: "Handle to a table."
|
||||
type: DT_RESOURCE
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "container"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.\nOtherwise, a default container is used."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "shared_name"
|
||||
type: "string"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
s: ""
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across\nmultiple sessions."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "use_node_name_sharing"
|
||||
type: "bool"
|
||||
default_value {
|
||||
b: false
|
||||
}
|
||||
description: "If true and shared_name is empty, the table is shared\nusing the node name."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "key_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
description: "Type of the table keys."
|
||||
}
|
||||
attr {
|
||||
name: "value_dtype"
|
||||
type: "type"
|
||||
description: "Type of the table values."
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Creates an empty hash table."
|
||||
description: "This op creates a mutable hash table, specifying the type of its keys and\nvalues. Each value must be a scalar. Data can be inserted into the table using\nthe insert operations. It does not support the initialization operation."
|
||||
is_stateful: true
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "Neg"
|
||||
input_arg {
|
||||
@ -12884,7 +13342,7 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Compute the polygamma function \\\\(\\psi^{(n)}(x)\\\\)."
|
||||
description: "The polygamma function is defined as:\n\n```\n\\psi^{(n)}(x) = \\frac{d^n}{dx^n} \\psi(x)\n```\nwhere \\\\(\\psi(x)\\\\) is the digamma function."
|
||||
description: "The polygamma function is defined as:\n\n\n\\\\(\\psi^{(n)}(x) = \\frac{d^n}{dx^n} \\psi(x)\\\\)\n\nwhere \\\\(\\psi(x)\\\\) is the digamma function."
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "Pow"
|
||||
@ -19650,7 +20108,7 @@ op {
|
||||
minimum: 1
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Distributed version of Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent (SDCA) optimizer for"
|
||||
description: "linear models with L1 + L2 regularization. As global optimization objective is\nstrongly-convex, the optimizer optimizes the dual objective at each step. The\noptimizer applies each update one example at a time. Examples are sampled\nuniformly, and the optimizer is learning rate free and enjoys linear convergence\nrate.\n\nProximal Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent, Shalev-Shwartz, Shai; Zhang, Tong.\n2012 arXiv1211.2717S: http://arxiv.org/pdf/1211.2717v1.pdf\n\n Loss objective = \\sum f_{i}(wx_{i}) + (l2 / 2) * |w|^2 + l1 * |w|\n\nAdding vs. Averaging in Distributed Primal-Dual Optimization.\nChenxin Ma, Virginia Smith, Martin Jaggi, Michael I. Jordan, Peter Richtarik,\nMartin Takac http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03508\n\nStochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent with Adaptive Probabilities\nDominik Csiba, Zheng Qu, Peter Richtarik https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.08053"
|
||||
description: "linear models with L1 + L2 regularization. As global optimization objective is\nstrongly-convex, the optimizer optimizes the dual objective at each step. The\noptimizer applies each update one example at a time. Examples are sampled\nuniformly, and the optimizer is learning rate free and enjoys linear convergence\nrate.\n\n[Proximal Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent](http://arxiv.org/pdf/1211.2717v1.pdf).<br>\nShai Shalev-Shwartz, Tong Zhang. 2012\n\n$$Loss Objective = \\sum f_{i} (wx_{i}) + (l2 / 2) * |w|^2 + l1 * |w|$$\n\n[Adding vs. Averaging in Distributed Primal-Dual Optimization](http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03508).<br>\nChenxin Ma, Virginia Smith, Martin Jaggi, Michael I. Jordan,\nPeter Richtarik, Martin Takac. 2015\n\n[Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent with Adaptive Probabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.08053).<br>\nDominik Csiba, Zheng Qu, Peter Richtarik. 2015"
|
||||
}
|
||||
op {
|
||||
name: "SdcaShrinkL1"
|
||||
@ -26527,5 +26985,5 @@ op {
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
summary: "Compute the Hurwitz zeta function \\\\(\\zeta(x, q)\\\\)."
|
||||
description: "The Hurwitz zeta function is defined as:\n\n```\n\\zeta(x, q) = \\sum_{n=0}^{\\infty} (q + n)^{-x}\n```"
|
||||
description: "The Hurwitz zeta function is defined as:\n\n\n\\\\(\\zeta(x, q) = \\sum_{n=0}^{\\infty} (q + n)^{-x}\\\\)"
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
@ -72,17 +72,17 @@ optimizer applies each update one example at a time. Examples are sampled
|
||||
uniformly, and the optimizer is learning rate free and enjoys linear convergence
|
||||
rate.
|
||||
|
||||
Proximal Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent, Shalev-Shwartz, Shai; Zhang, Tong.
|
||||
2012 arXiv1211.2717S: http://arxiv.org/pdf/1211.2717v1.pdf
|
||||
[Proximal Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent](http://arxiv.org/pdf/1211.2717v1.pdf).<br>
|
||||
Shai Shalev-Shwartz, Tong Zhang. 2012
|
||||
|
||||
Loss objective = \sum f_{i}(wx_{i}) + (l2 / 2) * |w|^2 + l1 * |w|
|
||||
$$Loss Objective = \sum f_{i} (wx_{i}) + (l2 / 2) * |w|^2 + l1 * |w|$$
|
||||
|
||||
Adding vs. Averaging in Distributed Primal-Dual Optimization.
|
||||
Chenxin Ma, Virginia Smith, Martin Jaggi, Michael I. Jordan, Peter Richtarik,
|
||||
Martin Takac http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03508
|
||||
[Adding vs. Averaging in Distributed Primal-Dual Optimization](http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03508).<br>
|
||||
Chenxin Ma, Virginia Smith, Martin Jaggi, Michael I. Jordan,
|
||||
Peter Richtarik, Martin Takac. 2015
|
||||
|
||||
Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent with Adaptive Probabilities
|
||||
Dominik Csiba, Zheng Qu, Peter Richtarik https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.08053
|
||||
[Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent with Adaptive Probabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.08053).<br>
|
||||
Dominik Csiba, Zheng Qu, Peter Richtarik. 2015
|
||||
|
||||
loss_type: Type of the primal loss. Currently SdcaSolver supports logistic,
|
||||
squared and hinge losses.
|
||||
|
||||
429
tensorflow/docs_src/performance/benchmarks.md
Normal file
429
tensorflow/docs_src/performance/benchmarks.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,429 @@
|
||||
# TensorFlow Performance Benchmarks
|
||||
|
||||
## Overview
|
||||
|
||||
A selection of image classification models were tested across multiple platforms
|
||||
to create a point of reference for the TensorFlow community. The methodology,
|
||||
links to the scripts, and commands to reproduce the results are in the
|
||||
[appendix](#appendix).
|
||||
|
||||
## Results for image classification models
|
||||
|
||||
InceptionV3 ([arXiv:1512.00567](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.00567)),
|
||||
ResNet-50 ([arXiv:1512.03385](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385)),
|
||||
ResNet-152 ([arXiv:1512.03385](https://arxiv.org/abs/1512.03385)), VGG16
|
||||
([arXiv:1409.1556](https://arxiv.org/abs/1409.1556)), and
|
||||
[AlexNet](http://papers.nips.cc/paper/4824-imagenet-classification-with-deep-convolutional-neural-networks.pdf)
|
||||
were tested using the [ImageNet](http://www.image-net.org/) data set. Tests were
|
||||
run on Google Compute Engine, Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (Amazon EC2), and an
|
||||
NVIDIA® DGX-1™. Most of the tests were run with both synthetic and real data.
|
||||
Testing with synthetic data was done by using a `tf.Variable` set to the same
|
||||
shape as the data expected by each model for ImageNet. We believe it is
|
||||
important to include real data measurements when benchmarking a platform. This
|
||||
load tests both the underlying hardware and the framework at preparing data for
|
||||
actual training. We start with synthetic data to remove disk I/O as a variable
|
||||
and to set a baseline. Real data is then used to verify that the TensorFlow
|
||||
input pipeline and the underlying disk I/O are saturating the compute units.
|
||||
|
||||
### Training with NVIDIA® DGX-1™ (NVIDIA® Tesla® P100)
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:100%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:100%" src="../images/perf_summary_p100_single_server.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Details and additional results are in the [Details for NVIDIA® DGX-1™ (NVIDIA®
|
||||
Tesla® P100)](#details-for-nvidia®-dgx-1™-nvidia®-tesla®-p100) section.
|
||||
|
||||
### Training with NVIDIA® Tesla® K80
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:95%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:100%" src="../images/perf_summary_k80_single_server.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Details and additional results are in the [Details for Google Compute Engine
|
||||
(NVIDIA® Tesla® K80)](#details-for-google-compute-engine-nvidia®-tesla®-k80) and
|
||||
[Details for Amazon EC2 (NVIDIA® Tesla®
|
||||
K80)](#details-for-amazon-ec2-nvidia®-tesla®-k80) sections.
|
||||
|
||||
### Distributed training with NVIDIA® Tesla® K80
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:95%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:100%" src="../images/perf_summary_k80_aws_distributed.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
Details and additional results are in the [Details for Amazon EC2 Distributed
|
||||
(NVIDIA® Tesla® K80)](#details-for-amazon-ec2-distributed-nvidia®-tesla®-k80)
|
||||
section.
|
||||
|
||||
### Compare synthetic with real data training
|
||||
|
||||
**NVIDIA® Tesla® P100**
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:95%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:35%" src="../images/perf_summary_p100_data_compare_inceptionv3.png">
|
||||
<img style="width:35%" src="../images/perf_summary_p100_data_compare_resnet50.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
**NVIDIA® Tesla® K80**
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:95%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:35%" src="../images/perf_summary_k80_data_compare_inceptionv3.png">
|
||||
<img style="width:35%" src="../images/perf_summary_k80_data_compare_resnet50.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
## Details for NVIDIA® DGX-1™ (NVIDIA® Tesla® P100)
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment
|
||||
|
||||
* **Instance type**: NVIDIA® DGX-1™
|
||||
* **GPU:** 8x NVIDIA® Tesla® P100
|
||||
* **OS:** Ubuntu 16.04 LTS with tests run via Docker
|
||||
* **CUDA / cuDNN:** 8.0 / 5.1
|
||||
* **TensorFlow GitHub hash:** b1e174e
|
||||
* **Build Command:** `bazel build -c opt --copt=-march="haswell" --config=cuda
|
||||
//tensorflow/tools/pip_package:build_pip_package`
|
||||
* **Disk:** local SSD
|
||||
* **DataSet:** ImageNet
|
||||
|
||||
Batch size and optimizer used for each model.
|
||||
|
||||
| InceptionV3 | ResNet-50 | ResNet-152 | Alexnet | VGG16
|
||||
------------------ | ----------- | --------- | ---------- | ------- | -----
|
||||
Batch size per GPU | 64 | 64 | 64 | 512 | 64
|
||||
Optimizer | sgd | sgd | sgd | sgd | sgd
|
||||
|
||||
Configuration used for each model.
|
||||
|
||||
Model | variable_update | local_parameter_device
|
||||
----------- | ---------------------- | ----------------------
|
||||
InceptionV3 | parameter_server | cpu
|
||||
ResNet50 | parameter_server | cpu
|
||||
ResNet152 | parameter_server | cpu
|
||||
AlexNet | replicated (with NCCL) | n/a
|
||||
VGG16 | replicated (with NCCL) | n/a
|
||||
|
||||
### Results
|
||||
|
||||
Batch size and optimizer used for each model are listed in the table below.
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:95%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:100%" src="../images/perf_summary_p100_single_server.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:95%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:35%" src="../images/perf_dgx1_synth_p100_single_server_scaling.png">
|
||||
<img style="width:35%" src="../images/perf_dgx1_real_p100_single_server_scaling.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
**Training synthetic data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 | ResNet-50 | ResNet-152 | Alexnet | VGG16
|
||||
---- | ----------- | --------- | ---------- | ------- | -----
|
||||
1 | 142 | 238 | 95.6 | 2987 | 132
|
||||
2 | 284 | 479 | 187 | 5658 | 259
|
||||
4 | 569 | 948 | 374 | 10509 | 511
|
||||
8 | 1131 | 1886 | 744 | 17822 | 959
|
||||
|
||||
**Training real data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 | ResNet-50 | ResNet-152 | Alexnet | VGG16
|
||||
---- | ----------- | --------- | ---------- | ------- | -----
|
||||
1 | 142 | 239 | 95.5 | 2890 | 132
|
||||
2 | 278 | 468 | 187 | 4448 | 245
|
||||
4 | 551 | 938 | 373 | 7105 | 466
|
||||
8 | 1079 | 1802 | 721 | N/A | 794
|
||||
|
||||
Training AlexNet with real data on 8 GPUs was excluded from the graph and table
|
||||
above due to it maxing out the input pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
## Details for Google Compute Engine (NVIDIA® Tesla® K80)
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment
|
||||
|
||||
* **Instance type**: n1-standard-32-k80x8
|
||||
* **GPU:** 8x NVIDIA® Tesla® K80
|
||||
* **OS:** Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
|
||||
* **CUDA / cuDNN:** 8.0 / 5.1
|
||||
* **TensorFlow GitHub hash:** b1e174e
|
||||
* **Build Command:** `bazel build -c opt --copt=-march="haswell" --config=cuda
|
||||
//tensorflow/tools/pip_package:build_pip_package`
|
||||
* **Disk:** 1.7 TB Shared SSD persistent disk (800 MB/s)
|
||||
* **DataSet:** ImageNet
|
||||
* **Test Date:** April 2017
|
||||
|
||||
Batch size and optimizer used for each model are listed in the table below. In
|
||||
addition to the batch sizes listed in the table, InceptionV3 and ResNet-50 were
|
||||
tested with a batch size of 32. Those results are in the *other results*
|
||||
section.
|
||||
|
||||
| InceptionV3 | ResNet-50 | ResNet-152 | Alexnet | VGG16
|
||||
------------------ | ----------- | --------- | ---------- | ------- | -----
|
||||
Batch size per GPU | 64 | 64 | 32 | 512 | 32
|
||||
Optimizer | sgd | sgd | sgd | sgd | sgd
|
||||
|
||||
The configuration used for each model was `variable_update` equal to
|
||||
`parameter_server` and `local_parameter_device` equal to `cpu`.
|
||||
|
||||
### Results
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:95%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:35%" src="../images/perf_gce_synth_k80_single_server_scaling.png">
|
||||
<img style="width:35%" src="../images/perf_gce_real_k80_single_server_scaling.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
**Training synthetic data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 | ResNet-50 | ResNet-152 | Alexnet | VGG16
|
||||
---- | ----------- | --------- | ---------- | ------- | -----
|
||||
1 | 30.5 | 56.8 | 20.8 | 656 | 30.3
|
||||
2 | 57.8 | 107 | 39.1 | 1210 | 56.2
|
||||
4 | 116 | 212 | 77.2 | 2330 | 106
|
||||
8 | 227 | 419 | 151 | 4640 | 222
|
||||
|
||||
**Training real data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 | ResNet-50 | ResNet-152 | Alexnet | VGG16
|
||||
---- | ----------- | --------- | ---------- | ------- | -----
|
||||
1 | 30.5 | 56.7 | 20.7 | 639 | 30.2
|
||||
2 | 57.8 | 107 | 39 | 1136 | 55.5
|
||||
4 | 115 | 211 | 77.3 | 2067 | 106
|
||||
8 | 225 | 418 | 150 | 4056 | 213
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Results
|
||||
|
||||
**Training synthetic data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 (batch size 32) | ResNet-50 (batch size 32)
|
||||
---- | --------------------------- | -------------------------
|
||||
1 | 29.3 | 53.9
|
||||
2 | 55.0 | 101
|
||||
4 | 109 | 200
|
||||
8 | 216 | 398
|
||||
|
||||
**Training real data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 (batch size 32) | ResNet-50 (batch size 32)
|
||||
---- | --------------------------- | -------------------------
|
||||
1 | 29.3 | 53.6
|
||||
2 | 55 | 102
|
||||
4 | 109 | 200
|
||||
8 | 215 | 387
|
||||
|
||||
## Details for Amazon EC2 (NVIDIA® Tesla® K80)
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment
|
||||
|
||||
* **Instance type**: p2.8xlarge
|
||||
* **GPU:** 8x NVIDIA® Tesla® K80
|
||||
* **OS:** Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
|
||||
* **CUDA / cuDNN:** 8.0 / 5.1
|
||||
* **TensorFlow GitHub hash:** b1e174e
|
||||
* **Build Command:** `bazel build -c opt --copt=-march="haswell" --config=cuda
|
||||
//tensorflow/tools/pip_package:build_pip_package`
|
||||
* **Disk:** 1TB Amazon EFS (burst 100 MiB/sec for 12 hours, continuous 50
|
||||
MiB/sec)
|
||||
* **DataSet:** ImageNet
|
||||
* **Test Date:** April 2017
|
||||
|
||||
Batch size and optimizer used for each model are listed in the table below. In
|
||||
addition to the batch sizes listed in the table, InceptionV3 and ResNet-50 were
|
||||
tested with a batch size of 32. Those results are in the *other results*
|
||||
section.
|
||||
|
||||
| InceptionV3 | ResNet-50 | ResNet-152 | Alexnet | VGG16
|
||||
------------------ | ----------- | --------- | ---------- | ------- | -----
|
||||
Batch size per GPU | 64 | 64 | 32 | 512 | 32
|
||||
Optimizer | sgd | sgd | sgd | sgd | sgd
|
||||
|
||||
Configuration used for each model.
|
||||
|
||||
Model | variable_update | local_parameter_device
|
||||
----------- | ------------------------- | ----------------------
|
||||
InceptionV3 | parameter_server | cpu
|
||||
ResNet-50 | replicated (without NCCL) | gpu
|
||||
ResNet-152 | replicated (without NCCL) | gpu
|
||||
AlexNet | parameter_server | gpu
|
||||
VGG16 | parameter_server | gpu
|
||||
|
||||
### Results
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:95%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:35%" src="../images/perf_aws_synth_k80_single_server_scaling.png">
|
||||
<img style="width:35%" src="../images/perf_aws_real_k80_single_server_scaling.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
**Training synthetic data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 | ResNet-50 | ResNet-152 | Alexnet | VGG16
|
||||
---- | ----------- | --------- | ---------- | ------- | -----
|
||||
1 | 30.8 | 56.3 | 20.9 | 684 | 32.4
|
||||
2 | 58.7 | 108 | 39.3 | 1244 | 61.5
|
||||
4 | 117 | 217 | 79.1 | 2479 | 123
|
||||
8 | 230 | 419 | 156 | 4853 | 234
|
||||
|
||||
**Training real data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 | ResNet-50 | ResNet-152 | Alexnet | VGG16
|
||||
---- | ----------- | --------- | ---------- | ------- | -----
|
||||
1 | 30.5 | 56.0 | 20.6 | 674 | 32.0
|
||||
2 | 58.7 | 107 | 39.0 | 1227 | 61.0
|
||||
4 | 118 | 205 | 77.9 | 2201 | 120
|
||||
8 | 228 | 405 | 152 | N/A | 191
|
||||
|
||||
Training AlexNet with real data on 8 GPUs was excluded from the graph and table
|
||||
above due to our EFS setup not providing enough throughput.
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Results
|
||||
|
||||
**Training synthetic data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 (batch size 32) | ResNet-50 (batch size 32)
|
||||
---- | --------------------------- | -------------------------
|
||||
1 | 29.9 | 53.5
|
||||
2 | 57.5 | 101
|
||||
4 | 114 | 202
|
||||
8 | 216 | 380
|
||||
|
||||
**Training real data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 (batch size 32) | ResNet-50 (batch size 32)
|
||||
---- | --------------------------- | -------------------------
|
||||
1 | 30.0 | 53.6
|
||||
2 | 57.5 | 101
|
||||
4 | 113 | 202
|
||||
8 | 212 | 379
|
||||
|
||||
## Details for Amazon EC2 Distributed (NVIDIA® Tesla® K80)
|
||||
|
||||
### Environment
|
||||
|
||||
* **Instance type**: p2.8xlarge
|
||||
* **GPU:** 8x NVIDIA® Tesla® K80
|
||||
* **OS:** Ubuntu 16.04 LTS
|
||||
* **CUDA / cuDNN:** 8.0 / 5.1
|
||||
* **TensorFlow GitHub hash:** b1e174e
|
||||
* **Build Command:** `bazel build -c opt --copt=-march="haswell" --config=cuda
|
||||
//tensorflow/tools/pip_package:build_pip_package`
|
||||
* **Disk:** 1.0 TB EFS (burst 100 MB/sec for 12 hours, continuous 50 MB/sec)
|
||||
* **DataSet:** ImageNet
|
||||
* **Test Date:** April 2017
|
||||
|
||||
The batch size and optimizer used for the tests are listed in the table. In
|
||||
addition to the batch sizes listed in the table, InceptionV3 and ResNet-50 were
|
||||
tested with a batch size of 32. Those results are in the *other results*
|
||||
section.
|
||||
|
||||
| InceptionV3 | ResNet-50 | ResNet-152
|
||||
------------------ | ----------- | --------- | ----------
|
||||
Batch size per GPU | 64 | 64 | 32
|
||||
Optimizer | sgd | sgd | sgd
|
||||
|
||||
Configuration used for each model.
|
||||
|
||||
Model | variable_update | local_parameter_device
|
||||
----------- | ---------------------- | ----------------------
|
||||
InceptionV3 | distributed_replicated | n/a
|
||||
ResNet-50 | distributed_replicated | n/a
|
||||
ResNet-152 | distributed_replicated | n/a
|
||||
|
||||
To simplify server setup, EC2 instances (p2.8xlarge) running worker servers also
|
||||
ran parameter servers. Equal numbers of parameter servers and work servers were
|
||||
used with the following exceptions:
|
||||
|
||||
* InceptionV3: 8 instances / 6 parameter servers
|
||||
* ResNet-50: (batch size 32) 8 instances / 4 parameter servers
|
||||
* ResNet-152: 8 instances / 4 parameter servers
|
||||
|
||||
### Results
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:95%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:95%" src="../images/perf_summary_k80_aws_distributed.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:95%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:70%" src="../images/perf_aws_synth_k80_distributed_scaling.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
**Training synthetic data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 | ResNet-50 | ResNet-152
|
||||
---- | ----------- | --------- | ----------
|
||||
1 | 29.7 | 55.0 | 19.8
|
||||
8 | 229 | 410 | 150
|
||||
16 | 459 | 825 | 300
|
||||
32 | 902 | 1468 | 575
|
||||
64 | 1783 | 3051 | 1004
|
||||
|
||||
### Other Results
|
||||
|
||||
<div style="width:95%; margin:auto; margin-bottom:10px; margin-top:20px;">
|
||||
<img style="width:50%" src="../images/perf_aws_synth_k80_multi_server_batch32.png">
|
||||
</div>
|
||||
|
||||
**Training synthetic data**
|
||||
|
||||
GPUs | InceptionV3 (batch size 32) | ResNet-50 (batch size 32)
|
||||
---- | --------------------------- | -------------------------
|
||||
1 | 29.2 | 53.0
|
||||
8 | 219 | 363
|
||||
16 | 427 | 719
|
||||
32 | 820 | 1265
|
||||
64 | 1608 | 2623
|
||||
|
||||
## Appendix
|
||||
|
||||
### Executing benchmark tests
|
||||
|
||||
The code for the benchmarks was created to be both used for benchmarking
|
||||
TensorFlow as well as used as a tool to test hardware platforms. The benchmark
|
||||
code includes modes such as `trivial` that run a virtually empty model that is
|
||||
useful for testing the maximum possibly samples/sec for the input pipeline among
|
||||
other things. Not only does this test TensorFlow but also the throughput of the
|
||||
underlying systems. There are two ways to execute the benchmarks in
|
||||
[tf_cnn_benchmarks.py](TODO: LINK TO GITHUB):
|
||||
|
||||
1. Execute [tf_cnn_benchmarks.py](TODO: LINK TO GITHUB) directly
|
||||
2. Utilize the [small wrapper](TODO: LINK TO GITHUB) that helps pick the
|
||||
correct config
|
||||
|
||||
The wrapper is suggested as a starting point. Then investigate the variety of
|
||||
options available in `tf_cnn_benchmarks.py`. While the wrapper extensive
|
||||
examples, below are a couple highlights.
|
||||
|
||||
Run ResNet-50 on a single instance with 8 GPUs. The `system` argument is used to
|
||||
determine the optimal configuration. The supported values are gce, aws, and
|
||||
dgx1. If `system` is not passeed, the best config for the most widely available
|
||||
hardware is used.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
python main.py --model=resnet50 --num_gpus=8
|
||||
python main.py --system=aws --model=resnet50 --num_gpus=8
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Run ResNet-50 on 2 hosts, e.g. host_0 (10.0.0.1) and host_1 (10.0.0.2), with 8
|
||||
GPUs each on aws.
|
||||
|
||||
```bash
|
||||
# Run the following commands on host_0 (10.0.0.1):
|
||||
$ python main.py --system=aws --model=resnet50 --job_name=worker
|
||||
--hosts=10.0.0.1,10.0.0.2 --task_index=0
|
||||
|
||||
$ python main.py --system=aws --model=resnet50 --job_name=ps
|
||||
--hosts=10.0.0.1,10.0.0.2 --task_index=0
|
||||
|
||||
# Run the following commands on host_1 (10.0.0.2):
|
||||
$ python main.py --system=aws --model=resnet50 --job_name=worker
|
||||
--hosts=10.0.0.1,10.0.0.2 --task_index=1
|
||||
|
||||
$ python main.py --system=aws --model=resnet50 --job_name=ps
|
||||
--hosts=10.0.0.1,10.0.0.2 --task_index=1
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### Methodology
|
||||
|
||||
Unless otherwise stated, each test is run 5 times and then the times are
|
||||
averaged together. GPUs are run in their default state on the given platform.
|
||||
For NVIDIA® Tesla® K80 this means leaving on [GPU
|
||||
Boost](https://devblogs.nvidia.com/parallelforall/increase-performance-gpu-boost-k80-autoboost/)
|
||||
unless it has been turned off by the provider. For a given test, 10 warmup steps
|
||||
are done and then the next 100 steps are averaged.
|
||||
389
tensorflow/docs_src/performance/performance_models.md
Normal file
389
tensorflow/docs_src/performance/performance_models.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,389 @@
|
||||
# High-Performance Models
|
||||
|
||||
TensorFlow is a powerful and flexible machine learning platform.
|
||||
It can be used to distribute model training and inference across a large number
|
||||
of machines and computation devices.
|
||||
|
||||
Its software stack is made of a few layers:
|
||||
|
||||
* a fast and powerful C++ core
|
||||
* low-level Python primitives that sit right above individual kernels
|
||||
* a diverse range of high-level libraries that aim to make building real models
|
||||
easier
|
||||
|
||||
There are many existing examples and tutorials that explain useful features in
|
||||
TensorFlow. The goal of this set of scripts is to demonstrate that we can build
|
||||
flexible and powerful high-performance models using the low-level APIs.
|
||||
In the future, many of the high-performance primitives will be incorporated into
|
||||
high-level APIs, and made available to more users transparently.
|
||||
But meanwhile, we show that it is fairly easy for advanced users to build highly
|
||||
scalable models targeting different system types, network topologies, etc.
|
||||
|
||||
We divide our effort to build high-performance models into three categories:
|
||||
|
||||
1. A fast input pipeline to read data from disk, preprocess it, and make it
|
||||
ready on the GPU.
|
||||
2. A high-throughput model that trains on GPU very efficiently.
|
||||
3. Fast variable and gradients distribution mechanisms that scale well across
|
||||
many machines and computation devices.
|
||||
|
||||
## Input Pipeline
|
||||
|
||||
The input pipeline is the part of a TensorFlow program that reads input data,
|
||||
shuffles it, and preprocesses it.
|
||||
|
||||
Among the most important features to build a fast input pipeline:
|
||||
|
||||
* Avoid using feed-dictionary to feed a large amount of data for each step.
|
||||
* Instead, use reader ops to get data into TensorFlow directly.
|
||||
* Parallelize data processing.
|
||||
* Use software pipelining to feed data, so that data is available immediately
|
||||
when needed.
|
||||
|
||||
One way to implement software pipelining in TensorFlow is through
|
||||
`tf.FifoQueue`, and it is possible to parallelize data processing through
|
||||
`tf.train.queue_runner`, which uses Python threads as its underlying
|
||||
implementation.
|
||||
This lays the foundation for the current Inception input pipeline.
|
||||
This design is well built for feeding older generation of GPUs,
|
||||
but the overhead of Python threads is too large to feed newer GPUs that are four
|
||||
to five times faster.
|
||||
|
||||
In this model, we explore an alternative design that uses the native
|
||||
parallelism in TensorFlow. In our example of an image model input pipeline,
|
||||
there are a few important parts:
|
||||
|
||||
* Choose and read the image files from the disk.
|
||||
* Decode the image data into images, transform and add distortion so they are
|
||||
ready to be used.
|
||||
* Organize the transformed images into a minibatch.
|
||||
* Transfer the images from CPU to GPU, so they are ready for model training.
|
||||
|
||||
It is important to note that the dominant part of each stage can happen in
|
||||
parallel with that of other stages:
|
||||
the file IO uses DMA to transfer the data from hard disk to memory;
|
||||
image decoding, transformation and distortion are CPU-heavy;
|
||||
the data transfer from CPU to GPU uses the GPU's copy-engine unit;
|
||||
and the GPU kernels use the main SMs of the GPU.
|
||||
It is natural to cut our pipeline into those parts so they can run in parallel
|
||||
with each other.
|
||||
|
||||
Also, as mentioned earlier, most of the current input pipeline heavily uses
|
||||
Python threads. However, the large overhead introduced by Python threads
|
||||
severely limits its scalability when the newer GPUs are a lot faster; we can
|
||||
alleviate this by making a single `session.run` call execute all parts of the
|
||||
pipeline.
|
||||
|
||||
### Parallelize IO Reads
|
||||
|
||||
In this new model, we use the native parallelism in TensorFlow: TensorFlow
|
||||
subscribes to an eager-execution model, which means that when nodes in the graph
|
||||
became available, TensorFlow will try to execute as many of them as possible.
|
||||
|
||||
In order to parallelize reading from hard disk, we use `data_flow_ops.RecordInput`
|
||||
in this model.
|
||||
Given a list of input files of TFRecords, `RecordInput` continuously reads
|
||||
records using background threads, placing the records into its own large,
|
||||
internal pool of records.
|
||||
When it is has loaded at least half of its capacity, it produces output tensors.
|
||||
|
||||
Since this op has its internal threads, and is dominated by IO time that doesn’t
|
||||
consume much CPU time, it naturally runs in parallel with the rest of the model.
|
||||
|
||||
### Parallelize Image Processing
|
||||
|
||||
After reading from “RecordInput”, the tensors are passed to the input processing
|
||||
pipeline. For example, if we need to feed 8 GPUs, each with a batch-size of 32,
|
||||
then for each step we do the following.
|
||||
|
||||
First, read 32x8=256 records, and process them individually, in
|
||||
parallel. This starts with 256 independent RecordInput read ops in the graph.
|
||||
|
||||
Then, follow each read with identical set of ops for processing. Each set is
|
||||
considered independent and will execute in parallel. The operations include
|
||||
image decoding, image distortion, and resizing.
|
||||
|
||||
Finally, once the images are ready, they will be concatenated together into 8
|
||||
batch-size 32 tensors.
|
||||
Note that we can use “tf.concat” for this purpose.
|
||||
However, “tf.concat” is implemented as a single op, which waits for all
|
||||
the inputs to be ready, and then concatenates them together. Since all
|
||||
inputs are produced in parallel, there will be a long tail waiting for all
|
||||
inputs to be available; and when concatenation happens, the op becomes memory
|
||||
limited as all input tensors compete for memory bandwidth.
|
||||
So for the final concatenation, we use `tf.parallel_stack` instead. This
|
||||
allocates an uninitialized tensor as an output, and each input tensor is written
|
||||
to its designated portion of the output tensor as soon as the input is
|
||||
available. When all the input tensors are finished, the output tensor is passed
|
||||
along in the graph. This effectively hides all the memory latency with the long
|
||||
tail of producing all the input tensors.
|
||||
|
||||
### Parallelize CPU-to-GPU Data Transfer
|
||||
|
||||
In our example, once all the input images are processed and concatenated
|
||||
together by the CPU, we have 8 tensors, each of which has a batch-size of 32.
|
||||
These tensors are then to be used by the GPU for the model training.
|
||||
|
||||
In TensorFlow, users can use tensors from one device on any other device
|
||||
directly. TensorFlow inserts implicit copies to make the tensors available on
|
||||
any devices where they are used. The runtime schedules the copy between devices
|
||||
to run before the tensors are actually used. However, if the copy cannot finish
|
||||
in time, the computation that needs those tensors will stall.
|
||||
|
||||
For high-performance models, it is helpful to explicitly schedule the copy ahead
|
||||
of the time in parallel, so when the computation starts on GPU, all the tensors
|
||||
are already available on the right device.
|
||||
|
||||
### Software Pipelining
|
||||
|
||||
With all the stages capable of being driven by different processors, we insert
|
||||
`data_flow_ops.StagingArea` in between them so they run in parallel.
|
||||
`StagingArea` is a queue-like operator similar to `tf.FifoQueue`.
|
||||
But it offers simpler functionalities and can be executed on both CPU and GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
Before the model starts running all the stages, we warm up the stages in order
|
||||
so the staging buffers in between all have one set of data in them.
|
||||
During each run step that follows, we will run all the stages.
|
||||
They read one set of data from the staging buffers at the beginning of each
|
||||
stage, and push one set at end end.
|
||||
|
||||
For example: if there are three stages: A, B and C.
|
||||
There are two staging areas in between: S1 and S2.
|
||||
During the warm up, we run:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
Warm up:
|
||||
Step 1: A0
|
||||
Step 2: A1 B0
|
||||
|
||||
Actual execution:
|
||||
Step 3: A2 B1 C0
|
||||
Step 4: A3 B2 C1
|
||||
Step 5: A4 B3 C2
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
After the warm up, S1 and S2 each have one set of data in them.
|
||||
For each step of the actual execution, one set of data is consumed from each
|
||||
staging area, and one set is added to each.
|
||||
|
||||
There are a few nice properties about the scheme:
|
||||
|
||||
* All the stages are non-blocking, since the staging areas always have one set
|
||||
of data after the warm up.
|
||||
* Each stage can run in parallel since they can all start immediately.
|
||||
* The staging buffers have a fixed memory overhead. They will have at most one
|
||||
extra set of data.
|
||||
* Only a single`session.run()` call is needed to run all stages of the step,
|
||||
which makes profiling and debugging much easier.
|
||||
|
||||
## Best Practices in Building High-Performance Models
|
||||
|
||||
The computation on GPU can happen immediately since the input data have already
|
||||
been transferred onto GPU when the step starts.
|
||||
But it is still important to build the model that runs as fast as possible.
|
||||
Here are some tips for a high-performance convolutional neural network (CNN)
|
||||
model:
|
||||
|
||||
### Build the model with both NHWC and NCHW
|
||||
|
||||
Most TensorFlow operations used by a CNN support both NHWC and NCHW data format.
|
||||
On GPU, NCHW is faster.
|
||||
But on CPU, NHWC is sometimes faster.
|
||||
|
||||
So it is a good idea to build the model that can work in both ways.
|
||||
Our model shows a good way to do that effectively.
|
||||
For GPU training, we should always use NCHW.
|
||||
But if the model needs inference on CPU, we could use NHWC; weights obtained
|
||||
from training with NCHW data format can be used for inference in NHWC data
|
||||
format.
|
||||
|
||||
### Use Fused Batch-Normalization
|
||||
|
||||
The default batch-normalization in TensorFlow is implemented as composite
|
||||
operations.
|
||||
This is very general, but often leads to suboptimal performance.
|
||||
An alternative is the fused batch-normalization, and the performance on GPU
|
||||
is often much faster.
|
||||
|
||||
## Variable Distribution and Gradient Aggregation
|
||||
|
||||
During training, training variable values are updated using aggregated gradients
|
||||
and deltas. In this model, we demonstrate that with the flexible and
|
||||
general-purpose TensorFlow primitives, it is fairly easy to build a diverse
|
||||
range of high-performance distribution and aggregation schemes for different
|
||||
types of systems.
|
||||
|
||||
For example:
|
||||
|
||||
* The standard parameter-server where each replica of the training model reads
|
||||
the variables directly, and updates the variable independently. When each
|
||||
model needs the variables, they are copied over through the standard implicit
|
||||
copies added by the TensorFlow runtime. It is shown how to use this method
|
||||
in either local training, distributed synchronous training, and distributed
|
||||
asynchronous training.
|
||||
* A replicated mode for local training where each GPU has an identical
|
||||
copy of the training parameters. The forward and backward computation can
|
||||
start immediately as the variable data is immediately available. Gradients
|
||||
are accumulated across all GPUs, and the aggregated total is applied to
|
||||
each GPU's copy of the variables so that they stay in sync.
|
||||
* A distributed replicated mode of training where each GPU has an identical copy
|
||||
of the training parameters, and a master copy of the variables is stored
|
||||
on the parameter-servers. The forward and backward computation can
|
||||
start immediately as the variable data is immediately available. Gradients
|
||||
are accumulated across all GPUs on each server and then the per-server
|
||||
aggregated gradients are applied to the master copy. After all workers do
|
||||
this, each worker updates its copy of the variable from the master copy.
|
||||
|
||||
We show that most of the variable distribution and aggregation subsystem can
|
||||
be implemented through TensorFlow low-level primitives with manageable
|
||||
complexity at the model level. Here we discuss some more details.
|
||||
|
||||
### Parameter-server Variables
|
||||
|
||||
The most common way trainable variables are managed in TensorFlow models is the
|
||||
parameter server mode.
|
||||
|
||||
In a distributed system, this means that each worker process runs the same
|
||||
model, and parameter server processes own the master copies of the variables.
|
||||
When a worker needs a variable from a parameter server, it refers to it
|
||||
directly. The TensorFlow runtime adds implicit copies to the graph to make the
|
||||
variable value available on the computation device that needs it. When a
|
||||
gradient is computed on a worker, it is sent to the parameter server that owns
|
||||
the particular variable, and the corresponding optimizer is used to update the
|
||||
variable.
|
||||
|
||||
There are some techniques to improve throughput:
|
||||
|
||||
* The variables are spread among parameter servers based on their size, for load
|
||||
balancing.
|
||||
* When each worker has multiple GPUs, gradients are accumulated across the GPUs
|
||||
and a single aggregated gradient is sent to the parameter server. This reduces
|
||||
the network bandwidth and the amount of work done by the parameter servers.
|
||||
|
||||
For coordinating between workers, a very common mode is async updates, where
|
||||
each worker updates the master copy of the variables without synchronizing with
|
||||
other workers. In our model, we demonstrate that it is fairly easy to introduce
|
||||
synchronization across workers so updates for all workers are finished in one
|
||||
step before the next step can start.
|
||||
|
||||
The parameter-server method can also be used for local training, In this case,
|
||||
instead of spreading the master copies of variables across parameters servers,
|
||||
they are either on the CPU or spread across the available GPUs.
|
||||
|
||||
Due to the simple nature of this setup, this architecture has gained a lot of
|
||||
popularity within the community.
|
||||
|
||||
This is available in the benchmark scripts as the 'parameter_server'
|
||||
variable_update mode.
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
width="900" style="max-width: inherit"}
|
||||
|
||||
### Replicated Variables
|
||||
|
||||
In this design, each GPU on the server has its own copy of each variable. The
|
||||
values are kept in sync across GPUs by applying the fully aggregated gradient to
|
||||
each GPU's copy of the variable.
|
||||
|
||||
The variables and data are available at the start of training, so the forward
|
||||
pass of training can start immediately. Gradients are aggregated across the
|
||||
devices and the fully aggregated gradient is then applied to each local copy.
|
||||
|
||||
Gradient aggregation across the server can be done in different ways:
|
||||
|
||||
* Using standard TensorFlow operations to accumulate the total on a single
|
||||
device (CPU or GPU) and then copy it back to all GPUs.
|
||||
* Using NVIDIA NCCL, described below in the NCCL section.
|
||||
|
||||
This is available in the benchmark scripts for local execution only, as the
|
||||
'replicated' variable_update mode.
|
||||
|
||||
### Replicated Variables in Distributed Training
|
||||
|
||||
The replicated method for variables can be extended to distributed training.
|
||||
One way to do this like the replicated mode: aggregate the gradients fully
|
||||
across the cluster and apply them to each local copy of the variable. This may
|
||||
be shown in a future version of this scripts; the scripts do present a different
|
||||
variation, described here.
|
||||
|
||||
In this mode, in addition to each GPU's copy of the variables, a master copy is
|
||||
stored on the parameter servers. As with the replicated mode, training can start
|
||||
immediately using the local copies of the variables.
|
||||
|
||||
As the gradients of the weights become available, they are sent back to the
|
||||
parameter servers and all local copies are updated:
|
||||
|
||||
1. All the gradients from the GPU on the same worker are aggregated together.
|
||||
2. Aggregated gradients from each worker are sent to the parameter server that
|
||||
owns the variable, where the specified optimizer is used to update the
|
||||
master copy of the variable.
|
||||
3. Each worker updates its local copy of the variable from the master. In
|
||||
the example model, this is done with a cross-replica barrier that waits for
|
||||
all the workers to finish updating the variables, and fetches the new
|
||||
variable only after the barrier has been released by all replicas. Once the
|
||||
copy finishes for all variables, this marks the end of a training step, and a
|
||||
new step can start.
|
||||
|
||||
Although this sounds similar to the standard use of parameter servers, the
|
||||
performance is often better in many cases. This is largely due to the fact the
|
||||
computation can happen without any delay, and much of the copy latency of early
|
||||
gradients can be hidden by later computation layers.
|
||||
|
||||
This is available in the benchmark scripts as the 'distributed_replicated'
|
||||
variable_update mode.
|
||||
|
||||
{
|
||||
width="900" style="max-width: inherit"}
|
||||
|
||||
#### NCCL
|
||||
|
||||
In order to broadcast variables and aggregate gradients across different GPUs
|
||||
within the same host machine, we can use the default TensorFlow implicit copy
|
||||
mechanism.
|
||||
|
||||
However, we can instead use the optional NCCL support. NCCL is an NVIDIA
|
||||
library that can efficiently broadcast and aggregate data across different GPUs.
|
||||
It schedules a cooperating kernel on each GPU that knows how to best utilize the
|
||||
underlying hardware topology; this kernel uses a single SM of the GPU.
|
||||
|
||||
In our experiment, we demonstrate that although NCCL often leads to much faster
|
||||
data aggregation by itself, it doesn't necessarily lead to faster training. Our
|
||||
hypothesis is that the implicit copies are essentially free since they go to the
|
||||
copy engine on GPU, as long as its latency can be hidden by the main computation
|
||||
itself. Although NCCL can transfer data faster, it takes one SM away, and adds
|
||||
more pressure to the underlying L2 cache. Our results show that for 8-GPUs,
|
||||
NCCL often leads to better performance. However, for fewer GPUs, the implicit
|
||||
copies often perform better.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Staged Variables
|
||||
|
||||
We further introduce a staged-variable mode where we use staging areas for both
|
||||
the variable reads, and their updates.
|
||||
Similar to software pipelining of the input pipeline, this can hide the data
|
||||
copy latency.
|
||||
If the computation time takes longer than the copy and aggregation, the copy
|
||||
itself becomes essentially free.
|
||||
|
||||
The downside is that all the weights read are from the previous training step.
|
||||
So it is a different algorithm from SGD.
|
||||
But it is possible to improve its convergence by adjusting learning rate and
|
||||
other hyperparameters.
|
||||
|
||||
## Conclusions
|
||||
|
||||
In this high-performance model, we present a number of options to build
|
||||
high-performance models in TensorFlow.
|
||||
Due to the flexible design in TensorFlow, advanced features like this often
|
||||
requires no system-level changes, and can be largely achieved through
|
||||
model-level changes.
|
||||
|
||||
We do not claim which combination works best for a particular model.
|
||||
That should be left to the engineers who build the model and the training system.
|
||||
Many of the ingredients of the high-performance model will find their ways
|
||||
to high-level primitives that become transparent to users.
|
||||
However, we have shown that advanced users can easily tune and modify the
|
||||
underlying model behavior using low-level primitives.
|
||||
This could be very useful when improving performance for particular system
|
||||
setups and model configurations.
|
||||
@ -8,6 +8,7 @@ supervisor.md
|
||||
debugger.md
|
||||
tfdbg-tflearn.md
|
||||
meta_graph.md
|
||||
saved_model_cli.md
|
||||
version_semantics.md
|
||||
data_versions.md
|
||||
faq.md
|
||||
|
||||
251
tensorflow/docs_src/programmers_guide/saved_model_cli.md
Normal file
251
tensorflow/docs_src/programmers_guide/saved_model_cli.md
Normal file
@ -0,0 +1,251 @@
|
||||
# SavedModel CLI (Command-Line Interface)
|
||||
|
||||
[`SavedModel`](https://github.com/tensorflow/tensorflow/blob/master/tensorflow/python/saved_model/README.md)
|
||||
is a universal serialization format for Tensorflow. It provides a
|
||||
language-neutral format to save machine-learned models and enables higher-level
|
||||
systems and tools to produce, consume and transform TensorFlow models.
|
||||
|
||||
We provide SavedModel CLI(command-line interface) as a tool to inspect and
|
||||
execute a [`MetaGraph`](https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/meta_graph)
|
||||
in a SavedModel. You can inspect for example, what
|
||||
[`SignatureDefs`](https://github.com/tensorflow/serving/blob/master/tensorflow_serving/g3doc/signature_defs.md),
|
||||
including their input and output tensors, are in the model without writing any
|
||||
code. This can be useful in situations such as when you want to quickly check
|
||||
your input dtype and shape match with the model. Moreover, if you want to test
|
||||
out the model, it also allows you to do a sanity check by passing in sample
|
||||
inputs in the format of for example, python expressions, and fetch the outputs
|
||||
simply through command line.
|
||||
|
||||
## Get SavedModel CLI
|
||||
|
||||
If TensorFlow is installed on your system through pip, the `saved_model_cli`
|
||||
binary can be invoked directly from command line.
|
||||
|
||||
To build the binary from source, run the following command:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$bazel build tensorflow/python/tools:saved_model_cli
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
## Commands
|
||||
|
||||
SavedModel CLI allows users to both show and run computations on a
|
||||
[`MetaGraphDef`](https://www.tensorflow.org/code/tensorflow/core/protobuf/meta_graph.proto)
|
||||
in a SavedModel. These are done through `show` and `run` commands. We will
|
||||
explain the usages of both commands with detailed examples. SavedModel CLI will
|
||||
also display this information with `-h` option.
|
||||
|
||||
### `show` command
|
||||
|
||||
A SavedModel contains one or more MetaGraphs, identified by their tag-sets. Each
|
||||
MetaGraph contains both a TensorFlow GraphDef as well as associated metadata
|
||||
necessary for running computation in a graph. In order to serve a model, you
|
||||
might wonder what kind of SignatureDefs are in each model, and what are their
|
||||
inputs and outputs etc. The `show` command let you examine the content of the
|
||||
SavedModel in a hierarchical order.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
usage: saved_model_cli show [-h] --dir DIR [--all]
|
||||
[--tag_set TAG_SET] [--signature_def SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
#### Examples
|
||||
|
||||
To show all available MetaGraphDef tag-sets in the SavedModel:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$saved_model_cli show --dir /tmp/saved_model_dir
|
||||
The given SavedModel contains the following tag-sets:
|
||||
serve
|
||||
serve, gpu
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To show all available SignatureDef keys in a MetaGraphDef:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$saved_model_cli show --dir /tmp/saved_model_dir --tag_set serve
|
||||
The given SavedModel MetaGraphDef contains SignatureDefs with the following keys:
|
||||
SignatureDef key: "classify_x2_to_y3"
|
||||
SignatureDef key: "classify_x_to_y"
|
||||
SignatureDef key: "regress_x2_to_y3"
|
||||
SignatureDef key: "regress_x_to_y"
|
||||
SignatureDef key: "regress_x_to_y2"
|
||||
SignatureDef key: "serving_default"
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
For a MetaGraphDef with multiple tags in the tag-set, all tags must be passed
|
||||
in, separated by ',':
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$saved_model_cli show --dir /tmp/saved_model_dir --tag_set serve,gpu
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To show all inputs and outputs TensorInfo for a specific SignatureDef, pass in
|
||||
the SignatureDef key to `signature_def` option. This is very useful when you
|
||||
want to know the tensor key value, dtype and shape of the input tensors for
|
||||
executing the computation graph later.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$saved_model_cli show --dir \
|
||||
/tmp/saved_model_dir --tag_set serve --signature_def serving_default
|
||||
The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following input(s):
|
||||
inputs['x'] tensor_info:
|
||||
dtype: DT_FLOAT
|
||||
shape: (-1, 1)
|
||||
name: x:0
|
||||
The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following output(s):
|
||||
outputs['y'] tensor_info:
|
||||
dtype: DT_FLOAT
|
||||
shape: (-1, 1)
|
||||
name: y:0
|
||||
Method name is: tensorflow/serving/predict
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To show all available information in the SavedModel, use `--all` option:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$saved_model_cli show --dir /tmp/saved_model_dir --all
|
||||
MetaGraphDef with tag-set: 'serve' contains the following SignatureDefs:
|
||||
|
||||
signature_def['classify_x2_to_y3']:
|
||||
The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following input(s):
|
||||
inputs['inputs'] tensor_info:
|
||||
dtype: DT_FLOAT
|
||||
shape: (-1, 1)
|
||||
name: x2:0
|
||||
The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following output(s):
|
||||
outputs['scores'] tensor_info:
|
||||
dtype: DT_FLOAT
|
||||
shape: (-1, 1)
|
||||
name: y3:0
|
||||
Method name is: tensorflow/serving/classify
|
||||
|
||||
...
|
||||
|
||||
signature_def['serving_default']:
|
||||
The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following input(s):
|
||||
inputs['x'] tensor_info:
|
||||
dtype: DT_FLOAT
|
||||
shape: (-1, 1)
|
||||
name: x:0
|
||||
The given SavedModel SignatureDef contains the following output(s):
|
||||
outputs['y'] tensor_info:
|
||||
dtype: DT_FLOAT
|
||||
shape: (-1, 1)
|
||||
name: y:0
|
||||
Method name is: tensorflow/serving/predict
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
### `run` command
|
||||
|
||||
SavedModel CLI also allows you to run a graph computation by passing in inputs,
|
||||
displaying, and saving the outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
usage: saved_model_cli run [-h] --dir DIR --tag_set TAG_SET --signature_def
|
||||
SIGNATURE_DEF_KEY [--inputs INPUTS]
|
||||
[--input_exprs INPUT_EXPRS] [--outdir OUTDIR]
|
||||
[--overwrite] [--tf_debug]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Tensor keys are used to specify which input we are passing in the values for.
|
||||
There are two ways to pass inputs to the model. With '--inputs' option, you can
|
||||
pass in numpy ndarray by files. With '--input_exprs' option, you can use python
|
||||
expressions as inputs.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Input By File
|
||||
|
||||
To pass in inputs by files, use `--inputs` option in the format of
|
||||
`<input_key>=<filename>`, or `<input_key>=<filename>[<variable_name>]`. Each
|
||||
input is separated by semicolon. File specified by `filename` will be loaded
|
||||
using `numpy.load`. Inputs can be loaded from only `.npy`, `.npz` or pickle
|
||||
files. The `variable_name` key is optional depending on the input file type as
|
||||
descripted in more details below.
|
||||
|
||||
When loading from a `.npy` file, which always contains a numpy ndarray, the
|
||||
content will be directly assigned to the specified input tensor. If a
|
||||
`variable_name` is specified, it will be ignored and a warning will be issued.
|
||||
|
||||
When loading from a `.npz` zip file, user can specify which variable within the
|
||||
zip file to load for the input tensor key with `variable_name`. If nothing is
|
||||
specified, SavedModel CLI will check that only one file is included in the zip
|
||||
file and load it for the specified input tensor key.
|
||||
|
||||
When loading from a pickle file, if no `variable_name` is specified in the
|
||||
square brackets, whatever that is inside the pickle file will be passed to the
|
||||
specified input tensor key. Else SavedModel CLI will assume a dictionary is
|
||||
stored in the pickle file and the value corresponding to the variable_name will
|
||||
be used.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Input By Python Expression
|
||||
|
||||
To pass in inputs by python expressions, use `--input_exprs` option. `numpy`
|
||||
module is available as `np`. For example, `input_key=np.ones((32, 32, 3))` or
|
||||
`input_key=[[1], [2], [3]]`. This can be useful for when you don't have data
|
||||
files lying around, but still want to sanity check the model with some simple
|
||||
inputs that match the dtype and shape of the model signature.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Save Output
|
||||
|
||||
By default, SavedModel CLI will print outputs to console. If a directory is
|
||||
passed to `--outdir` option, the outputs will be saved as npy files named after
|
||||
output tensor keys under the given directory. Use `--overwite` to overwrite
|
||||
existing output files.
|
||||
|
||||
#### TensorFlow Debugger (tfdbg) Integration
|
||||
|
||||
If `--tf_debug` option is set, SavedModel CLI will use TensorFlow Debugger
|
||||
(tfdbg) to watch the intermediate Tensors and runtime GraphDefs while running
|
||||
the SavedModel.
|
||||
|
||||
#### Examples
|
||||
|
||||
If we have a simple model that adds `x1` and `x2` to get output `y`, where all
|
||||
tensors are of shape `(-1, 1)`, and we have two `npz` files. File
|
||||
`/tmp/my_data1.npy` contains a numpy ndarray `[[1], [2], [3]]`, file
|
||||
`/tmp/my_data2.npy` contains another numpy ndarray `[[0.5], [0.5], [0.5]]`. Now
|
||||
let's run these two `npy` files through the model to get `y`:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$saved_model_cli run --dir /tmp/saved_model_dir --tag_set serve \
|
||||
--signature_def x1_x2_to_y --inputs x1=/tmp/my_data1.npy;x2=/tmp/my_data2.npy \
|
||||
--outdir /tmp/out
|
||||
Result for output key y:
|
||||
[[ 1.5]
|
||||
[ 2.5]
|
||||
[ 3.5]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
Similarly, we can run input tensors from `npz` file and pickle file, as well as
|
||||
overwrite the previous output file:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$saved_model_cli run --dir /tmp/saved_model_dir --tag_set serve \
|
||||
--signature_def x1_x2_to_y \
|
||||
--inputs x1=/tmp/my_data1.npz[x];x2=/tmp/my_data2.pkl --outdir /tmp/out \
|
||||
--overwrite
|
||||
Result for output key y:
|
||||
[[ 1.5]
|
||||
[ 2.5]
|
||||
[ 3.5]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
You can also use python expression instead of input file. Here we replace input
|
||||
`x2` with a python expression:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$saved_model_cli run --dir /tmp/saved_model_dir --tag_set serve \
|
||||
--signature_def x1_x2_to_y --inputs x1=/tmp/my_data1.npz[x] \
|
||||
--input_exprs 'x2=np.ones((3,1))'
|
||||
Result for output key y:
|
||||
[[ 2]
|
||||
[ 3]
|
||||
[ 4]]
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
To run model with TensorFlow Debugger on:
|
||||
|
||||
```
|
||||
$saved_model_cli run --dir /tmp/saved_model_dir --tag_set serve \
|
||||
--signature_def serving_default --inputs x=/tmp/data.npz[x] --tf_debug
|
||||
```
|
||||
@ -62,7 +62,7 @@ with tf.device("/job:ps/task:7"):
|
||||
v = tf.Variable(...)
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
**N.B.** Operations that mutate a variable, such as
|
||||
**NOTE** Operations that mutate a variable, such as
|
||||
@{tf.Variable.assign} and the parameter
|
||||
update operations in a
|
||||
@{tf.train.Optimizer} *must* run on
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3522,6 +3522,256 @@ func Stage(scope *Scope, values []tf.Output, optional ...StageAttr) (o *tf.Opera
|
||||
return scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Table initializer that takes two tensors for keys and values respectively.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// table_handle: Handle to a table which will be initialized.
|
||||
// keys: Keys of type Tkey.
|
||||
// values: Values of type Tval.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns the created operation.
|
||||
func InitializeTableV2(scope *Scope, table_handle tf.Output, keys tf.Output, values tf.Output) (o *tf.Operation) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "InitializeTableV2",
|
||||
Input: []tf.Input{
|
||||
table_handle, keys, values,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
return scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableHashTableV2Attr is an optional argument to MutableHashTableV2.
|
||||
type MutableHashTableV2Attr func(optionalAttr)
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableHashTableV2Container sets the optional container attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.
|
||||
// Otherwise, a default container is used.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to ""
|
||||
func MutableHashTableV2Container(value string) MutableHashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["container"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableHashTableV2SharedName sets the optional shared_name attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across
|
||||
// multiple sessions.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to ""
|
||||
func MutableHashTableV2SharedName(value string) MutableHashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["shared_name"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableHashTableV2UseNodeNameSharing sets the optional use_node_name_sharing attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: If true and shared_name is empty, the table is shared
|
||||
// using the node name.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to false
|
||||
func MutableHashTableV2UseNodeNameSharing(value bool) MutableHashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["use_node_name_sharing"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Creates an empty hash table.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This op creates a mutable hash table, specifying the type of its keys and
|
||||
// values. Each value must be a scalar. Data can be inserted into the table using
|
||||
// the insert operations. It does not support the initialization operation.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// key_dtype: Type of the table keys.
|
||||
// value_dtype: Type of the table values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns Handle to a table.
|
||||
func MutableHashTableV2(scope *Scope, key_dtype tf.DataType, value_dtype tf.DataType, optional ...MutableHashTableV2Attr) (table_handle tf.Output) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
attrs := map[string]interface{}{"key_dtype": key_dtype, "value_dtype": value_dtype}
|
||||
for _, a := range optional {
|
||||
a(attrs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "MutableHashTableV2",
|
||||
|
||||
Attrs: attrs,
|
||||
}
|
||||
op := scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
return op.Output(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HashTableV2Attr is an optional argument to HashTableV2.
|
||||
type HashTableV2Attr func(optionalAttr)
|
||||
|
||||
// HashTableV2Container sets the optional container attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.
|
||||
// Otherwise, a default container is used.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to ""
|
||||
func HashTableV2Container(value string) HashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["container"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HashTableV2SharedName sets the optional shared_name attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across
|
||||
// multiple sessions.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to ""
|
||||
func HashTableV2SharedName(value string) HashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["shared_name"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// HashTableV2UseNodeNameSharing sets the optional use_node_name_sharing attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: If true and shared_name is empty, the table is shared
|
||||
// using the node name.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to false
|
||||
func HashTableV2UseNodeNameSharing(value bool) HashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["use_node_name_sharing"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Creates a non-initialized hash table.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This op creates a hash table, specifying the type of its keys and values.
|
||||
// Before using the table you will have to initialize it. After initialization the
|
||||
// table will be immutable.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// key_dtype: Type of the table keys.
|
||||
// value_dtype: Type of the table values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns Handle to a table.
|
||||
func HashTableV2(scope *Scope, key_dtype tf.DataType, value_dtype tf.DataType, optional ...HashTableV2Attr) (table_handle tf.Output) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
attrs := map[string]interface{}{"key_dtype": key_dtype, "value_dtype": value_dtype}
|
||||
for _, a := range optional {
|
||||
a(attrs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "HashTableV2",
|
||||
|
||||
Attrs: attrs,
|
||||
}
|
||||
op := scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
return op.Output(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Replaces the contents of the table with the specified keys and values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The tensor `keys` must be of the same type as the keys of the table.
|
||||
// The tensor `values` must be of the type of the table values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// table_handle: Handle to the table.
|
||||
// keys: Any shape. Keys to look up.
|
||||
// values: Values to associate with keys.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns the created operation.
|
||||
func LookupTableImportV2(scope *Scope, table_handle tf.Output, keys tf.Output, values tf.Output) (o *tf.Operation) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "LookupTableImportV2",
|
||||
Input: []tf.Input{
|
||||
table_handle, keys, values,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
return scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Outputs all keys and values in the table.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// table_handle: Handle to the table.
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns Vector of all keys present in the table.Tensor of all values in the table. Indexed in parallel with `keys`.
|
||||
func LookupTableExportV2(scope *Scope, table_handle tf.Output, Tkeys tf.DataType, Tvalues tf.DataType) (keys tf.Output, values tf.Output) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
attrs := map[string]interface{}{"Tkeys": Tkeys, "Tvalues": Tvalues}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "LookupTableExportV2",
|
||||
Input: []tf.Input{
|
||||
table_handle,
|
||||
},
|
||||
Attrs: attrs,
|
||||
}
|
||||
op := scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
return op.Output(0), op.Output(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Updates the table to associates keys with values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The tensor `keys` must be of the same type as the keys of the table.
|
||||
// The tensor `values` must be of the type of the table values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// table_handle: Handle to the table.
|
||||
// keys: Any shape. Keys to look up.
|
||||
// values: Values to associate with keys.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns the created operation.
|
||||
func LookupTableInsertV2(scope *Scope, table_handle tf.Output, keys tf.Output, values tf.Output) (o *tf.Operation) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "LookupTableInsertV2",
|
||||
Input: []tf.Input{
|
||||
table_handle, keys, values,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
return scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Looks up keys in a table, outputs the corresponding values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The tensor `keys` must of the same type as the keys of the table.
|
||||
// The output `values` is of the type of the table values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The scalar `default_value` is the value output for keys not present in the
|
||||
// table. It must also be of the same type as the table values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// table_handle: Handle to the table.
|
||||
// keys: Any shape. Keys to look up.
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns Same shape as `keys`. Values found in the table, or `default_values`
|
||||
// for missing keys.
|
||||
func LookupTableFindV2(scope *Scope, table_handle tf.Output, keys tf.Output, default_value tf.Output) (values tf.Output) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "LookupTableFindV2",
|
||||
Input: []tf.Input{
|
||||
table_handle, keys, default_value,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
op := scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
return op.Output(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// FakeQuantWithMinMaxArgsAttr is an optional argument to FakeQuantWithMinMaxArgs.
|
||||
type FakeQuantWithMinMaxArgsAttr func(optionalAttr)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -7941,17 +8191,17 @@ func SdcaOptimizerAdaptative(value bool) SdcaOptimizerAttr {
|
||||
// uniformly, and the optimizer is learning rate free and enjoys linear convergence
|
||||
// rate.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Proximal Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent, Shalev-Shwartz, Shai; Zhang, Tong.
|
||||
// 2012 arXiv1211.2717S: http://arxiv.org/pdf/1211.2717v1.pdf
|
||||
// [Proximal Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent](http://arxiv.org/pdf/1211.2717v1.pdf).<br>
|
||||
// Shai Shalev-Shwartz, Tong Zhang. 2012
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Loss objective = \sum f_{i}(wx_{i}) + (l2 / 2) * |w|^2 + l1 * |w|
|
||||
// $$Loss Objective = \sum f_{i} (wx_{i}) + (l2 / 2) * |w|^2 + l1 * |w|$$
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Adding vs. Averaging in Distributed Primal-Dual Optimization.
|
||||
// Chenxin Ma, Virginia Smith, Martin Jaggi, Michael I. Jordan, Peter Richtarik,
|
||||
// Martin Takac http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03508
|
||||
// [Adding vs. Averaging in Distributed Primal-Dual Optimization](http://arxiv.org/abs/1502.03508).<br>
|
||||
// Chenxin Ma, Virginia Smith, Martin Jaggi, Michael I. Jordan,
|
||||
// Peter Richtarik, Martin Takac. 2015
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent with Adaptive Probabilities
|
||||
// Dominik Csiba, Zheng Qu, Peter Richtarik https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.08053
|
||||
// [Stochastic Dual Coordinate Ascent with Adaptive Probabilities](https://arxiv.org/abs/1502.08053).<br>
|
||||
// Dominik Csiba, Zheng Qu, Peter Richtarik. 2015
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// sparse_example_indices: a list of vectors which contain example indices.
|
||||
@ -10019,6 +10269,70 @@ func QuantizedRelu(scope *Scope, features tf.Output, min_features tf.Output, max
|
||||
return op.Output(0), op.Output(1), op.Output(2)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InitializeTableFromTextFileV2Attr is an optional argument to InitializeTableFromTextFileV2.
|
||||
type InitializeTableFromTextFileV2Attr func(optionalAttr)
|
||||
|
||||
// InitializeTableFromTextFileV2VocabSize sets the optional vocab_size attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: Number of elements of the file, use -1 if unknown.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to -1
|
||||
//
|
||||
// REQUIRES: value >= -1
|
||||
func InitializeTableFromTextFileV2VocabSize(value int64) InitializeTableFromTextFileV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["vocab_size"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// InitializeTableFromTextFileV2Delimiter sets the optional delimiter attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: Delimiter to separate fields in a line.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to "\t"
|
||||
func InitializeTableFromTextFileV2Delimiter(value string) InitializeTableFromTextFileV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["delimiter"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Initializes a table from a text file.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// It inserts one key-value pair into the table for each line of the file.
|
||||
// The key and value is extracted from the whole line content, elements from the
|
||||
// split line based on `delimiter` or the line number (starting from zero).
|
||||
// Where to extract the key and value from a line is specified by `key_index` and
|
||||
// `value_index`.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// - A value of -1 means use the line number(starting from zero), expects `int64`.
|
||||
// - A value of -2 means use the whole line content, expects `string`.
|
||||
// - A value >= 0 means use the index (starting at zero) of the split line based
|
||||
// on `delimiter`.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// table_handle: Handle to a table which will be initialized.
|
||||
// filename: Filename of a vocabulary text file.
|
||||
// key_index: Column index in a line to get the table `key` values from.
|
||||
// value_index: Column index that represents information of a line to get the table
|
||||
// `value` values from.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns the created operation.
|
||||
func InitializeTableFromTextFileV2(scope *Scope, table_handle tf.Output, filename tf.Output, key_index int64, value_index int64, optional ...InitializeTableFromTextFileV2Attr) (o *tf.Operation) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
attrs := map[string]interface{}{"key_index": key_index, "value_index": value_index}
|
||||
for _, a := range optional {
|
||||
a(attrs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "InitializeTableFromTextFileV2",
|
||||
Input: []tf.Input{
|
||||
table_handle, filename,
|
||||
},
|
||||
Attrs: attrs,
|
||||
}
|
||||
return scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResourceSparseApplyProximalGradientDescentAttr is an optional argument to ResourceSparseApplyProximalGradientDescent.
|
||||
type ResourceSparseApplyProximalGradientDescentAttr func(optionalAttr)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -10875,6 +11189,75 @@ func IFFT2D(scope *Scope, input tf.Output) (output tf.Output) {
|
||||
return op.Output(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2Attr is an optional argument to MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2.
|
||||
type MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2Attr func(optionalAttr)
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2Container sets the optional container attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.
|
||||
// Otherwise, a default container is used.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to ""
|
||||
func MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2Container(value string) MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["container"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2SharedName sets the optional shared_name attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across
|
||||
// multiple sessions.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to ""
|
||||
func MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2SharedName(value string) MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["shared_name"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2UseNodeNameSharing sets the optional use_node_name_sharing attribute to value.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to false
|
||||
func MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2UseNodeNameSharing(value bool) MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["use_node_name_sharing"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2ValueShape sets the optional value_shape attribute to value.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to <>
|
||||
func MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2ValueShape(value tf.Shape) MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["value_shape"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Creates an empty hash table.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This op creates a mutable hash table, specifying the type of its keys and
|
||||
// values. Each value must be a vector. Data can be inserted into the table using
|
||||
// the insert operations. It does not support the initialization operation.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// key_dtype: Type of the table keys.
|
||||
// value_dtype: Type of the table values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns Handle to a table.
|
||||
func MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2(scope *Scope, key_dtype tf.DataType, value_dtype tf.DataType, optional ...MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2Attr) (table_handle tf.Output) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
attrs := map[string]interface{}{"key_dtype": key_dtype, "value_dtype": value_dtype}
|
||||
for _, a := range optional {
|
||||
a(attrs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2",
|
||||
|
||||
Attrs: attrs,
|
||||
}
|
||||
op := scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
return op.Output(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResourceApplyProximalAdagradAttr is an optional argument to ResourceApplyProximalAdagrad.
|
||||
type ResourceApplyProximalAdagradAttr func(optionalAttr)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13270,6 +13653,104 @@ func ReaderReadV2(scope *Scope, reader_handle tf.Output, queue_handle tf.Output)
|
||||
return op.Output(0), op.Output(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableDenseHashTableV2Attr is an optional argument to MutableDenseHashTableV2.
|
||||
type MutableDenseHashTableV2Attr func(optionalAttr)
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableDenseHashTableV2Container sets the optional container attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: If non-empty, this table is placed in the given container.
|
||||
// Otherwise, a default container is used.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to ""
|
||||
func MutableDenseHashTableV2Container(value string) MutableDenseHashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["container"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableDenseHashTableV2SharedName sets the optional shared_name attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: If non-empty, this table is shared under the given name across
|
||||
// multiple sessions.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to ""
|
||||
func MutableDenseHashTableV2SharedName(value string) MutableDenseHashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["shared_name"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableDenseHashTableV2UseNodeNameSharing sets the optional use_node_name_sharing attribute to value.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to false
|
||||
func MutableDenseHashTableV2UseNodeNameSharing(value bool) MutableDenseHashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["use_node_name_sharing"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableDenseHashTableV2ValueShape sets the optional value_shape attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: The shape of each value.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to <>
|
||||
func MutableDenseHashTableV2ValueShape(value tf.Shape) MutableDenseHashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["value_shape"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableDenseHashTableV2InitialNumBuckets sets the optional initial_num_buckets attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: The initial number of hash table buckets. Must be a power
|
||||
// to 2.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to 131072
|
||||
func MutableDenseHashTableV2InitialNumBuckets(value int64) MutableDenseHashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["initial_num_buckets"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// MutableDenseHashTableV2MaxLoadFactor sets the optional max_load_factor attribute to value.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// value: The maximum ratio between number of entries and number of
|
||||
// buckets before growing the table. Must be between 0 and 1.
|
||||
// If not specified, defaults to 0.8
|
||||
func MutableDenseHashTableV2MaxLoadFactor(value float32) MutableDenseHashTableV2Attr {
|
||||
return func(m optionalAttr) {
|
||||
m["max_load_factor"] = value
|
||||
}
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Creates an empty hash table that uses tensors as the backing store. It uses
|
||||
//
|
||||
// "open addressing" with quadratic reprobing to resolve collisions.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// This op creates a mutable hash table, specifying the type of its keys and
|
||||
// values. Each value must be a scalar. Data can be inserted into the table using
|
||||
// the insert operations. It does not support the initialization operation.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// empty_key: The key used to represent empty key buckets internally. Must not
|
||||
// be used in insert or lookup operations.
|
||||
// value_dtype: Type of the table values.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns Handle to a table.
|
||||
func MutableDenseHashTableV2(scope *Scope, empty_key tf.Output, value_dtype tf.DataType, optional ...MutableDenseHashTableV2Attr) (table_handle tf.Output) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
attrs := map[string]interface{}{"value_dtype": value_dtype}
|
||||
for _, a := range optional {
|
||||
a(attrs)
|
||||
}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "MutableDenseHashTableV2",
|
||||
Input: []tf.Input{
|
||||
empty_key,
|
||||
},
|
||||
Attrs: attrs,
|
||||
}
|
||||
op := scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
return op.Output(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// LRNAttr is an optional argument to LRN.
|
||||
type LRNAttr func(optionalAttr)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -13835,9 +14316,9 @@ func SoftsignGrad(scope *Scope, gradients tf.Output, features tf.Output) (backpr
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The polygamma function is defined as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
// \psi^{(n)}(x) = \frac{d^n}{dx^n} \psi(x)
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
//
|
||||
// \\(\psi^{(n)}(x) = \frac{d^n}{dx^n} \psi(x)\\)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// where \\(\psi(x)\\) is the digamma function.
|
||||
func Polygamma(scope *Scope, a tf.Output, x tf.Output) (z tf.Output) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
@ -15059,9 +15540,8 @@ func Any(scope *Scope, input tf.Output, reduction_indices tf.Output, optional ..
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The Hurwitz zeta function is defined as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
// \zeta(x, q) = \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} (q + n)^{-x}
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
//
|
||||
// \\(\zeta(x, q) = \sum_{n=0}^{\infty} (q + n)^{-x}\\)
|
||||
func Zeta(scope *Scope, x tf.Output, q tf.Output) (z tf.Output) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
@ -18239,13 +18719,12 @@ func Pow(scope *Scope, x tf.Output, y tf.Output) (z tf.Output) {
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The upper regularized incomplete Gamma function is defined as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
// Q(a, x) = Gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - P(a, x)
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
// \\(Q(a, x) = Gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - P(a, x)\\)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// where
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
// Gamma(a, x) = int_{x}^{\infty} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
//
|
||||
// \\(Gamma(a, x) = int_{x}^{\infty} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt\\)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// is the upper incomplete Gama function.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note, above `P(a, x)` (`Igamma`) is the lower regularized complete
|
||||
@ -18268,13 +18747,13 @@ func Igammac(scope *Scope, a tf.Output, x tf.Output) (z tf.Output) {
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The lower regularized incomplete Gamma function is defined as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
// P(a, x) = gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - Q(a, x)
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
//
|
||||
// \\(P(a, x) = gamma(a, x) / Gamma(a) = 1 - Q(a, x)\\)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// where
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
// gamma(a, x) = int_{0}^{x} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
//
|
||||
// \\(gamma(a, x) = int_{0}^{x} t^{a-1} exp(-t) dt\\)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// is the lower incomplete Gamma function.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Note, above `Q(a, x)` (`Igammac`) is the upper regularized complete
|
||||
@ -18297,14 +18776,14 @@ func Igamma(scope *Scope, a tf.Output, x tf.Output) (z tf.Output) {
|
||||
//
|
||||
// The regularized incomplete beta integral is defined as:
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
// I_x(a, b) = \frac{B(x; a, b)}{B(a, b)}
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
//
|
||||
// \\(I_x(a, b) = \frac{B(x; a, b)}{B(a, b)}\\)
|
||||
//
|
||||
// where
|
||||
//
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
// B(x; a, b) = \int_0^x t^{a-1} (1 - t)^{b-1} dt
|
||||
// ```
|
||||
//
|
||||
// \\(B(x; a, b) = \int_0^x t^{a-1} (1 - t)^{b-1} dt\\)
|
||||
//
|
||||
//
|
||||
// is the incomplete beta function and \\(B(a, b)\\) is the *complete*
|
||||
// beta function.
|
||||
@ -18744,6 +19223,44 @@ func SparseReshape(scope *Scope, input_indices tf.Output, input_shape tf.Output,
|
||||
return op.Output(0), op.Output(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Bucketizes 'input' based on 'boundaries'.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// For example, if the inputs are
|
||||
// boundaries = [0, 10, 100]
|
||||
// input = [[-5, 10000]
|
||||
// [150, 10]
|
||||
// [5, 100]]
|
||||
//
|
||||
// then the output will be
|
||||
// output = [[0, 3]
|
||||
// [3, 2]
|
||||
// [1, 3]]
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// input: Any shape of Tensor contains with int or float type.
|
||||
// boundaries: A sorted list of floats gives the boundary of the buckets.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns Same shape with 'input', each value of input replaced with bucket index.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// @compatibility(numpy)
|
||||
// Equivalent to np.digitize.
|
||||
// @end_compatibility
|
||||
func Bucketize(scope *Scope, input tf.Output, boundaries []float32) (output tf.Output) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
attrs := map[string]interface{}{"boundaries": boundaries}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "Bucketize",
|
||||
Input: []tf.Input{
|
||||
input,
|
||||
},
|
||||
Attrs: attrs,
|
||||
}
|
||||
op := scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
return op.Output(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes the product along segments of a tensor.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Read @{$math_ops#segmentation$the section on segmentation} for an explanation of
|
||||
@ -20516,6 +21033,26 @@ func SoftmaxCrossEntropyWithLogits(scope *Scope, features tf.Output, labels tf.O
|
||||
return op.Output(0), op.Output(1)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// Computes the number of elements in the given table.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Arguments:
|
||||
// table_handle: Handle to the table.
|
||||
//
|
||||
// Returns Scalar that contains number of elements in the table.
|
||||
func LookupTableSizeV2(scope *Scope, table_handle tf.Output) (size tf.Output) {
|
||||
if scope.Err() != nil {
|
||||
return
|
||||
}
|
||||
opspec := tf.OpSpec{
|
||||
Type: "LookupTableSizeV2",
|
||||
Input: []tf.Input{
|
||||
table_handle,
|
||||
},
|
||||
}
|
||||
op := scope.AddOperation(opspec)
|
||||
return op.Output(0)
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
// ResizeBilinearGradAttr is an optional argument to ResizeBilinearGrad.
|
||||
type ResizeBilinearGradAttr func(optionalAttr)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -328,7 +328,7 @@ class OpDefLibrary(object):
|
||||
# Need to flatten all the arguments into a list.
|
||||
# pylint: disable=protected-access
|
||||
g = ops._get_graph_from_inputs(_Flatten(keywords.values()))
|
||||
# pyline: enable=protected-access
|
||||
# pylint: enable=protected-access
|
||||
except AssertionError as e:
|
||||
raise RuntimeError(
|
||||
"Cannot determine graph for Op '%s' due to: %s"
|
||||
|
||||
@ -3981,9 +3981,13 @@ class GraphKeys(object):
|
||||
for more details.
|
||||
* `REGULARIZATION_LOSSES`: regularization losses collected during graph
|
||||
construction.
|
||||
* `WEIGHTS`: weights inside neural network layers
|
||||
* `BIASES`: biases inside neural network layers
|
||||
* `ACTIVATIONS`: activations of neural network layers
|
||||
|
||||
The following standard keys are _defined_, but their collections are **not**
|
||||
automatically populated as many of the others are:
|
||||
|
||||
* `WEIGHTS`
|
||||
* `BIASES`
|
||||
* `ACTIVATIONS`
|
||||
"""
|
||||
|
||||
# Key to collect Variable objects that are global (shared across machines).
|
||||
|
||||
@ -629,10 +629,10 @@ static string GetPythonOp(const OpDef& op_def, bool is_hidden, string op_name) {
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
void GenerateLowerCaseOpName(const string& str, string* result) {
|
||||
char joiner = '_';
|
||||
int last_index = str.size() - 1;
|
||||
const char joiner = '_';
|
||||
const int last_index = str.size() - 1;
|
||||
for (int i = 0; i <= last_index; ++i) {
|
||||
char c = str[i];
|
||||
const char c = str[i];
|
||||
// Emit a joiner only if a previous-lower-to-now-upper or a
|
||||
// now-upper-to-next-lower transition happens.
|
||||
if (isupper(c) && (i > 0)) {
|
||||
@ -731,8 +731,8 @@ void PrintPythonOps(const OpList& ops, const std::vector<string>& hidden_ops,
|
||||
printf("%s", GetPythonOps(ops, hidden_ops, require_shapes).c_str());
|
||||
}
|
||||
|
||||
string GetPythonWrappers(const char* op_wrapper_buf, size_t op_wrapper_len) {
|
||||
string op_list_str(op_wrapper_buf, op_wrapper_len);
|
||||
string GetPythonWrappers(const char* op_list_buf, size_t op_list_len) {
|
||||
string op_list_str(op_list_buf, op_list_len);
|
||||
OpList ops;
|
||||
ops.ParseFromString(op_list_str);
|
||||
return GetPythonOps(ops, {}, false);
|
||||
|
||||
@ -33,9 +33,10 @@ string GetPythonOps(const OpList& ops, const std::vector<string>& hidden_ops,
|
||||
bool require_shapes);
|
||||
|
||||
// Get the python wrappers for a list of ops in a OpList.
|
||||
// buf should be a pointer to a buffer containing the binary encoded OpList
|
||||
// proto, and len should be the length of that buffer.
|
||||
string GetPythonWrappers(const char* op_wrapper_buf, size_t op_wrapper_len);
|
||||
// `op_list_buf` should be a pointer to a buffer containing
|
||||
// the binary encoded OpList proto, and `op_list_len` should be the
|
||||
// length of that buffer.
|
||||
string GetPythonWrappers(const char* op_list_buf, size_t op_list_len);
|
||||
|
||||
} // namespace tensorflow
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -25,7 +25,7 @@ limitations under the License.
|
||||
// going from python bytes to const char* tries to decode the
|
||||
// contents from utf-8 to unicode for Python version >= 3, but
|
||||
// we want the bytes to be uninterpreted.
|
||||
%typemap(in) (const char* op_wrapper_buf, size_t op_wrapper_len) {
|
||||
%typemap(in) (const char* op_list_buf, size_t op_list_len) {
|
||||
char* c_string;
|
||||
Py_ssize_t py_size;
|
||||
if (PyBytes_AsStringAndSize($input, &c_string, &py_size) == -1) {
|
||||
|
||||
@ -2569,6 +2569,18 @@ tf_py_test(
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
tf_py_test(
|
||||
name = "bucketize_op_test",
|
||||
size = "small",
|
||||
srcs = ["bucketize_op_test.py"],
|
||||
additional_deps = [
|
||||
"//third_party/py/numpy",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:client_testlib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:framework_for_generated_wrappers",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:math_ops",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
filegroup(
|
||||
name = "all_files",
|
||||
srcs = glob(
|
||||
|
||||
@ -12,35 +12,57 @@
|
||||
# See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
|
||||
# limitations under the License.
|
||||
# ==============================================================================
|
||||
"""Tests for bucketization_op."""
|
||||
"""Tests for bucketize_op."""
|
||||
|
||||
from __future__ import absolute_import
|
||||
from __future__ import division
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.layers.python.ops import bucketization_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import errors_impl
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import test
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class BucketizationOpTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def test_normal_usecase(self):
|
||||
op = bucketization_op.bucketize(
|
||||
def testInt(self):
|
||||
op = math_ops._bucketize(
|
||||
constant_op.constant([-5, 0, 2, 3, 5, 8, 10, 11, 12]),
|
||||
boundaries=[0, 3, 8, 11])
|
||||
expected_out = [0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4]
|
||||
with self.test_session() as sess:
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(expected_out, sess.run(op))
|
||||
|
||||
def test_invalid_boundaries_order(self):
|
||||
op = bucketization_op.bucketize(
|
||||
def testFloat(self):
|
||||
op = math_ops._bucketize(
|
||||
constant_op.constant([-5., 0., 2., 3., 5., 8., 10., 11., 12.]),
|
||||
boundaries=[0., 3., 8., 11.])
|
||||
expected_out = [0, 1, 1, 2, 2, 3, 3, 4, 4]
|
||||
with self.test_session() as sess:
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(expected_out, sess.run(op))
|
||||
|
||||
def test2DInput(self):
|
||||
op = math_ops._bucketize(
|
||||
constant_op.constant([[-5, 0, 2, 3, 5], [8, 10, 11, 12, 0]]),
|
||||
boundaries=[0, 3, 8, 11])
|
||||
expected_out = [[0, 1, 1, 2, 2], [3, 3, 4, 4, 1]]
|
||||
with self.test_session() as sess:
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(expected_out, sess.run(op))
|
||||
|
||||
def testInvalidBoundariesOrder(self):
|
||||
op = math_ops._bucketize(
|
||||
constant_op.constant([-5, 0]), boundaries=[0, 8, 3, 11])
|
||||
with self.test_session() as sess:
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(errors_impl.InvalidArgumentError):
|
||||
with self.assertRaisesRegexp(
|
||||
errors_impl.InvalidArgumentError, "Expected sorted boundaries"):
|
||||
sess.run(op)
|
||||
|
||||
def testBoundariesNotList(self):
|
||||
with self.assertRaisesRegexp(
|
||||
TypeError, "Expected list for attr boundaries"):
|
||||
math_ops._bucketize(constant_op.constant([-5, 0]), boundaries=0)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
test.main()
|
||||
@ -29,6 +29,52 @@ cuda_py_test(
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
cuda_py_test(
|
||||
name = "kullback_leibler_test",
|
||||
size = "small",
|
||||
srcs = ["kullback_leibler_test.py"],
|
||||
additional_deps = [
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python/ops/distributions",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:array_ops",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:client_testlib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:platform_test",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
cuda_py_test(
|
||||
name = "normal_test",
|
||||
size = "medium",
|
||||
srcs = ["normal_test.py"],
|
||||
additional_deps = [
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python/ops/distributions",
|
||||
"//third_party/py/numpy",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:array_ops",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:client_testlib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:framework_for_generated_wrappers",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:framework_test_lib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:gradients",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:nn_ops",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:platform_test",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:variables",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
cuda_py_test(
|
||||
name = "special_math_test",
|
||||
size = "medium",
|
||||
srcs = ["special_math_test.py"],
|
||||
additional_deps = [
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python/ops/distributions",
|
||||
"//third_party/py/numpy",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:client_testlib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:framework_for_generated_wrappers",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:framework_test_lib",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:gradients",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:platform_test",
|
||||
"//tensorflow/python:variables",
|
||||
],
|
||||
)
|
||||
|
||||
filegroup(
|
||||
name = "all_files",
|
||||
srcs = glob(
|
||||
|
||||
@ -18,9 +18,9 @@ from __future__ import absolute_import
|
||||
from __future__ import division
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import normal
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import normal
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import test
|
||||
|
||||
# pylint: disable=protected-access
|
||||
@ -43,7 +43,7 @@ class KLTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
return name
|
||||
|
||||
a = MyDist(loc=0.0, scale=1.0)
|
||||
self.assertEqual("OK", kullback_leibler.kl(a, a, name="OK"))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("OK", kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(a, a, name="OK"))
|
||||
|
||||
def testDomainErrorExceptions(self):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -60,11 +60,11 @@ class KLTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
a = MyDistException(loc=0.0, scale=1.0)
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl(a, a, allow_nan_stats=False)
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(a, a, allow_nan_stats=False)
|
||||
with self.assertRaisesOpError(
|
||||
"KL calculation between .* and .* returned NaN values"):
|
||||
kl.eval()
|
||||
kl_ok = kullback_leibler.kl(a, a)
|
||||
kl_ok = kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(a, a)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual([float("nan")], kl_ok.eval())
|
||||
|
||||
def testRegistrationFailures(self):
|
||||
@ -116,16 +116,16 @@ class KLTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
sub2 = Sub2(loc=0.0, scale=1.0)
|
||||
sub11 = Sub11(loc=0.0, scale=1.0)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-1", kullback_leibler.kl(sub1, sub1))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-2", kullback_leibler.kl(sub1, sub2))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub2-1", kullback_leibler.kl(sub2, sub1))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-1", kullback_leibler.kl(sub11, sub11))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-1", kullback_leibler.kl(sub11, sub1))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-2", kullback_leibler.kl(sub11, sub2))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-1", kullback_leibler.kl(sub11, sub1))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-2", kullback_leibler.kl(sub11, sub2))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub2-1", kullback_leibler.kl(sub2, sub11))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-1", kullback_leibler.kl(sub1, sub11))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-1", kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(sub1, sub1))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-2", kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(sub1, sub2))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub2-1", kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(sub2, sub1))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-1", kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(sub11, sub11))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-1", kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(sub11, sub1))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-2", kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(sub11, sub2))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-1", kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(sub11, sub1))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-2", kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(sub11, sub2))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub2-1", kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(sub2, sub11))
|
||||
self.assertEqual("sub1-1", kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(sub1, sub11))
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
if __name__ == "__main__":
|
||||
@ -18,13 +18,11 @@ from __future__ import absolute_import
|
||||
from __future__ import division
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
import importlib
|
||||
import math
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from scipy import stats
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import normal as normal_lib
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
@ -33,7 +31,21 @@ from tensorflow.python.ops import array_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import gradients_impl
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import variables
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import normal as normal_lib
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import test
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import tf_logging
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def try_import(name): # pylint: disable=invalid-name
|
||||
module = None
|
||||
try:
|
||||
module = importlib.import_module(name)
|
||||
except ImportError as e:
|
||||
tf_logging.warning("Could not import %s: %s" % (name, str(e)))
|
||||
return module
|
||||
|
||||
stats = try_import("scipy.stats")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
@ -90,10 +102,8 @@ class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
sigma = constant_op.constant([math.sqrt(10.0)] * batch_size)
|
||||
x = np.array([-2.5, 2.5, 4.0, 0.0, -1.0, 2.0], dtype=np.float32)
|
||||
normal = normal_lib.Normal(loc=mu, scale=sigma)
|
||||
expected_log_pdf = stats.norm(mu.eval(), sigma.eval()).logpdf(x)
|
||||
|
||||
log_pdf = normal.log_prob(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_log_pdf, log_pdf.eval())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(),
|
||||
log_pdf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(),
|
||||
@ -102,12 +112,17 @@ class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, log_pdf.eval().shape)
|
||||
|
||||
pdf = normal.prob(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(np.exp(expected_log_pdf), pdf.eval())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), pdf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), pdf.eval().shape)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, pdf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, pdf.eval().shape)
|
||||
|
||||
if not stats:
|
||||
return
|
||||
expected_log_pdf = stats.norm(mu.eval(), sigma.eval()).logpdf(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_log_pdf, log_pdf.eval())
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(np.exp(expected_log_pdf), pdf.eval())
|
||||
|
||||
def testNormalLogPDFMultidimensional(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
batch_size = 6
|
||||
@ -116,12 +131,10 @@ class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
batch_size)
|
||||
x = np.array([[-2.5, 2.5, 4.0, 0.0, -1.0, 2.0]], dtype=np.float32).T
|
||||
normal = normal_lib.Normal(loc=mu, scale=sigma)
|
||||
expected_log_pdf = stats.norm(mu.eval(), sigma.eval()).logpdf(x)
|
||||
|
||||
log_pdf = normal.log_prob(x)
|
||||
log_pdf_values = log_pdf.eval()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(log_pdf.get_shape(), (6, 2))
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_log_pdf, log_pdf_values)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(),
|
||||
log_pdf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(),
|
||||
@ -132,12 +145,17 @@ class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
pdf = normal.prob(x)
|
||||
pdf_values = pdf.eval()
|
||||
self.assertEqual(pdf.get_shape(), (6, 2))
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(np.exp(expected_log_pdf), pdf_values)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), pdf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), pdf_values.shape)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, pdf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, pdf_values.shape)
|
||||
|
||||
if not stats:
|
||||
return
|
||||
expected_log_pdf = stats.norm(mu.eval(), sigma.eval()).logpdf(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_log_pdf, log_pdf_values)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(np.exp(expected_log_pdf), pdf_values)
|
||||
|
||||
def testNormalCDF(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
batch_size = 50
|
||||
@ -146,14 +164,15 @@ class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
x = np.linspace(-8.0, 8.0, batch_size).astype(np.float64)
|
||||
|
||||
normal = normal_lib.Normal(loc=mu, scale=sigma)
|
||||
expected_cdf = stats.norm(mu, sigma).cdf(x)
|
||||
|
||||
cdf = normal.cdf(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_cdf, cdf.eval(), atol=0)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), cdf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), cdf.eval().shape)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, cdf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, cdf.eval().shape)
|
||||
if not stats:
|
||||
return
|
||||
expected_cdf = stats.norm(mu, sigma).cdf(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_cdf, cdf.eval(), atol=0)
|
||||
|
||||
def testNormalSurvivalFunction(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
@ -163,14 +182,16 @@ class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
x = np.linspace(-8.0, 8.0, batch_size).astype(np.float64)
|
||||
|
||||
normal = normal_lib.Normal(loc=mu, scale=sigma)
|
||||
expected_sf = stats.norm(mu, sigma).sf(x)
|
||||
|
||||
sf = normal.survival_function(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_sf, sf.eval(), atol=0)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), sf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), sf.eval().shape)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, sf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, sf.eval().shape)
|
||||
if not stats:
|
||||
return
|
||||
expected_sf = stats.norm(mu, sigma).sf(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_sf, sf.eval(), atol=0)
|
||||
|
||||
def testNormalLogCDF(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
@ -180,15 +201,18 @@ class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
x = np.linspace(-100.0, 10.0, batch_size).astype(np.float64)
|
||||
|
||||
normal = normal_lib.Normal(loc=mu, scale=sigma)
|
||||
expected_cdf = stats.norm(mu, sigma).logcdf(x)
|
||||
|
||||
cdf = normal.log_cdf(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_cdf, cdf.eval(), atol=0, rtol=1e-5)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), cdf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), cdf.eval().shape)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, cdf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, cdf.eval().shape)
|
||||
|
||||
if not stats:
|
||||
return
|
||||
expected_cdf = stats.norm(mu, sigma).logcdf(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_cdf, cdf.eval(), atol=0, rtol=1e-5)
|
||||
|
||||
def testFiniteGradientAtDifficultPoints(self):
|
||||
for dtype in [np.float32, np.float64]:
|
||||
g = ops.Graph()
|
||||
@ -217,15 +241,18 @@ class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
x = np.linspace(-10.0, 100.0, batch_size).astype(np.float64)
|
||||
|
||||
normal = normal_lib.Normal(loc=mu, scale=sigma)
|
||||
expected_sf = stats.norm(mu, sigma).logsf(x)
|
||||
|
||||
sf = normal.log_survival_function(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_sf, sf.eval(), atol=0, rtol=1e-5)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), sf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), sf.eval().shape)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, sf.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, sf.eval().shape)
|
||||
|
||||
if not stats:
|
||||
return
|
||||
expected_sf = stats.norm(mu, sigma).logsf(x)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_sf, sf.eval(), atol=0, rtol=1e-5)
|
||||
|
||||
def testNormalEntropyWithScalarInputs(self):
|
||||
# Scipy.stats.norm cannot deal with the shapes in the other test.
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
@ -233,16 +260,18 @@ class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
sigma_v = 4.56
|
||||
normal = normal_lib.Normal(loc=mu_v, scale=sigma_v)
|
||||
|
||||
# scipy.stats.norm cannot deal with these shapes.
|
||||
expected_entropy = stats.norm(mu_v, sigma_v).entropy()
|
||||
entropy = normal.entropy()
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_entropy, entropy.eval())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(),
|
||||
entropy.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(),
|
||||
entropy.eval().shape)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, entropy.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, entropy.eval().shape)
|
||||
# scipy.stats.norm cannot deal with these shapes.
|
||||
if not stats:
|
||||
return
|
||||
expected_entropy = stats.norm(mu_v, sigma_v).entropy()
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_entropy, entropy.eval())
|
||||
|
||||
def testNormalEntropy(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
@ -288,15 +317,18 @@ class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
p = np.hstack((p, np.exp(-33), 1. - np.exp(-33)))
|
||||
|
||||
normal = normal_lib.Normal(loc=mu, scale=sigma)
|
||||
expected_x = stats.norm(mu, sigma).ppf(p)
|
||||
x = normal.quantile(p)
|
||||
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_x, x.eval(), atol=0.)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), x.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape_tensor().eval(), x.eval().shape)
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, x.get_shape())
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual(normal.batch_shape, x.eval().shape)
|
||||
|
||||
if not stats:
|
||||
return
|
||||
expected_x = stats.norm(mu, sigma).ppf(p)
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(expected_x, x.eval(), atol=0.)
|
||||
|
||||
def _baseQuantileFiniteGradientAtDifficultPoints(self, dtype):
|
||||
g = ops.Graph()
|
||||
with g.as_default():
|
||||
@ -450,7 +482,7 @@ class NormalTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
n_a = normal_lib.Normal(loc=mu_a, scale=sigma_a)
|
||||
n_b = normal_lib.Normal(loc=mu_b, scale=sigma_b)
|
||||
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl(n_a, n_b)
|
||||
kl = kullback_leibler.kl_divergence(n_a, n_b)
|
||||
kl_val = sess.run(kl)
|
||||
|
||||
kl_expected = ((mu_a - mu_b)**2 / (2 * sigma_b**2) + 0.5 * (
|
||||
@ -19,18 +19,30 @@ from __future__ import division
|
||||
from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
import collections
|
||||
import importlib
|
||||
|
||||
import numpy as np
|
||||
from scipy import special
|
||||
from scipy import stats
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import special_math
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import gradient_checker
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import gradients_impl
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import variables
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import special_math
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import test
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import tf_logging
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def try_import(name): # pylint: disable=invalid-name
|
||||
module = None
|
||||
try:
|
||||
module = importlib.import_module(name)
|
||||
except ImportError as e:
|
||||
tf_logging.warning("Could not import %s: %s" % (name, str(e)))
|
||||
return module
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
special = try_import("scipy.special")
|
||||
stats = try_import("scipy.stats")
|
||||
sm = special_math
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -66,6 +78,9 @@ class NdtriTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
def testNdtri(self):
|
||||
"""Verifies that ndtri computation is correct."""
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
if not special:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
p = np.linspace(0., 1.0, 50).astype(np.float64)
|
||||
# Quantile performs piecewise rational approximation so adding some
|
||||
# special input values to make sure we hit all the pieces.
|
||||
@ -113,6 +128,9 @@ class NdtrTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
self._test_grid_no_log(dtype, grid_spec, error_spec)
|
||||
|
||||
def _test_grid_log(self, dtype, grid_spec, error_spec):
|
||||
if not special:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
grid = _make_grid(dtype, grid_spec)
|
||||
actual = sm.log_ndtr(grid).eval()
|
||||
@ -137,6 +155,9 @@ class NdtrTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
atol=error_spec.atol)
|
||||
|
||||
def _test_grid_no_log(self, dtype, grid_spec, error_spec):
|
||||
if not special:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
grid = _make_grid(dtype, grid_spec)
|
||||
actual = sm.ndtr(grid).eval()
|
||||
@ -267,6 +288,9 @@ class NdtrGradientTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
self.assert_all_true(np.isfinite(grad_eval))
|
||||
|
||||
# Versus scipy.
|
||||
if not (special and stats):
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
expected = stats.norm.pdf(raw_grid)
|
||||
if self._use_log:
|
||||
expected /= special.ndtr(raw_grid)
|
||||
@ -323,6 +347,9 @@ class LogCDFLaplaceTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
_check_strictly_increasing(actual)
|
||||
|
||||
# Versus scipy.
|
||||
if not stats:
|
||||
return
|
||||
|
||||
scipy_dist = stats.laplace(loc=0., scale=1.)
|
||||
expected = scipy_dist.logcdf(grid.astype(scipy_dtype))
|
||||
self.assertAllClose(
|
||||
@ -1128,7 +1128,7 @@ class TensorArrayTest(test.TestCase):
|
||||
dtype=dtypes.float32, size=0, dynamic_size=False, infer_shape=True)
|
||||
self.assertEqual(0, ta.size().eval())
|
||||
# Don't actually perform the pack. This stores the static shape.
|
||||
ta.unstack(array_ops.zeros([0, 3, 5]))
|
||||
ta.unstack(array_ops.zeros([0, 3, 5])).mark_used()
|
||||
packed = ta.stack()
|
||||
self.assertAllEqual([0, 3, 5], packed.eval().shape)
|
||||
# Concatenating zero tensors along their first dimension gives a
|
||||
|
||||
@ -71,7 +71,9 @@ from tensorflow.python.ops import tensor_array_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.gen_control_flow_ops import *
|
||||
# pylint: enable=wildcard-import
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.platform import tf_logging as logging
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.util import deprecation
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.util import nest
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.util import tf_should_use
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
# We override the 'tuple' for a control flow op, so we keep python's
|
||||
@ -84,6 +86,7 @@ _basetuple = tuple
|
||||
|
||||
# Assert and Print are special symbols in python, so we must
|
||||
# use an upper-case version of them.
|
||||
@tf_should_use.should_use_result
|
||||
def Assert(condition, data, summarize=None, name=None):
|
||||
"""Asserts that the given condition is true.
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1677,14 +1680,20 @@ def _UnpackIfSingleton(res):
|
||||
return res
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def cond(pred, fn1, fn2, strict=False, name=None):
|
||||
"""Return either `fn1()` or `fn2()` based on the boolean predicate `pred`.
|
||||
# pylint: disable=g-doc-args
|
||||
@deprecation.deprecated_args(
|
||||
None,
|
||||
"fn1/fn2 are deprecated in favor of the true_fn/false_fn arguments.",
|
||||
"fn1", "fn2")
|
||||
def cond(pred, true_fn=None, false_fn=None, strict=False, name=None,
|
||||
fn1=None, fn2=None):
|
||||
"""Return `true_fn()` if the predicate `pred` is true else `false_fn()`.
|
||||
|
||||
`fn1` and `fn2` both return lists of output tensors. `fn1` and `fn2` must have
|
||||
the same non-zero number and type of outputs.
|
||||
`true_fn` and `false_fn` both return lists of output tensors. `true_fn` and
|
||||
`false_fn` must have the same non-zero number and type of outputs.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that the conditional execution applies only to the operations defined in
|
||||
`fn1` and `fn2`. Consider the following simple program:
|
||||
`true_fn` and `false_fn`. Consider the following simple program:
|
||||
|
||||
```python
|
||||
z = tf.multiply(a, b)
|
||||
@ -1698,28 +1707,35 @@ def cond(pred, fn1, fn2, strict=False, name=None):
|
||||
Although this behavior is consistent with the dataflow model of TensorFlow,
|
||||
it has occasionally surprised some users who expected a lazier semantics.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that `cond` calls `true_fn` and `false_fn` *exactly once* (inside the
|
||||
call to `cond`, and not at all during `Session.run()`). `cond`
|
||||
stitches together the graph fragments created during the `true_fn` and
|
||||
`false_fn` calls with some additional graph nodes to ensure that the right
|
||||
branch gets executed depending on the value of `pred`.
|
||||
|
||||
`tf.cond` supports nested structures as implemented in
|
||||
`tensorflow.python.util.nest`. Both `fn1` and `fn2` must return the same
|
||||
(possibly nested) value structure of lists, tuples, and/or named tuples.
|
||||
`tensorflow.python.util.nest`. Both `true_fn` and `false_fn` must return the
|
||||
same (possibly nested) value structure of lists, tuples, and/or named tuples.
|
||||
Singleton lists and tuples form the only exceptions to this: when returned by
|
||||
`fn1` and/or `fn2`, they are implicitly unpacked to single values. This
|
||||
behavior is disabled by passing `strict=True`.
|
||||
`true_fn` and/or `false_fn`, they are implicitly unpacked to single values.
|
||||
This behavior is disabled by passing `strict=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
pred: A scalar determining whether to return the result of `fn1` or `fn2`.
|
||||
fn1: The callable to be performed if pred is true.
|
||||
fn2: The callable to be performed if pred is false.
|
||||
pred: A scalar determining whether to return the result of `true_fn` or
|
||||
`false_fn`.
|
||||
true_fn: The callable to be performed if pred is true.
|
||||
false_fn: The callable to be performed if pred is false.
|
||||
strict: A boolean that enables/disables 'strict' mode; see above.
|
||||
name: Optional name prefix for the returned tensors.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
Tensors returned by the call to either `fn1` or `fn2`. If the callables
|
||||
return a singleton list, the element is extracted from the list.
|
||||
Tensors returned by the call to either `true_fn` or `false_fn`. If the
|
||||
callables return a singleton list, the element is extracted from the list.
|
||||
|
||||
Raises:
|
||||
TypeError: if `fn1` or `fn2` is not callable.
|
||||
ValueError: if `fn1` and `fn2` do not return the same number of tensors, or
|
||||
return tensors of different types.
|
||||
TypeError: if `true_fn` or `false_fn` is not callable.
|
||||
ValueError: if `true_fn` and `false_fn` do not return the same number of
|
||||
tensors, or return tensors of different types.
|
||||
|
||||
Example:
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1734,12 +1750,30 @@ def cond(pred, fn1, fn2, strict=False, name=None):
|
||||
```
|
||||
|
||||
"""
|
||||
with ops.name_scope(name, "cond", [pred]) as name:
|
||||
if not callable(fn1):
|
||||
raise TypeError("fn1 must be callable.")
|
||||
if not callable(fn2):
|
||||
raise TypeError("fn2 must be callable.")
|
||||
# We needed to make true_fn/false_fn keyword arguments for
|
||||
# backwards-compatibility. This check exists so that we can convert back to
|
||||
# having them be positional arguments.
|
||||
# TODO(josh11b): Make `true_fn` and `false_fn` positional arguments after
|
||||
# `fn1` and `fn2` are deleted.
|
||||
if fn1 is not None:
|
||||
if true_fn is not None:
|
||||
raise TypeError("cond(): true_fn and fn1 may not be set simultaneously.")
|
||||
true_fn = fn1
|
||||
elif true_fn is None:
|
||||
raise TypeError("cond(): true_fn argument required")
|
||||
if fn2 is not None:
|
||||
if false_fn is not None:
|
||||
raise TypeError("cond(): false_fn and fn2 may not be set simultaneously.")
|
||||
false_fn = fn2
|
||||
elif false_fn is None:
|
||||
raise TypeError("cond(): false_fn argument required")
|
||||
|
||||
if not callable(true_fn):
|
||||
raise TypeError("true_fn must be callable.")
|
||||
if not callable(false_fn):
|
||||
raise TypeError("false_fn must be callable.")
|
||||
|
||||
with ops.name_scope(name, "cond", [pred]) as name:
|
||||
# Add the Switch to the graph.
|
||||
if isinstance(pred, bool):
|
||||
raise TypeError("pred must not be a Python bool")
|
||||
@ -1754,18 +1788,18 @@ def cond(pred, fn1, fn2, strict=False, name=None):
|
||||
# Build the graph for the true branch in a new context.
|
||||
context_t = CondContext(pred, pivot_1, branch=1)
|
||||
context_t.Enter()
|
||||
orig_res_t, res_t = context_t.BuildCondBranch(fn1)
|
||||
orig_res_t, res_t = context_t.BuildCondBranch(true_fn)
|
||||
if orig_res_t is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("fn1 must have a return value.")
|
||||
raise ValueError("true_fn must have a return value.")
|
||||
context_t.ExitResult(res_t)
|
||||
context_t.Exit()
|
||||
|
||||
# Build the graph for the false branch in a new context.
|
||||
context_f = CondContext(pred, pivot_2, branch=0)
|
||||
context_f.Enter()
|
||||
orig_res_f, res_f = context_f.BuildCondBranch(fn2)
|
||||
orig_res_f, res_f = context_f.BuildCondBranch(false_fn)
|
||||
if orig_res_f is None:
|
||||
raise ValueError("fn2 must have a return value.")
|
||||
raise ValueError("false_fn must have a return value.")
|
||||
context_f.ExitResult(res_f)
|
||||
context_f.Exit()
|
||||
|
||||
@ -1778,14 +1812,14 @@ def cond(pred, fn1, fn2, strict=False, name=None):
|
||||
nest.assert_same_structure(orig_res_t, orig_res_f)
|
||||
except TypeError as e:
|
||||
raise TypeError(
|
||||
"Incompatible return types of fn1 and fn2: {}".format(e))
|
||||
"Incompatible return types of true_fn and false_fn: {}".format(e))
|
||||
except ValueError as e:
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Incompatible return values of fn1 and fn2: {}".format(e))
|
||||
"Incompatible return values of true_fn and false_fn: {}".format(e))
|
||||
|
||||
# Add the final merge to the graph.
|
||||
if not res_t:
|
||||
raise ValueError("fn1 and fn2 must return at least one result.")
|
||||
raise ValueError("true_fn and false_fn must return at least one result.")
|
||||
|
||||
res_t_flat = nest.flatten(res_t)
|
||||
res_f_flat = nest.flatten(res_f)
|
||||
@ -1799,8 +1833,9 @@ def cond(pred, fn1, fn2, strict=False, name=None):
|
||||
val_x = x if isinstance(x, ops.Tensor) else x.values
|
||||
val_y = y if isinstance(y, ops.Tensor) else y.values
|
||||
if val_x.dtype.base_dtype != val_y.dtype.base_dtype:
|
||||
raise ValueError("Outputs of fn1 and fn2 must have the same type: "
|
||||
"%s, %s" % (val_x.dtype.name, val_y.dtype.name))
|
||||
raise ValueError(
|
||||
"Outputs of true_fn and false_fn must have the same type: %s, %s" %
|
||||
(val_x.dtype.name, val_y.dtype.name))
|
||||
|
||||
merges = [merge(pair)[0] for pair in zip(res_f_flat, res_t_flat)]
|
||||
merges = _convert_flows_to_tensorarrays(nest.flatten(orig_res_t), merges)
|
||||
@ -1815,6 +1850,7 @@ def cond(pred, fn1, fn2, strict=False, name=None):
|
||||
if not strict:
|
||||
merges = _UnpackIfSingleton(merges)
|
||||
return merges
|
||||
# pylint: enable=g-doc-args
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def _resource_safe_shape(t):
|
||||
@ -2546,12 +2582,16 @@ def while_loop(cond, body, loop_vars, shape_invariants=None,
|
||||
`cond` and `body`. `cond` and `body` both take as many arguments as there are
|
||||
`loop_vars`.
|
||||
|
||||
While `cond` evaluates to true, `body` is executed.
|
||||
|
||||
In addition to regular Tensors or IndexedSlices, the body may accept and
|
||||
return TensorArray objects. The flows of the TensorArray objects will
|
||||
be appropriately forwarded between loops and during gradient calculations.
|
||||
|
||||
Note that `while_loop` calls `cond` and `body` *exactly once* (inside the
|
||||
call to `while_loop`, and not at all during `Session.run()`). `while_loop`
|
||||
stitches together the graph fragments created during the `cond` and `body`
|
||||
calls with some additional graph nodes to make something the repeats
|
||||
`body` until `cond` returns false.
|
||||
|
||||
For correctness, `tf.while_loop()` strictly enforces shape invariants for
|
||||
the loop variables. A shape invariant is a (possibly partial) shape that
|
||||
is unchanged across the iterations of the loop. An error will be raised
|
||||
@ -2880,10 +2920,10 @@ def case(pred_fn_pairs, default, exclusive=False, strict=False, name="case"):
|
||||
operation returns the tensors generated by `default`.
|
||||
|
||||
`tf.case` supports nested structures as implemented in
|
||||
`tensorflow.python.util.nest`. Both `fn1` and `fn2` must return the same
|
||||
`tensorflow.python.util.nest`. All of the callables must return the same
|
||||
(possibly nested) value structure of lists, tuples, and/or named tuples.
|
||||
Singleton lists and tuples form the only exceptions to this: when returned by
|
||||
`fn1` and/or `fn2`, they are implicitly unpacked to single values. This
|
||||
a callable, they are implicitly unpacked to single values. This
|
||||
behavior is disabled by passing `strict=True`.
|
||||
|
||||
Example 1:
|
||||
@ -2911,9 +2951,6 @@ def case(pred_fn_pairs, default, exclusive=False, strict=False, name="case"):
|
||||
|
||||
Expressions:
|
||||
```
|
||||
x = tf.constant(0)
|
||||
y = tf.constant(1)
|
||||
z = tf.constant(2)
|
||||
def f1(): return tf.constant(17)
|
||||
def f2(): return tf.constant(23)
|
||||
def f3(): return tf.constant(-1)
|
||||
|
||||
@ -324,6 +324,69 @@ class SwitchTestCase(TensorFlowTestCase):
|
||||
self.assertEquals(grad_x_false.eval(), 0.)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class CondTest(TensorFlowTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def testCondTrue(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
x = constant_op.constant(2)
|
||||
y = constant_op.constant(5)
|
||||
z = control_flow_ops.cond(
|
||||
math_ops.less(x, y), lambda: math_ops.multiply(x, 17),
|
||||
lambda: math_ops.add(y, 23))
|
||||
self.assertEquals(z.eval(), 34)
|
||||
|
||||
def testCondFalse(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
x = constant_op.constant(2)
|
||||
y = constant_op.constant(1)
|
||||
z = control_flow_ops.cond(
|
||||
math_ops.less(x, y), lambda: math_ops.multiply(x, 17),
|
||||
lambda: math_ops.add(y, 23))
|
||||
self.assertEquals(z.eval(), 24)
|
||||
|
||||
def testCondTrueLegacy(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
x = constant_op.constant(2)
|
||||
y = constant_op.constant(5)
|
||||
z = control_flow_ops.cond(
|
||||
math_ops.less(x, y), fn1=lambda: math_ops.multiply(x, 17),
|
||||
fn2=lambda: math_ops.add(y, 23))
|
||||
self.assertEquals(z.eval(), 34)
|
||||
|
||||
def testCondFalseLegacy(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
x = constant_op.constant(2)
|
||||
y = constant_op.constant(1)
|
||||
z = control_flow_ops.cond(
|
||||
math_ops.less(x, y), fn1=lambda: math_ops.multiply(x, 17),
|
||||
fn2=lambda: math_ops.add(y, 23))
|
||||
self.assertEquals(z.eval(), 24)
|
||||
|
||||
def testCondMissingArg1(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
x = constant_op.constant(1)
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
|
||||
control_flow_ops.cond(True, false_fn=lambda: x)
|
||||
|
||||
def testCondMissingArg2(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
x = constant_op.constant(1)
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
|
||||
control_flow_ops.cond(True, lambda: x)
|
||||
|
||||
def testCondDuplicateArg1(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
x = constant_op.constant(1)
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
|
||||
control_flow_ops.cond(True, lambda: x, lambda: x, fn1=lambda: x)
|
||||
|
||||
def testCondDuplicateArg2(self):
|
||||
with self.test_session():
|
||||
x = constant_op.constant(1)
|
||||
with self.assertRaises(TypeError):
|
||||
control_flow_ops.cond(True, lambda: x, lambda: x, fn2=lambda: x)
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
class ContextTest(TensorFlowTestCase):
|
||||
|
||||
def testCondContext(self):
|
||||
|
||||
@ -44,11 +44,13 @@ def _registered_kl(type_a, type_b):
|
||||
return kl_fn
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
def kl(dist_a, dist_b, allow_nan_stats=True, name=None):
|
||||
"""Get the KL-divergence KL(dist_a || dist_b).
|
||||
def kl_divergence(distribution_a, distribution_b,
|
||||
allow_nan_stats=True, name=None):
|
||||
"""Get the KL-divergence KL(distribution_a || distribution_b).
|
||||
|
||||
If there is no KL method registered specifically for `type(dist_a)` and
|
||||
`type(dist_b)`, then the class hierarchies of these types are searched.
|
||||
If there is no KL method registered specifically for `type(distribution_a)`
|
||||
and `type(distribution_b)`, then the class hierarchies of these types are
|
||||
searched.
|
||||
|
||||
If one KL method is registered between any pairs of classes in these two
|
||||
parent hierarchies, it is used.
|
||||
@ -58,11 +60,11 @@ def kl(dist_a, dist_b, allow_nan_stats=True, name=None):
|
||||
|
||||
If more than one such shortest path exists, the first method
|
||||
identified in the search is used (favoring a shorter MRO distance to
|
||||
`type(dist_a)`).
|
||||
`type(distribution_a)`).
|
||||
|
||||
Args:
|
||||
dist_a: The first distribution.
|
||||
dist_b: The second distribution.
|
||||
distribution_a: The first distribution.
|
||||
distribution_b: The second distribution.
|
||||
allow_nan_stats: Python `bool`, default `True`. When `True`,
|
||||
statistics (e.g., mean, mode, variance) use the value "`NaN`" to
|
||||
indicate the result is undefined. When `False`, an exception is raised
|
||||
@ -70,20 +72,22 @@ def kl(dist_a, dist_b, allow_nan_stats=True, name=None):
|
||||
name: Python `str` name prefixed to Ops created by this class.
|
||||
|
||||
Returns:
|
||||
A Tensor with the batchwise KL-divergence between dist_a and dist_b.
|
||||
A Tensor with the batchwise KL-divergence between `distribution_a`
|
||||
and `distribution_b`.
|
||||
|
||||
Raises:
|
||||
NotImplementedError: If no KL method is defined for distribution types
|
||||
of dist_a and dist_b.
|
||||
of `distribution_a` and `distribution_b`.
|
||||
"""
|
||||
kl_fn = _registered_kl(type(dist_a), type(dist_b))
|
||||
kl_fn = _registered_kl(type(distribution_a), type(distribution_b))
|
||||
if kl_fn is None:
|
||||
raise NotImplementedError(
|
||||
"No KL(dist_a || dist_b) registered for dist_a type %s and dist_b "
|
||||
"type %s" % (type(dist_a).__name__, type(dist_b).__name__))
|
||||
"No KL(distribution_a || distribution_b) registered for distribution_a "
|
||||
"type %s and distribution_b type %s"
|
||||
% (type(distribution_a).__name__, type(distribution_b).__name__))
|
||||
|
||||
with ops.name_scope("KullbackLeibler"):
|
||||
kl_t = kl_fn(dist_a, dist_b, name=name)
|
||||
kl_t = kl_fn(distribution_a, distribution_b, name=name)
|
||||
if allow_nan_stats:
|
||||
return kl_t
|
||||
|
||||
@ -96,7 +100,7 @@ def kl(dist_a, dist_b, allow_nan_stats=True, name=None):
|
||||
math_ops.reduce_any(math_ops.is_nan(kl_t))),
|
||||
["KL calculation between %s and %s returned NaN values "
|
||||
"(and was called with allow_nan_stats=False). Values:"
|
||||
% (dist_a.name, dist_b.name), kl_t])]):
|
||||
% (distribution_a.name, distribution_b.name), kl_t])]):
|
||||
return array_ops.identity(kl_t, name="checked_kl")
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
@ -20,8 +20,6 @@ from __future__ import print_function
|
||||
|
||||
import math
|
||||
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.contrib.distributions.python.ops import special_math
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import constant_op
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import dtypes
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.framework import ops
|
||||
@ -32,6 +30,8 @@ from tensorflow.python.ops import math_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import nn
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops import random_ops
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import distribution
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import kullback_leibler
|
||||
from tensorflow.python.ops.distributions import special_math
|
||||
|
||||
|
||||
__all__ = [
|
||||
@ -63,16 +63,27 @@ GetSessionHandle
|
||||
GetSessionHandleV2
|
||||
GetSessionTensor
|
||||
HashTable
|
||||
HashTableV2
|
||||
InitializeTable
|
||||
InitializeTableV2
|
||||
InitializeTableFromTextFile
|
||||
InitializeTableFromTextFileV2
|
||||
LookupTableExport
|
||||
LookupTableExportV2
|
||||
LookupTableFind
|
||||
LookupTableFindV2
|
||||
LookupTableImport
|
||||
LookupTableImportV2
|
||||
LookupTableInsert
|
||||
LookupTableInsertV2
|
||||
LookupTableSize
|
||||
LookupTableSizeV2
|
||||
MutableDenseHashTable
|
||||
MutableDenseHashTableV2
|
||||
MutableHashTable
|
||||
MutableHashTableV2
|
||||
MutableHashTableOfTensors
|
||||
MutableHashTableOfTensorsV2
|
||||
Mutex
|
||||
MutexAcquire
|
||||
MutexRelease
|
||||
@ -220,6 +231,7 @@ BatchFFT3D
|
||||
BatchIFFT
|
||||
BatchIFFT2D
|
||||
BatchIFFT3D
|
||||
Bucketize
|
||||
Complex
|
||||
ComplexAbs
|
||||
Conj
|
||||
|
||||
Some files were not shown because too many files have changed in this diff Show More
Loading…
Reference in New Issue
Block a user